British Agricultural Revolution
The British Agricultural Revolution, or Second Agricultural Revolution, was the unprecedented increase in agricultural production in Britain due to increases in labour and land productivity between the mid-17th and late 19th centuries. Agricultural output grew faster than the population over the century to 1770, and thereafter productivity remained among the highest in the world. This increase in the food s…
What effect did the Industrial Revolution have on agriculture?
- Chemical fertilizers were made that helped the land’s fertility.
- Iron and steel was used as tools.
- Mechanical seed drills were used.
- Wooden plows were replaced by iron (and then) steel plows. ...
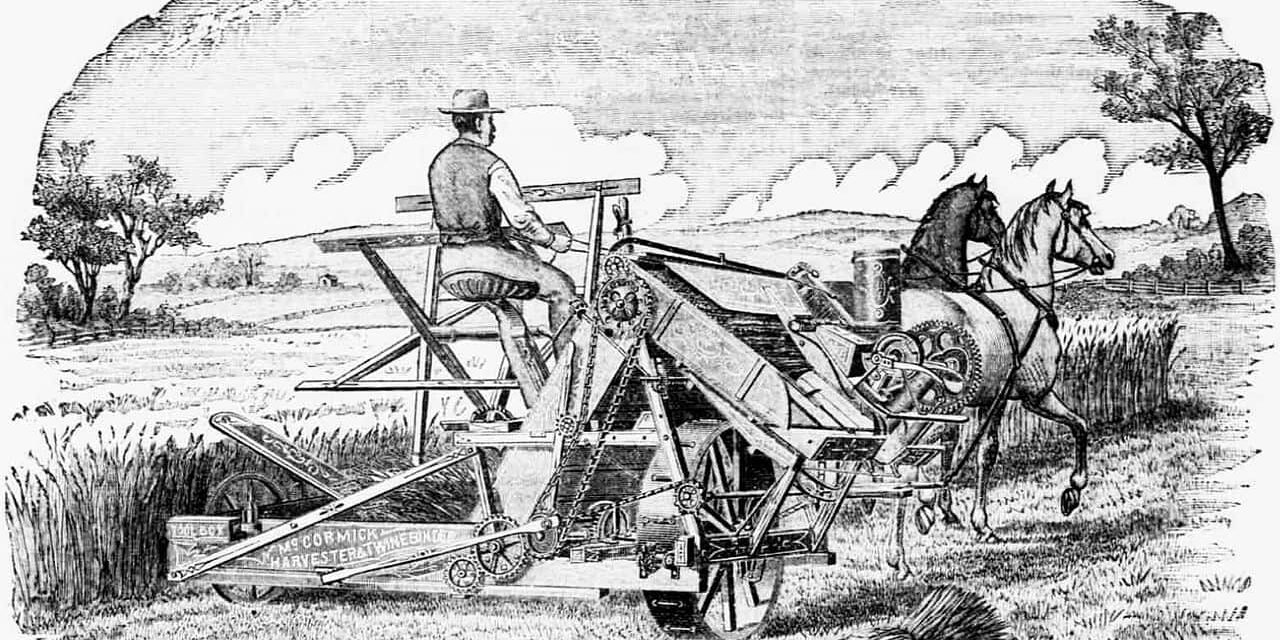
- Steam-powered threshing machines and reapers started to be used.
- Tractors started to be used, which replaced horses
What was the Agricultural Revolution and what causes it?
Causes of the Agricultural Revolution. What might be deemed the first agricultural revolution was when prehistoric man discovered how to cultivate his own food. This marked the move from a nomadic hunter-gatherer society to one of permanent settlements, villages, towns and eventually, cities. Another development that many historians consider to ...
What were the 4 results of the Agricultural Revolution?
What were the 4 results of the Agricultural Revolution? T his transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, improved efficiency of water power, the increasing use of steam power, the development of machine tools, and the rise of the factory system.
What are the pros and cons of Agricultural Revolution?
Pros Helped to improve food production to feed more than just the farmer and a village New technologies Take off of the textile industry Cons: Farmers turned more towards commercial farming and...

What is the difference between the agricultural and Industrial Revolution?
The basic difference between industrial technology and agricultural technology is that while agriculture stopped at effective reproduction through the application of natural phenomena, industrial technology made it possible to transform natural phenomena.
What do you mean by Agricultural Revolution?
The agricultural revolution is the name given to a number of cultural transformations that initially allowed humans to change from a hunting and gathering subsistence to one of agriculture and animal domestications.
What is the importance of the agricultural and Industrial Revolution?
