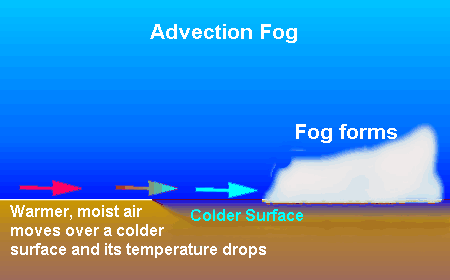
advection fog A type of fog caused by the advection of moist air over a cold surface, and the consequent cooling of that air to below its dewpoint
Dew point
The dew point (dew point temperature or dewpoint) is the temperature at which dew forms and is a measure of atmospheric moisture. It is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure and water content to reach saturation.
What are the 5 types of fog?
What are the different types of fog?
- Radiation fog. Radiation fog usually occurs in the winter, aided by clear skies and calm conditions. ...
- Valley fog. Valley fog forms where cold dense air settles into the lower parts of a valley, condensing and forming fog.
- Advection fog. Advection fog occurs when moist, warm air passes over a colder surface and is cooled. ...
- Upslope fog. ...
- Evaporation fog. ...
What is fog and how it is formed?
Specifically, fog is produced by cooling of the air, by increasing the humidity of the air, or some combination, with the end result that water vapor content in the air reaches saturation. Fog forms in several distinct settings, each of which causes air at or near ground level to become saturated.
What causes fog to form over water?
Types of Fog
- Radiation Fog. Anything bearing a temperature emits electromagnetic radiation, also known as light. ...
- Advection Fog. Advection fog occurs when warm, moist air flows horizontally over much colder ocean water or land. ...
- Upslope Fog. ...
- Frontal Fog. ...
- Cold Climate Fog. ...
What causes dense fog to form?
What causes Dense Fog to Form. Fog is caused when water vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets. Essentially fog is cloud at ground level. According to the International Meteorological Code, fog is a visibility of less than 1 km, and in the UK a thick fog represents a visibility of less than 200 m. ...

What is the causes of advection?
Very simply, advection occurs any time an airmass moves. When a warm airmass moves into an area previously occupied by a cooler airmass, Warm Air Advection (WAA) occurs. Cold air replacing warm air is known as Cold Air Advection (CAA).
Where does advection fog occur?
Advection fog shows up mostly in places where warm, tropical air meets cooler ocean water. The Pacific coast of the United States, from Washington to California, is often covered in advection fog.
What is the main cause of fog?
When the cool air mixes with the warm moist air over the water, the moist air cools until its humidity reaches 100% and fog forms.
Under which condition does advection fog usually form?
Under what condition does advection fog usually form? a) Moist air moving over colder ground or water.
How does an advection fog form quizlet?
Advection fog forms when warm, moist air blows into an area where the surface is cooler, causing condensation. They often form where warm ocean air blows over cooler offshore waters.
How do you predict advection fog?
The setup for advection fog will often include an advection pattern bringing in warmer and more moist air from the south. The set-up for the ground surface will be a snow covered ground or a saturated ground that has been chilled by cold temperatures before the winds shift back from a southerly type direction.
What are the 3 types of fog?
Associated with frontal zones and frontal passages, this type of fog can be divided into three types: warm-front pre-frontal fog; cold front post-frontal fog; and frontal-passage fog. Pre and post-frontal fog are caused by rain falling into cold stable air thus raising the dew point.
Is fog caused by pollution?
An increased frequency of fog in urban areas has often been mentioned as a result of air pollutant emissions[4].
Does humidity create fog?
Fog normally occurs at a relative humidity near 100%. This occurs from either added moisture in the air, or falling ambient air temperature. However, fog can form at lower humidities, and can sometimes fail to form with relative humidity at 100%.
In which situation is advection fog most likely to form quizlet?
In which situation is advection fog most likely to form? An air mass moving inland from the coast in winter. (Advection fog forms when moist air moves over colder ground or water. It is most common along coastal areas.
Why does fog form when the sun rises?
The initial heating of the surface just after sunrise can create the same effect as a light wind, causing existing fog to thicken or new fog to develop.
What is the difference between radiation and advection fog?
Radiation fog forms over land only, where advection fog can form over sea too: cold and warm stream fog. Advection fog needs a surface that is already cool (water or land). Radiation fog disappears some time after sunrise but advection fog can persist for days, given the right conditions.
In which situation is advection fog most likely to form quizlet?
In which situation is advection fog most likely to form? An air mass moving inland from the coast in winter. (Advection fog forms when moist air moves over colder ground or water. It is most common along coastal areas.
