What is the function of ADP and ATP?
What Does ADP in Biology Do?
- Structure. ADP is built with a few component molecules. ...
- Energy in ADP and ATP. Without ADP and ATP, there would be almost no life on Earth. ...
- Using Energy. Just about every cell in your body uses ATP to supply energy. ...
- Other Uses for ADP. ...
What is the chemical structure of ADP?
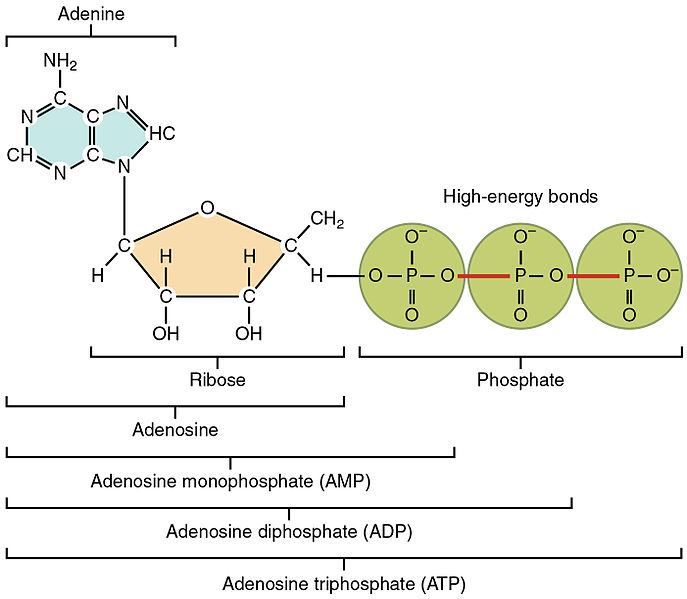
Structure. The structure of ADP is similar to ATP. An ADP molecule consists of a 5-carbon sugar called ribose, a nitrogen base called adenine, and two phosphate groups covalently bonded to each other.
What is ATP and ADP?
ATP and ADP are two types of nucleotides mainly involved in the transfer of energy between biochemical reactions in the cell. Both ATP and ADP are composed of a ribose sugar, adenosine, and phosphate groups. ATP molecule is composed of three phosphate molecules while ADP is composed of two phosphate molecules.
What is the meaning of ADP?
The Applications Developer Program ( ADP) enables customers to develop the skills and proficiency to create novel chip-based microfluidic applications utilizing Caliper's proprietary LabChip technology and developmental tool set.

What is ADP and where is it found in the cell?
If a cell needs to spend energy to accomplish a task, the ATP molecule splits off one of its three phosphates, becoming ADP (Adenosine di-phosphate) + phosphate. The energy holding that phosphate molecule is now released and available to do work for the cell.
What is ADP and its uses?
We are a comprehensive global provider of cloud-based human capital management (HCM) solutions that unite HR, payroll, talent, time, tax and benefits administration, and a leader in business outsourcing services, analytics and compliance expertise.
What is ADP short answer?
Adp definition Short for adenosine diphosphate. An organic compound that is composed of adenosine and two phosphate groups. With the addition of another phosphate group, it is converted to ATP for the storage of energy during cell metabolism.
What is ADP used for in biology?
Biological functions ADP is essential in photosynthesis and glycolysis. It is the end-product when adenosine triphosphate ATP loses one of its phosphate groups. The energy released in the process is used to power up many vital cellular processes. ADP reconverts to ATP by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP.
What is the difference between ATP and ADP?
Thus, ATP is the higher energy form (the recharged battery) while ADP is the lower energy form (the used battery). When the terminal (third) phosphate is cut loose, ATP becomes ADP (Adenosine diphosphate; di= two), and the stored energy is released for some biological process to utilize.
Is ADP an enzyme?
ADP-ribose diphosphatase (EC 3.6. 1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction in which water nucleophilically attacks ADP-ribose to produce AMP and D-ribose 5-phosphate.
What is ADP to ATP called?
The conversion of ADP to ATP in the inner membranes of mitochondria is technically known as chemiosmotic phosphorylation.
Does ADP store energy?
Energy in ADP and ATP Plants and animals use ADP and ATP to store and release energy. ATP has more energy than ADP, which means it takes energy to make ATP from ADP, but it also means that energy is released when ATP is converted to ADP. Living organisms constantly cycle between ATP and ADP.
What is ATP used for in cells?
In addition to providing energy, the breakdown of ATP through hydrolysis serves a broad range of cell functions, including signaling and DNA/RNA synthesis. ATP synthesis utilizes energy obtained from multiple catabolic mechanisms, including cellular respiration, beta-oxidation, and ketosis.
What is the role of ATP in living cells?
ATP plays a critical role in the transport of macromolecules such as proteins and lipids into and out of the cell. The hydrolysis of ATP provides the required energy for active transport mechanisms to carry such molecules across a concentration gradient.
How does ADP work for employees?
ADP's Basic Idea Rather than manually inputting an employee's worked hours, pay rates, tax rates and deductions into a spreadsheet, the ADP software performs each step quickly and automatically. HR managers can review the payroll before processing it and can then approve the payroll for payment.
What is an example of ADP?
As you have seen, your body has a lot of ADP around, and it's a handy molecule for storing and releasing energy, so the body has put it to many other uses. For example, ADP and ATP provide energy for receiving and sending ions that carry signals between neurons.
What is ATP used for?
ATP synthesized in mitochondria is the primary energy source for important biological functions, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis.
What is ADP in muscle contraction?
The Cross-Bridge Muscle Contraction Cycle The ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) by the enzyme ATPase. The energy released during ATP hydrolysis changes the angle of the myosin head into a “cocked” position, ready to bind to actin if the sites are available.
How do you convert ATP to ADP?