The Agricultural Revolution helped bring about the Industrial Revolution through innovations and inventions that altered how the farming process worked. These new processes in turn created a decline in both the intensity of the work and the number of agricultural laborers needed.
What is the difference between agriculture and industrial agriculture?
However, agriculture is focused on the working of soil and other facilities to produce crops, animals and trees for human consumption or further refinement into products, while industry is focused more on refining and processing raw materials into products for sale.
What is Industrial Revolution simple?
Industrial Revolution, in modern history, the process of change from an agrarian and handicraft economy to one dominated by industry and machine manufacturing. These technological changes introduced novel ways of working and living and fundamentally transformed society.
When was the Industrial Revolution?
1760 – 1840Industrial Revolution / Period
What factors contributed to the agricultural and industrial revolutions?
Terms in this set (8)Agricultural revolution. enclosures lead to new methods (crop rotation) ... abundant natural resources. water and coal for fuel. ... political stability. no wars, no debt.factors of production. land, labor, capital.textile industry advances. ... entrepreneurs. ... building of factories. ... railroad boom.
What are the effects of Industrial Revolution of agriculture?
With machines doing much of the work, farmers could produce more food with less manpower. The use of fertilizers and pesticides also became widespread during this time, which helped to increase crop yields even further. The industrial revolution also led to a shift in how food was distributed.
What is the relationship between agriculture and industrialization?
Agriculture and industries are interdependent i.e. they depend on each other. In other words, they both help each other and without one, the other cannot develop. Agriculture helps various industries by providing them raw materials, labour, a market for their goods and also food for workers in the industrial sector.
What is agriculture and industry?
The agriculture industry comprises enterprises or companies that are majorly involved in cleaning, processing, storing or packing various types of products that are mainly obtained from agricultural production. Some of the common agriculture products are categorized under fibers, foods and raw materials.
What is agriculture explain?
Encyclopedic Entry Vocabulary. Agriculture is the art and science of cultivating the soil, growing crops and raising livestock. It includes the preparation of plant and animal products for people to use and their distribution to markets. Agriculture provides most of the world's food and fabrics.
What is the importance of industrial agriculture?
Industrial agriculture has substantially increased global agricultural productivity, leading to much more food for a growing human population. Industrial agriculture has also impacted human society in a variety of other ways and has had major impacts on the environment, many of which are harmful.
What do you mean by Agricultural Revolution in England Class 11?
Agricultural Revolution – In the eighteenth century, England had been through a major economic change, later described as the 'agricultural revolution'. This was the process by which bigger landlords had bought up small farms near their own properties and enclosed the village common lands.
What is Agricultural Revolution in India?
Agricultural revolution refers to the significant changes in agriculture when there are inventions, discoveries or new technologies implemented. These revolutions change the ways of production and increase the production rate.
What is the first Agricultural Revolution?
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an increasingly large population possible.
What are the 3 agricultural revolutions?
There were three agricultural revolutions that changed history....Agriculture, Food Production, and Rural Land Use Key TermsFarming: The methodical cultivation of plants and/or animals.Hunting and gathering: The first way humans obtained food.More items...•
What is the first agricultural revolution?
The First Agricultural Revolution is also called the Neolithic Revolution. This revolution began around 10,000 B.C. Humans made significant changes...
What are the 3 agricultural revolutions?
The First Agricultural Revolution, or the Neolithic Revolution, began around 10,000 B.C. Humans shifted from being hunter-gathers to being subsiste...
What is the agricultural revolution and why is it important?
An agricultural revolution is when farming techniques drastically improve within a relatively short period of time. This leads to a greater product...
What caused the Agricultural Revolution?
Each of the Agricultural Revolutions have different causes. The first was caused by humans changing from being hunter-gatherers to farmers and herd...
What are the characteristics of the agricultural revolution?
The characteristics of the agricultural revolution are the changes in how food is produced and the amount of food produced.
How did the Agricultural Revolution affect people's lives?
The agricultural revolutions affected how people worked and got their food. The first caused people to grow crops and raise animals for food. The s...
What was the agricultural and industrial revolution?
From a rural to manufacturing economy, it spurred invention and trade.
How did agricultural change lead to industrial change?
Whilst it would eventually bring work to many people, in it's initial stages the Industrial Revolution threatened people and their livelihoods.
How did the Industrial Revolution affect society?
The Industrial Revolution forced people to look at not just the wealth of the nation but the health of the nation.
Who were the engineers who were responsible for the invention of the power plant?
