What is the AHS Heat Zone Map?
In the late 1990s, The American Horticultural Society (AHS) developed the Heat Zone Map, which parallels the USDA Hardiness Zone Map. This map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area. A heat day is defined as a day in which the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F.
What are heat zones?
Heat zones are the high-temperature equivalent of cold hardiness zones. The American Horticultural Society (AHS) developed a “ Plant Heat Zone Map ” that also divides the country into twelve numbered zones. So, what are heat zones?
What does AHS stand for?
In the late 1990s, The American Horticultural Society (AHS) developed the Heat Zone Map, which parallels the USDA Hardiness Zone Map. This map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area.
What is plant hardiness and heat zones?
Various initiatives have taken place to determine how well plants would withstand the cold winter temperatures (Plant Hardiness Zones) or when plants would start suffering from the heat (Plant Heat Zones).
What does heat zone mean?
Heat zones are the high-temperature equivalent of cold hardiness zones. The American Horticultural Society (AHS) developed a “Plant Heat Zone Map” that also divides the country into twelve numbered zones.
What is the difference between hardiness and heat zone?
While USDA Zones help measure the cold our plants can endure—that is, if they will survive during the local winter—AHS Heat Zones help to measure the “heat tolerance” of our plants. So to answer your question simply, AHS Zones track heat patterns while USDA Zones track cold hardiness.
What is AHS heat Zone 8?
Plants that will live in areas that experience 90-120 heat days (AHS Heat Zone 8) each year where temperatures exceed 86 degrees F. Except for a few limited areas in the Texas Panhandle, our AHS Heat Zone is 8. Plants rated lower than AHS Heat Zone 8 may not survive the summer's heat.
What is the difference between a USDA and a sunset zone?
In short, USDA Zones simply tell you where a plant will survive the winter (but not if they will burn to death in the heat of the summer). Sunset Zones allow you to determine where that plant will thrive on a year-round basis.
What does it mean if a plant is hardy to zone 4?
A plant listed as hardy in Zone 4 indicates it should survive winter temperatures as low as 30 degrees below zero F., which is the average minimum winter temperature according to the USDA map.
In which heat zone is the USA located?
North America - The warm temperate zone | Britannica.
What can be grown in zone 8a?
Asters, astilbe, bee balm, cannas, coneflowers, crocus, daffodils, dahlias, glads, hibiscus, hostas, hyacinths, irises, jasmine, lilies, peonies, phlox, salvia, sedum, succulents, tulips, and yarrow are among the Zone 8 plants we recommend....Zone 8.ZonesShipping DatesLast Order Date7AB - 10AB7/11/22 - 11/4/2210/31/20221 more row
Where is zone 9 in the US?
The Zone 9 map includes the following states: Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, Texas, Alabama, Louisiana, Mississippi, Utah, New Mexico, Arizona, Nevada, California, Oregon, Washington, and Hawaii.
Where is Zone 7 in the United States?
USDA Zone 7 The zone includes Long Island, coastal New Jersey, eastern Maryland, most of Virginia and North Carolina, western South Carolina, southern Tennessee, the northern halves of Georgia, Alabama and Mississippi and much of Arkansas.
What are the grow zones in the US?
USDA Hardiness Growing Zones USDA growing zones range from 1 to 13, but the continental US only ranges from 3 to 10. The official USDA zone map is now further divided into subcategories of a and b with a 5 degree margin. Growing zones are sometimes referred to as planting zones or USDA hardiness zones.
What grows well in Zone 9B?
Plants flowers of dianthus, pansy, petunia, viola, and snapdragon. This is a good month to plant some beautiful camellias. Continue planting cool-season crops, including, broccoli, cauliflower, Swiss chard, peas, collards, kale, kohlrabi, lettuce, onions, parsley, parsnips, beets, radishes, salsify and spinach.
What climate zone is Southern California?
ZONE 20: Cool winters in Southern California.
Which zone has the coldest winter?
