
Key Points on Aerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP.
- The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix.
- The Kreb’s cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of aerobic respiration?
What are the disadvantages of aerobic organisms?
- It can include high-impact exercises that could be bad for the body. The repetitive and high-impact steps in aerobics could not be good if you have ligament or bone problems. ...
- It can result to a body shape you did not desire. …
- It comes with issues on social environment.
What are the four steps in aerobic respiration?
The steps of aerobic cellular respiration are:
- Glycolysis (the break down of glucose)
- Link reaction.
- Krebs cycle.
- Electron transport chain, or ETC.
What are the 4 stages of aerobic respiration?
what are the stages of aerobic respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Prep Steps
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
- The stages of aerobic respiration
What are the different steps of aerobic respiration?
What are the 5 phases of respiration?
- Pulmonary Ventilation. …
- External Respiration. …
- Transport of gases through blood vessels. …
- Internal Respiration. …
- Cellular Respiration.
How does aerobic respiration work?
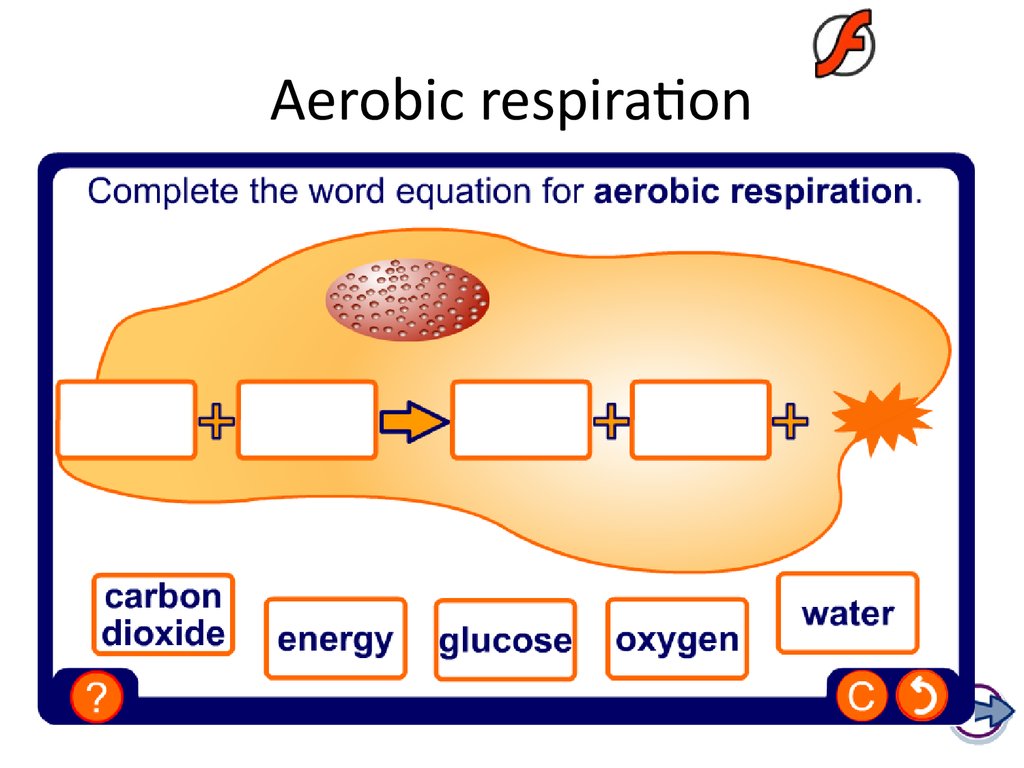
During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts. The overall equation for aerobic cellular respiration is: In cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen react to form ATP.
What is aerobic respiration in simple words?
Listen to pronunciation. (ayr-OH-bik RES-pih-RAY-shun) A chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from carbohydrates (sugars). Also called aerobic metabolism, cell respiration, and oxidative metabolism.
What is aerobic respiration and why is it important?
Aerobic cellular respiration is the process by which the cells of a living organism break down food and turn it into the energy they need to perform their essential functions. The importance of aerobic respiration in living things cannot be underestimated. Without this process, no living thing would survive.
What is aerobic respiration quizlet?
Define aerobic respiration. The release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen. Glucose is broken down to release energy in the presence of oxygen, forming carbon dioxide and water. Oxygen used to breakdown glucose.
How does anaerobic respiration work?
Answer: During anaerobic cellular respiration, glucose is broken down without oxygen. The chemical reaction transfers glucose energy to the cell. In fermentation, instead of carbon dioxide and water, lactic acid is produced which can lead to painful muscle cramps.
Why is it called aerobic respiration?
Respiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration . 'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate .
What is aerobic process?
An aerobic process refers to a process that requires the presence of oxygen or air as opposed to an anaerobic process that does not require it. An example of an aerobic process is aerobic respiration. The biological cell conducts respiration in a process called cellular respiration.
What are the main steps in aerobic respiration and where does it take place?
StepSite of occurrence1.GlycolysisCytoplasm2.Krebs cycleMatrix of mitochondria3.Electron transport systemInner mitochondrial membrane4.Oxidative phosphorylationF0-F1 particles in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Where does aerobic respiration occur?
mitochondriaWhile most aerobic respiration (with oxygen) takes place in the cell's mitochondria, and anaerobic respiration (without oxygen) takes place within the cell's cytoplasm.
What are the three steps that occur in aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is divided into three main stages: Glycolysis, Citric acid cycle and Electron transport chain.
What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic respiration?
There are two types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What is the final product of aerobic respiration?
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
What is aerobic cellular respiration for kids?
0:372:53What Is Aerobic Respiration? | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's start by looking at aerobic respiration aerobic respiration releases energy in cells byMoreLet's start by looking at aerobic respiration aerobic respiration releases energy in cells by breaking down food substances whilst in the presence of oxygen. It is represented by this simplified.