Engineers such as James Watt and Matthew Boulton could see the potential of manufacturing and knew they had the engineering foresight to deliver the power. As Mat thew Boulton said in 1776;
What were the main developments in agriculture during the agricultural revolution?
In China, humans used flood and fire control to create rice paddies beginning around 6,000 B .C. They domesticated water buffalos and yaks to eat their meat and milk and their hair and hide to make clothing. In Mexico, humans selectively bred a wild plant called teosinte to create maize or corn. The earliest known corn cob dates from 3,500 B.C. These same humans grew squash, which would become a staple food throughout the Americas. At the same time in the Andes Mountains of South America, humans grew potatoes.
Where Did the Agricultural Revolution Start?
Archeological sites in China yield evidence of early rice paddies, while sites in the Americas have tools for the cultivation of potatoes, corn, and squash. The Fertile Crescent of the Middle East contains the most evidence for the agricultural revolution. Archeological sites at Catalhoyuk, Abu Hureyra, and elsewhere reveal evidence of growing grain, cultivating fruit trees, and domesticating animals.
What are the three agricultural revolutions?
An agricultural revolution is when farming techniques drastically improve within a relatively short period of time. This leads to a greater production of food. Three agricultural revolutions have taken place in human history. The First Agricultural Revolution, or the Neolithic Revolution, began around 10,000 B.C. Humans shifted from being hunter-gathers to being subsistence farmers and herders. The Second Agricultural Revolution, or the British Agricultural Revolution, began around 300 years ago during the 18th century. Major changes to farming techniques included selectively breeding livestock and systematic crop rotation. The Third Agricultural Revolution, or the Green Revolution, took place during the 1940s, 50s, and 60s. Improvements to plant technology allowed for much greater crop yields.
How did agriculture change the world?
The innovations in agriculture radically changed how humans produced food. Crop rotation and livestock breeding resulted in higher yields, while new mechanical equipment required fewer workers. Because their work was no longer needed, people traveled to cities to find work. Some people were desperate for employment in factories or other city jobs. Their small family farms could not compete with larger, industrial farms, or modern farming equipment had rendered their labor obsolete. In contrast, the children of successful farmers could now leave their families to look for other employment without worrying about who would work on the farm. The surplus produce from industrial farms could be sold to city dwellers, which in turn allowed more people to have occupations other than farming.
Why was the Third Agricultural Revolution called the Green Revolution?
This time period received its name because of the emphasis on creating crops that yielded the most produce. Improvement in fertilizers and irrigation allowed crops to grow in climates previously too dry. Agricultural scientists like American researcher Norman Borlaug bred plants resistant to disease, produced more grain, and responded well to fertilizers. Industrial farms raised a single strain of highly productive plant. While these homogeneous crops increased yield, they were less disease-resistant and elevated the need for pesticides.
How did the first agricultural revolution affect humans?
Humans changed from a nomadic species of hunter-gatherers to a sedentary or settled species of farmers and herders. Humans developed diverse cultures, which included intellectual pursuits such as religion and art. Finally, the transition from hunting to farming triggered genetic mutations. Scientists who test the DNA of humans from this time period have found genes associated with changes in eye and skin color, height, immunity to diseases, and the ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk.
Why did the seed drill revolution start?
This revolution started because of developments in technology, a shift towards industrialization, and the growth of cities. In the early 18th century, British inventor Jethro Tull perfected the seed drill, which allowed farmers to efficiently sew seeds in rows rather than scattering seeds by hand.
What was the agricultural revolution?
Agricultural revolution, gradual transformation of the traditional agricultural system that began in Britain in the 18th century. Aspects of this complex transformation, which was not completed until the 19th century, included the reallocation of land ownership to make farms more compact and an increased investment in technical improvements, ...
What is crop rotation?
crop rotation, the successive cultivation of different crops in a specified order on the same fields, in contrast to a one-crop system or to haphazard crop successions. Throughout human history, wherever food crops have been produced, some kind of rotation cropping appears to have been practiced. One system in central Africa…
What was cut for feed in the fourth year?
The clover and ryegrass were cut for feed or grazed in the fourth year. In the winter, cattle and sheep were fed the turnips. The development of Shorthorn beef cattle through selective breeding of local cattle of the Teeswater district, Durham county, typified the advances brought about by scientific breeding.
What was farming before the Industrial Revolution?
Farming before the industrial revolution was traditional open-field farming which was based on subsistence farming. This meant that villagers would only produce enough food to satisfy the basic needs of the community which consisted of peasants or tenants of the landowner.