What are the 4 types of fog?
The different types of fogs we will discuss in this blog are: Radiation Fog, Advection Fog, Freezing Fog, Evaporation Fog and Mountain/Valley Fog. This type of fog is the one of most common in the country, especially in the fall and winter.
What creates fog in San Francisco?
The Northern California climate gets very hot, especially in the summer, creating a low-pressure zone. San Francisco, on the other hand, is surrounded by water on three sides. The hot air rises, creating a vacuum for the cold, high-pressure, moisture-filled ocean air to rush in – hence, the fog.
What determines the likelihood of advection fog?
Thus the temperature gradient between air and surface in conjunction with the degree of turbulence determines the likelihood of advection fog.
Where does fog develop?
Advection fog also develops over the southern and eastern areas of the United States of America, when warm air is advected from the Gulf of Mexico and the Bermuda region.
How does advection fog form?
Advection fog forms as warmer, moist air moves over cold ground. The air is cooled to saturation by the cold from the ground below cooling the air above. Unlike radiation fog, advection fog may form under cloudy skies and with moderate to strong winds.
What is advection fog?
Advection fog is fog produced when air that is warmer and more moist than the ground surface moves over the ground surface. The term advection means a horizontal movement of air. Unlike radiation fog, advection fog can occur even when it is windy.
What is the term for the fog that sends heat out of the atmosphere to space?
Radiation fog — ground under clear skies overnight sends its heat out to space and cools below the dew point of the air next to the ground. The layer is usually shallow.
What is lake effect fog?
That is sometimes called, lake-effect fog in the USA and canada. During the autumn, when the water is warmer that the air, along a coastline or lake, if the wind is onshore, it will bring mild moist air over the land and, as it cools down, it causes fog.
What are the different types of fog?
There are several different types of fog, including radiation fog, advection fog, valley fog, and freezing fog. Radiation fog forms in the evening when heat absorbed by the Earth's surface during the day is radiated into the air. As heat is transferred from the ground to the air, water droplets form.
What is fog in mountain ranges?
Orographic fog. As mild moist air reaches a mountain range, the air rises and cools down by the adiabatic effect of a lesser pressure aloft. Above a certain altitude, fog will form. Mind you, you will call it, fog, if you live up there but, simply cloud, if you live in the valleys.
What is the goal of fog lights?
the goal of fog lights is to shine on the road as much as possible and the fog as least as possible.
What is the cause of fog drizzle?
Drizzle occurs when the humidity of fog attains 100% and the minute cloud droplets begin to coalesce into larger droplets. This can occur when the fog layer is lifted and cooled sufficiently, or when it is forcibly compressed from above by descending air.
How does fog form?
Fog forms when the difference between air temperature and dew point is less than 2.5 °C (4.5 °F ). Fog begins to form when water vapor condenses into tiny water droplets that are suspended in the air. Some examples of ways that water vapor is added to the air are by wind convergence into areas of upward motion;
What is fog in science?
e. Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth 's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions.
How does fog affect humans?
In turn, fog has affected many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare. Fog shows up when water vapor, or water in its gaseous form , condenses. During condensation, molecules of water vapor combine to make tiny liquid water droplets that hang in the air. Sea fog, which shows up near bodies of salty water, ...
How is the thickness of a fog layer determined?
The thickness of a fog layer is largely determined by the altitude of the inversion boundary, which in coastal or oceanic locales is also the top of the marine layer, above which the air mass is warmer and drier. The inversion boundary varies its altitude primarily in response to the weight of the air above it, which is measured in terms of atmospheric pressure. The marine layer, and any fog-bank it may contain, will be "squashed" when the pressure is high, and conversely, may expand upwards when the pressure above it is lowering.
Why does hail fog occur?
Hail fog sometimes occurs in the vicinity of significant hail accumulations due to decreased temperature and increased moisture leading to saturation in a very shallow layer near the surface. It most often occurs when there is a warm, humid layer atop the hail and when wind is light. This ground fog tends to be localized but can be extremely dense and abrupt. It may form shortly after the hail falls; when the hail has had time to cool the air and as it absorbs heat when melting and evaporating.
Why does ice fog form?
Ice fog forms in very low temperatures and can be the result of other mechanisms mentioned here, as well as the exhalation of moist warm air by herds of animals. It can be associated with the diamond dust form of precipitation, in which very small crystals of ice form and slowly fall.
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/TQ4W5J77NZDLZBVGTUWNBXDX7E.jpg)