What is the definition of aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
There are two types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What is aerobic & anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a fixed metabolic reaction that takes place in the presence of oxygen, going on in a cell to transform chemical energy into ATPs. Anaerobic respiration is a process of cellular respiration in which the excessive energy electron acceptor is neither oxygen nor pyruvate derivatives.
What is aerobic process?
An aerobic process refers to a process that requires the presence of oxygen or air as opposed to an anaerobic process that does not require it. An example of an aerobic process is aerobic respiration. The biological cell conducts respiration in a process called cellular respiration.
What is aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Answer: Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form...
2. How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
Answer:Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of free oxygen and anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
3. How many ATP are produced in aerobic respiration?
Answer: 38 ATP molecules are produced during aerobic respiration.
4. Name the first product formed in the Krebs cycle.
Answer: The first product formed in the Krebs cycle is citric acid, hence it is also called the citric acid cycle.
5. What is the role of oxygen in aerobic respiration?
Answer: Oxygen is responsible for accepting electrons in the electron transport chain.
6. Name the pathway that is common between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer: Glycolysis or EMP pathway is the common pathway between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
7. Which step of aerobic respiration produces maximum ATP?
Answer: Oxidative phosphorylation produces maximum ATP, i.e. 34 ATP molecules are formed in this step.
Why do we need aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is why we need both food and oxygen, as both are required to produce the ATP that allows our cells to function.
How are aerobic and anaerobic respiration similar?
Similarities. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration are methods of generating energy. They also both start in the same way, with the process of glycolysis. “Glycolysis” literally means “sugar splitting,” and involves breaking a sugar molecule down into two smaller molecules. In the process of glycolysis, two ATP molecules are consumed ...
How does NADH work in cellular respiration?
This is important, as later in the process of cellular respiration, NADH will power the formation of much more ATP through the mitochondria ’s electron transport chain. In the next stage, pyruvate is processed to turn it into fuel for the citric acid cycle, using the process of oxidative decarboxylation.
What is the link reaction between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle?
Oxidative decarboxylation, sometimes referred to as the link reaction or the transition reaction, is the link between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate is transfered into the mitochondrial matrix via a protein known as pyruvate translocase.
What is the sugar molecule that is broken down in aerobic respiration?
In cells that have oxygen and aerobic respiration can proceed, a sugar molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. In cells that do not have oxygen, the sugar molecule is broken down into other forms, such as lactate.
Where does glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first stage of aerobic respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves the splitting of 1 six-carbon sugar molecule into 2 three-carbon pyruvate molecules. This process creates two ATP molecules.
Which is more efficient, aerobic or anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is much more efficient, and produces ATP much more quickly, than anaerobic respiration. This is because oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor for the chemical reactions involved in generating ATP. An overview of the stages of aerobic respiration.
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration plays a significant role in releasing a lot of energy which helps in the survival of life. These are the following importance of aerobic respiration: It releases a large amount of energy in comparison to anaerobic respiration. It carries out a complete breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide.
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell and produces ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ).
What are the two types of cellular respiration?
The cellular respiration is of two types, i.e. aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration . Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Anaerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP?
Cellular respiration is the process where a cell breaks down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP. Cellular respiration can take place in the presence or absence of molecular oxygen. Aerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration is a type ...
What is the first product of the Krebs cycle?
Citric acid is the first product of this cycle. Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). Since this pathway was discovered by Hans Krebs, it is also called Krebs cycle. Type of pathway: It is a cyclic, aerobic, oxidative, and biochemical pathway.
Which pathway is common between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Q.6. Name the pathway that is common between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Ans: Glycolysis or EMP pathway is the common pathway between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
What is the process of breakdown of primary metabolites in the cell with the release of energy in the form of
The process of breakdown of primary metabolites (like glucose, protein, fatty acids, etc.) in the cell with the release of energy in the form of ATP is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the living cells of organisms.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a series of biochemical reactions that convert oxygen and organic fuel into carbon dioxide, water and high-energy molecules. The process starts when organic fuel undergoes digestion in the stomach, intestines, and liver, which are then broken down and transferred into the blood.
Aerobic Respiration Equation and Summary
Aerobic Respiration: Cells in the human body use aerobic respiration to generate energy, where oxygen and organic fuel are converted into carbon dioxide, water and high-energy molecules.
What Is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the process by which glucose molecules are broken down into usable cellular energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) while in the presence of oxygen.
Aerobic Respiration Steps
Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products. In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. There are four large steps to the process:
Aerobic Respiration Analogy
In this activity, students will be writing an analogy for aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration has many steps and details, and one way to solidify this information is through analogy. For example, students might choose to compare the process of aerobic respiration to manufacturing their favorite shoes or creating their favorite meal.
What are the stages of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration has four stages: Glycolysis, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
What is the process of respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP). ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system.
How does the body respond to glucose?
By two minutes of exercise, the body responds to supply working muscles with oxygen. When oxygen is present, glucose can be completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water in a process called aerobic respiration. The glucose can come from three different places: 1 remaining glycogen supplies in the muscles 2 breakdown of the liver's glycogen into glucose, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream 3 absorption of glucose from food in the intestine, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream
Which process uses carbohydrates first, fats and proteins?
Aerobic respiration would use carbohydrates first, then fats and finally proteins, if necessary. Aerobic respiration takes even more chemical reactions to produce ATP than either of the above systems.
How does glycogen get to muscles?
remaining glycogen supplies in the muscles. breakdown of the liver's glycogen into glucose, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream. absorption of glucose from food in the intestine, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream. Aerobic respiration can also use fatty acids from fat reserves in muscle and the body to produce ATP.