WHAT WAS AGRICULTURE LIKE AFTER THE REVOLUTION?
The Industrial Revolution improved the agriculture and involved major developments such as the enclosure of open fields and the adoption of new farming techniques . The enclosures involved turning the large open fields into smaller farms owned by wealthy farmers. The farms were all separated by hedges or low stone walls. Smaller farms were then leased to the public. If you could not afford to buy land you were forced to become a paid employee or seek work in nearby towns.
How did the seed drill change farming?
The seed drill had changed the way we planted seeds. Traditionally farmers would plant the seeds by hand. Planting seeds increased wastage as the majority of seeds were blown away by the wind or eaten by flocks of birds. Jethro Tull developed a horse-drawn seed drill that plant three rows of seed at a time. A hole was drilled into the ground for the seeds to be dropped into and the hole was covered. The drill then moved forward to the next planting position. This invention produced five times more crop than the traditional methods.
Why did farmers start selective breeding sheep?
Farmers started cross-breeding different types of sheep to produce the best breeds for wool and meat production.
Who invented the triangular plough?
Joseph Foljambe patented the Rotherham triangular plough which has an iron blade that was lighter and easier to use than the traditional wooden plough. The Rotherham plough was handled by two horses and one person whilst the traditional plough required four oxen, a ploughman and an ox driver.
What was the agricultural revolution?
The agricultural revolution was the spread of knowledge of farming , both in cultivating crops and domestication of animals. So people did not have to spend the majority of their time as hunter gatherers, so they had time to spare for the accumulation of knowledge. Time to think and invent etc.
When did the agricultural revolution take place?
The agricultural revolution took place between 9,000B.C. and 7,500B.C, in which the majority of humans who survived the Younger Dryas Event and its extreme cold weather did so because they got most of their calories from domesticated animals and cultivated plants by:
How did seafaring advance the social hierarchies of agrarian cultures?
1.) The technologies of sea-faring advanced to the point that the social hierarchies of agrarian cultures could be circumvented through defying the “Chartered Company” favorites of those hierarchs, and trading around the world out of sight of land, or company “Factories”.
What is subsistence farming?
Subsistence agriculture is self-sufficiency farming in which the farmers focus on growing enough food to feed themselves and their families. The output is mostly for local requirements with little or no surplus for trade.
What were the major impediments to the growth of agrarian cultures?
4.) The changes in climate affecting how crops grew were a major impediment to stable social hierarchies in agrarian cultures, ravaging the wealth of agriculture-dependent social hierarchies, and contributing to the collapse of many of the agrarian culture Empires.
What is commercial farming?
In commercial Farming crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in the market, that is, for commercial purposes
What does shifting cultivation mean?
shifting cultivation. (Forest area cut down to cultivation of crop)
Agricultural Revolution Definition
The first way humans obtained food was through hunting and gathering. Nomadic groups across the globe depended on animals, fruits, berries, and edible roots for sustenance. Afterwards, the agricultural revolution changed the course of history.
First Agricultural Revolution Time period
The first agricultural revolution’s time period is at the start of around 10,000 B.C. It is said that early humans first took up farming in the Fertile Crescent. It can be identified as a boomerang-shaped region in the Middle East. This soon impacted the rest of the world.
First Agricultural Revolution Causes
The causes of the first agricultural revolution vary from region to region. These have been briefly elaborated upon:
First Agricultural Revolution Effects
The first agricultural revolution truly had a vast impact. Huge groups of people settled down. Hence, permanent settlements began to emerge as they sustained on farming and agriculture. The inception of the Bronze Age and Iron Age was due to the agricultural revolution. This led to an advanced stage of human learning.
First Agricultural Revolution in the World
The new agricultural revolution began in the modern world. It was a shift from the traditional agricultural system. It began in Britain in the 18th century. This is because Britain saw an unprecedented increase in agricultural production. The vast increase in labour and land productivity was a major contributing factor.
First Agricultural Revolution Example
The development of the Norfolk four-course rotation was indeed the most important innovation of the Agricultural Revolution. It greatly increased crop and livestock output through improvement in the fertility of the soil. Crop rotation is the system or pattern of growing different types of crops at a particular place.
First Agricultural Revolution in India
The Green Revolution is considered the first Agricultural revolution in India. It was a period of conversion of the agrarian economy into an industrial system with the adoption of modern methods and technology. India’s freedom came at the cost of a poor economy that was vulnerable to frequent famines and food shortages.
When was the Industrial Revolution?