Zone 1 has the coldest average winter temperatures, while zone 12 has the least cold average winter temperatures. However, USDA hardiness zones do not take summer heat into account.
What zone do tropical plants live in?
For example, a tropical plant might be described as thriving in USDA plant har diness zones 10-12.
How the Map Came to Be
In 1997, Dr. H. Marc Cathey, President Emeritus of the American Horticultural Society (AHS), teamed up with Meteorological Evaluation Service Co., Inc. to create a new hardiness map for gardening consumers.
How "Heat Days" Affect Your Plants
Depending on the plant, sustained periods of extreme heat can shut down physiological processes. Symptoms of heat stress can appear suddenly, or plants can linger in distress for years. Some plants turn a ghostly pale blue-green and appear droopy, while others stop blooming, drop their leaves, and in some cases, expire altogether.
Where the Map Shines
One of the biggest advantages that the AHS Heat Zone Map has over the USDA Hardiness Zone Map is that it assigns heat zone ratings not just to perennial plants, but also to annuals. This includes flowers, garden vegetables, and herbs, as well as field crops.
Where the Map Falls Short
Like the USDA Hardiness Zone Map, the AHS Heat Zone Map should only be used as a guide. The map is based solely on temperature and does not take into account unusual weather patterns, areas with sparse populations, humidity, or variances in nighttime temperatures-a significant factor in determining how far south a plant will grow.
Heat Zone Labeling
Although the AHS Heat Zone Map is not as widely used as USDA Hardiness Zone Map, it is showing up in more and more catalogs and an increasing number of plant labels-over 15,000 different plants have been assigned heat zones since the map was first released.
Determining Your Heat Zone
Plants are complicated and no map can accurately predict how they will ultimately respond to extreme temperatures-hot or cold. What the AHS Heat Zone Map can do is serve as a helpful guide as to how plants will perform in periods of heat under "normal" conditions.
What is the heat zone map?
The American Horticultural Society's Heat Zone Map is similar to the USDA's map for plant hardiness. Instead of being based on cold extremes, the Heat Zone Map is based on the number of "heat days" in a given area. For more detail, get a copy of the map from AHS. If you want to grow a successful garden, you need to know the growing conditions ...
What is a heat day?
A heat day is defined as a day in which the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F. At this temperature, many plants begin to experience physiological damage and start to shut down their functioning. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
What is the temperature in Zone 11?
Gardeners in Zone 1 can expect to see temperatures down to -50 degrees F, whereas those in Zone 11 will rarely see anything colder than 40 degrees F. Most catalogs, web sites and garden centers now provide a Hardiness Zone rating for almost every plant they sell.
Why do my plants die in heat?
When a plant is not cold hardy, it will simply die, but the signs of heat stress are usually more subtle. Plants that can't tolerate high heat may stop blooming, the leaves may turn pale, and the plants may become more susceptible to pests.
USDA Hardiness Zones and AHS Heat Zones
The USDA Hardiness Zones and AHS Heat Zones are tools to help in selecting plants that will grow, survive and flourish in a specific location. When purchasing plants, look on the plant tag to read what zone the plant is rated. Purchasing plants that are rated for the zone you live in gives your garden landscape a better chance for success.
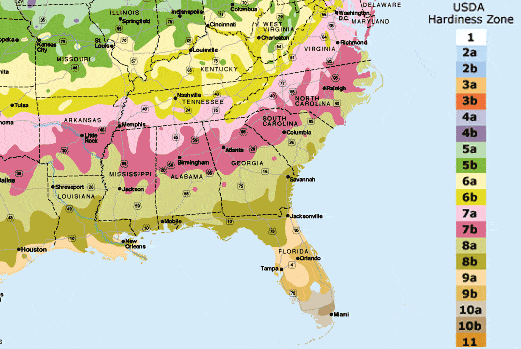
Southeast Region USDA Hardiness Zones
Winter hardiness is the ability of a plant to survive the winter conditions in a given location. The USDA Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into 11 separate zones, each zone is 10 F warmer ( or colder) in an average winter than the adjacent zone. These factors should be taken into account when selecting plants for your garden landscape.