ATP is converted to ADP by the enzyme ATP synthase. ATP is hydrolyzed (broken down in the presence of water) into ADP and inorganic phosphate.
What is ADP vs ATP?
Both ADP and ATP are biological molecules produced by the cell. ADP has two phosphate groups, and ATP has three. ATP has more energy because it con...
What is the role of ADP?
The primary role of ADP is to combine with inorganic phosphate to make ATP, the premier energy molecule that drives biochemical reactions. ADP also...
What are the steps in the ATP cycle?
ADP is converted to ATP by the enzyme ATP synthase by adding inorganic phosphate to ADP. ATP is then broken down to ADP and inorganic phosphate by...
ADP Meaning
ADP is an acronym for adenosine diphosphate. Adenosine is the term used when adenine is combined with a simple sugar (ribose or deoxyribose). Adenine is a purine base, while adenosine is a nucleoside (base bound to a sugar). Di means "two," and phosphate is a charged ion that contains the mineral phosphate.
ATP Meaning
ATP follows the same rules of nomenclature as ADP. Adenosine is the umbrella term for adenine and ribose combined. Tri means "three," which denotes that ATP contains three phosphate ions.
What Does ATP Do?
ATP provides the energy for many critical biochemical reactions and processes. This includes:
What is the last step of ATP synthase?
Out of those, the last step produces ATP. In last step, ATP synthase uses the difference in hydrogen ion concentration to make ATP. NADH catalyzes a series of reactions with several proteins to move hydrogen cations from mitochondrial matrix to intermembrane space. This creates a difference in hydrogen cation concentration.
What are the three parts of cellular respiration?
Explanation: Cellular respiration consists of three parts in order: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain. Glycolysis involves total of 10 steps. Out of those, step 1 and 3 use ATP. In step 1, hexokinase (HK) take a phosphate from ATP and add the phosphate to glucose to create glucose-6-phosphate.
What is the role of ATP in the cell?
What Is ATP and What Is Its Role in the Cell? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is the energy currency of life, the way that individual cells store and use chemical energy. Any food or other source of energy a cell takes in is converted to ATP, in which form the mechanisms of the cell can easily use it. It does this by shedding a phosphate group, ...
What organelle converts glucose into adenosine triphosphate?
In animals and other eukaryotic heterotrophs, organelles known as mitochondria use the energy from food to convert depleted adenosine diphosphate back into adenosine triphosphate. This process largely uses glucose in a process known as the Krebs cycle. In plants, chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for converting light, ...
How many phosphate groups are in adenosine triphosphate?
The molecule contains three phosphate groups in a chain. Each phosphate is bonded to four oxygen atoms. Three of these oxygen atoms are shared either by two phosphates or the first phosphate and the carbon-based group.
Which organelle converts water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates?
In plants, chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for converting light, water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates, also change ADP into ATP. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is the energy that a cell takes in?
Any food or other source of energy a cell takes in is converted to ATP, in which form the mechanisms of the cell can easily use it. It does this by shedding a phosphate group, becoming adenosine diphosphate, or ADP, a highly energetic reaction that powers all of a cell's molecular machinery.
What is the role of ADP in the cell?
The most important role of ADP is to store and release energy within the cell. ADP starts with adenine. Once adenine joins with a sugar molecule it becomes adenosine. Adenosine can now accept a phosphate group. If one phosphate group is accepted, the molecule becomes adenosine monophosphate.
What does ADP stand for in biology?
Image 4: A chemical presentation of ADP. Picture Source: shodor.org. ADP stands for adenosine diphosphate. It is a nucleotide that is similar to the one found in RNA and DNA. It has the ability to add and at the same time remove phosphate molecules so as to form a different molecule.
What are the two compounds that cells use to produce energy?
The cells cannot directly use the food as a source of energy. What it uses are two compounds; the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). ATP and ADP play an important role in cellular activities. In this article, we are going to tackle ATP and ADP, their functions, and key differences. (1, 2)
Why are ADP and ATP important?
ADP and ATP molecules are essential in cellular activities. They are a universal power source as without them it would be impossible for the cells to perform their vital functions.
How many phosphates are in adenosine triphosphate?
Two phosphate results in adenosine diphosphate and three phosphate results in adenosine triphosphate. (4, 5, 6)
What is the chemical reaction of ATP?
Image 1: The image shows the chemical reaction of ATP (adenosine triphosphate. ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, a molecule that can be found in every living thing. It is tagged as the cell’s energy currency; the primary carrier of energy in all living organisms on earth.
What is the function of ATP in muscle contraction?
What it does is it binds to myosin so as to provide energy and facilitates its binding to actin thereby forming a cross-bridge. ATP aids in the synthesis of DNA and RNA. ATP’s adenosine serves as the building block of RNA. (2, 3, 4, 5)
What is the energy of ATP?
ATP (Adenosine tri-phosphate) is an important molecule found in all living things. Think of it as the “energy currency” of the cell. If a cell needs to spend energy to accomplish a task, the ATP molecule splits off one of its three phosphates, becoming ADP (Adenosine di-phosphate) + phosphate. The energy holding that phosphate molecule is now released and available to do work for the cell. When the cell has extra energy (gained from breaking down food that has been consumed or, in the case of plants, made via photosynthesis), it stores that energy by reattaching a free phosphate molecule to ADP, turning it back into ATP. The ATP molecule is just like a rechargeable battery. When it’s fully charged, it’s ATP. When it’s run down, it’s ADP. However, the battery doesn’t get thrown away when it’s run down–it just gets charged up again.
What is the name of the phosphate that a cell needs to split off?
There are times when the cell needs even more energy, and it splits off another phosphate, so it goes from ADP, adenoside di-phosphate, to AMP, adenosine mono-phosphate.