The first Industrial Revolution. In the period 1760 to 1830 the Industrial Revolution was largely confined to Britain. Aware of their head start, the British forbade the export of machinery, skilled workers, and manufacturing techniques.
How did the Industrial Revolution change the economy?
The Industrial Revolution transformed economies that had been based on agriculture and handicrafts into economies based on large-scale industry, mechan ized manufacturing, and the factory system . New machines, new power sources, and new ways of organizing work made existing industries more productive and efficient.
How did the Industrial Revolution affect the middle class?
The Industrial Revolution increased the overall amount of wealth and distributed it more widely than had been the case in earlier centuries, helping to enlarge the middle class. However, the replacement of the domestic system of industrial production, in which independent craftspersons worked in or near their homes, with the factory system and mass production consigned large numbers of people, including women and children, to long hours of tedious and often dangerous work at subsistence wages. Their miserable conditions gave rise to the trade union movement in the mid-19th century.
What were the most important inventions of the Industrial Revolution?
Important inventions of the Industrial Revolution included the steam engine, used to power steam locomotives, steamboats, steamships, and machines in factories; electric generators and electric motors; the incandescent lamp (light bulb); the telegraph and telephone; and the internal-combustion engine and automobile, whose mass production was perfected by Henry Ford in the early 20th century.
What were the changes in nonindustrial society?
There were also many new developments in nonindustrial spheres, including the following: (1) agricultural improvements that made possible the provision of food for a larger nonagricultural population, (2) economic changes that resulted in a wider distribution of wealth, the decline of land as a source of wealth in the face of rising industrial production, and increased international trade, (3) political changes reflecting the shift in economic power, as well as new state policies corresponding to the needs of an industrialized society, (4) sweeping social changes, including the growth of cities, the development of working-class movements, and the emergence of new patterns of authority, and (5) cultural transformations of a broad order . Workers acquired new and distinctive skills, and their relation to their tasks shifted; instead of being craftsmen working with hand tools, they became machine operators, subject to factory discipline. Finally, there was a psychological change: confidence in the ability to use resources and to master nature was heightened.
How long did the Industrial Revolution last?
What is called the first Industrial Revolution lasted from the mid-18th century to about 1830 and was mostly confined to Britain. The second Industrial Revolution lasted from the mid-19th century until the early 20th century ...
Why is the Industrial Revolution convenient?
It is convenient because history requires division into periods for purposes of understanding and instruction and because there were sufficient innovations at the turn of the 18th and 19th… .
What was the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution marked a period of development in the latter half of the 18th century that transformed largely rural, agrarian societies in Europe and America into industrialized, urban ones.
How did the Industrial Revolution affect Britain?
Though many people in Britain had begun moving to the cities from rural areas before the Industrial Revolution, this process accelerated dramatically with industrialization, as the rise of large factories turned smaller towns into major cities over the span of decades. This rapid urbanization brought significant challenges, as overcrowded cities suffered from pollution, inadequate sanitation and a lack of clean drinking water.
How did industrialization affect the middle class?
Meanwhile, even as industrialization increased economic output overall and improved the standard of living for the middle and upper classes, poor and working class people continued to struggle. The mechanization of labor created by technological innovation had made working in factories increasingly tedious (and sometimes dangerous), and many workers were forced to work long hours for pitifully low wages. Such dramatic changes fueled opposition to industrialization, including the “ Luddites ,” known for their violent resistance to changes in Britain’s textile industry.
What were the major advances in communication during the Industrial Revolution?
The latter part of the Industrial Revolution also saw key advances in communication methods, as people increasingly saw the need to communicate efficiently over long distances. In 1837, British inventors William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone patented the first commercial telegraphy system, even as Samuel Morse and other inventors worked on their own versions in the United States. Cooke and Wheatstone’s system would be used for railroad signalling, as the speed of the new trains had created a need for more sophisticated means of communication.
What was the British textile industry before the Industrial Revolution?
But prior to the Industrial Revolution, the British textile business was a true “cottage industry,” with the work performed in small workshops or even homes by individual spinners, weavers and dyers.
Why did Britain make more mechanized factories?
More efficient, mechanized production meant Britain’s new textile factories could meet the growing demand for cloth both at home and abroad, where the nation’s many overseas colonies provided a captive market for its goods. In addition to textiles, the British iron industry also adopted new innovations.
What innovations made weaving easier?
Starting in the mid-18th century, innovations like the flying shuttle, the spinning jenny, the water frame and the power loom made weaving cloth and spinning yarn and thread much easier. Producing cloth became faster and required less time and far less human labor.