AHS Heat Zones
The amount of heat that plants are exposed to in summer is equally critical. The American Horticultural Society Plant Heat Zone Map was developed in 1997. The map divides the US into 12 heat zones according to their average annual number of heat days. A heat day is defined as a day in which temperatures reach or exceed 86 F (30 C).
When was the heat zone map created?
To partly resolve some of the above issues, a Heat Zone Map has been developed by the American Horticultural Society, based on the National Weather Service (NWS) daily high temperatures recorded between 1974 and 1995.
What is USDA hardiness zone?
The purpose of these hardiness zones is to identify how well plants will withstand ...
What are the heat tolerance zones for tulips?
For example, a tulip may be 3-8, 8-1. If you live in USDA Zone 7 and AHS Zone 7, you will know that you can leave tulips ...
What are the factors that determine the climate of a sunset plant?
A plant's performance is not only governed by its hardiness or heat tolerance but also by many other factors such as the length of growing season, timing and amount of rainfall, winter lows, summer highs, wind, and humidity.
Does the USDA map include microclimates?
While the USDA map reflects pretty well the garden climates of the eastern half of North America, it does not factor in any elevation or precipitation which have quite an impact in western climates. It does not include micro climates, humidity, summer heat tolerance either.
Arbor Day Foundation 2015 Hardiness Zone Map
The Arbor Day Foundation developed this U.S. Hardiness Zone Map based upon data from 5,000 National Climatic Data Center cooperative stations across the continental United States.
USDA Hardiness Zone Map
Search the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) plant hardiness zone map by zip code. This interactive map divides regions based on average minimum temperatures.
Sunset Climate Zone Maps
Sunset’s regional climate zone maps are designed to tell you where a plant will thrive year-round.

Oxygen
- Plants require oxygen. Too much or too little water can cut off the oxygen supply to roots resulting in a toxic situation. Supplying good aeration and adequate space between soil particles can control the amount of oxygen that gets to the plant’s roots.
Light
- Light is necessary for a plant to assure photosynthesis that provides energy to split water molecules, absorb carbon dioxide, and enhance growth and development. Light also creates heat. The entire spectrum of light can enter a living thing, however rays of shorter wavelengths can exit. The energy absorbed by the plant affects its temperature. Cloud cover, moisture in the air, and t…
Length of Day
- The length of a day regulates plant growth, flower initiation and development, and dormancy. The long days of summer adds to the potential for heat to have a major effect on a plant’s survival. In the case of herbaceous perennials and many woody plant species, there is a strong interaction between temperature and the length of the day. This is not a controllable factor for gardeners.
Air Movement
- Although a gentle breeze in the spring can cool a plant, fast moving air on a hot day can cause dehydration. Natural features of a garden including the proximity of water and the presence of surrounding vegetation and structures including buildings and roads can adversely effect air movement. If desired, air circulation can be reduced with the addition of fences and hedges.
Surrounding Structures
- A wooded area, trees and shrubs can assist in cooling an area. However, brick, stone, glass concrete, plastic or wood structures generate heat and help to raise the air temperature. Gardeners who want early producing plants or plants that survive in cold zones often place them on the south side of a brick wall. This is not a good location for plants at the southern limit of it…
Soil Ph
- The alkalinity or acidity of soil can affect the plant’s roots ability to absorb water and nutrients. Most plants do best in a neutral soil with a pH level of 7. However, there are exceptions. Plants of the heath family prefer acidic soil. Successful growing plants require a medium with a specific pH range. It is possible to manipulate the pH level of soil with amendments. However, it is easier to …
Nutrients
- The presence of appropriate nutrients depends on the recycling of residue from the decay of woody material and dropped leaves. (Source: ahsgardening.org)