What is the aerodynamics of a spin in aviation?
Aerodynamics: All that is required is sufficient yaw rate while an aircraft is stalled In a spin, one or both wings are in a stalled condition, if both are stalled one wing will be in a deeper stall condition than the other The wing that stalls first will drop, increasing its angle of attack and deepening the stall.
What is a spin and how does it work?
Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying.
What causes an airplane to spin?
How a spin occurs. Many types of airplanes spin only if the pilot simultaneously yaws and stalls the airplane (intentionally or unintentionally). Under these circumstances, one wing stalls, or stalls more deeply than the other. The wing that stalls first drops, increasing its angle of attack and deepening the stall.
What happens to the wings during a spin?
In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.

What is a spin in an aircraft?
A spin is a yaw aggravated stall which results in rotation about the spin axis. The aircraft follows a steep, "corkscrew" like, downward path. Spins can be entered, either intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude and at practically any airspeed.
What causes aircraft spins?
A spin is caused when the airplane's wing exceeds its critical angle of attack (stall) with a sideslip or yaw acting on the airplane at, or beyond, the actual stall.
How do planes recover from a spin?
And that's where the "PARE" acronym comes into play.Step 1) P: Power To Idle. The first step in spin recovery is reducing your throttle to idle. ... Step 2) A: Ailerons Neutral. ... Step 3) R: Rudder Opposite Spin. ... Step 4) E: Elevator Forward.
What are the 3 stages of a spin?
There are four phases of a spin: entry, incipient, developed, and recovery.
What two things must occur for an airplane to spin?
For an airplane to actually spin, as opposed to spiral, two elements must be present - yaw and an excessive angle of attack that results in a stall. If either one of these elements is missing, the airplane won't spin.
Can a plane recover from a flat spin?
A flat spin is a spin where, the aircraft is in a balanced state. It just spins round and around like a spinning top. It won't recover because the forces acting on the airplane are in equilibrium. Controls and engine power become completely ineffective.
Why don't you use ailerons in a spin?
Bringing the ailerons to neutral helps your wings reach the same angle of attack - decreasing the pitching and rolling moments. If you try to raise the low wing using aileron, it will stall even more, tightening the spin. Not good.
Why do we not use ailerons in a spin?
Misuse of Ailerons If, as the aileron goes down, the stall angle of attack is exceeded, the wing may drop quickly instead of rising, resulting in a spin. The application of aileron after a spin has developed may aggravate the spin.
In what flight condition must an aircraft be placed in order to spin?
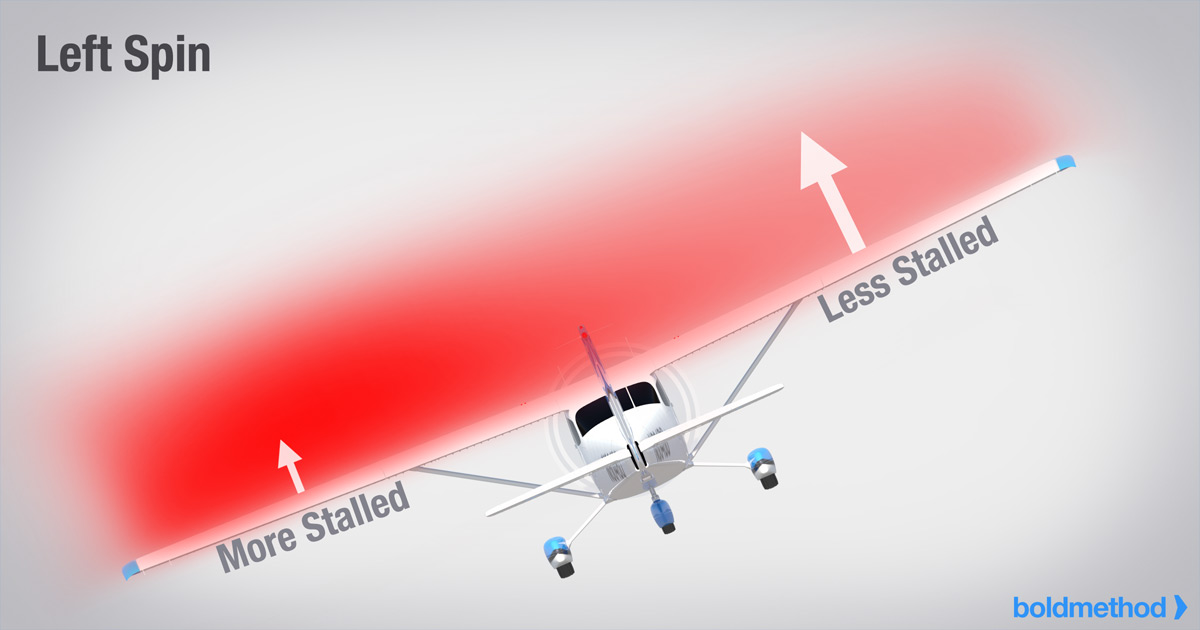
stalledIn order for an airplane to enter a spin, the airplane's wings must be stalled first. Then, an airplane begins to spin when one wing is "less" stalled than the other wing.
What are the different types of spins aviation?
NASA Spin Mode ClassificationSpin modeAngle-of-attack range, degreesFlat65 to 90Moderately flat45 to 65Moderately steep30 to 45Steep20 to 30
How do flaps affect a spin?
Flaps. Prolong the spin, because it induces a flatter spin attitude and lower spin rate. Incur damage from high speed or high loading, or both, in recovery from the dive.
Which wing is stalled in a spin?
In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.
In what flight condition must an aircraft be placed in order to spin?
stalledIn order for an airplane to enter a spin, the airplane's wings must be stalled first. Then, an airplane begins to spin when one wing is "less" stalled than the other wing.
How do you make a plane spin?
At least one wing must be stalled for a spin to occur. The other wing rises, decreasing its angle of attack, and the aircraft yaws towards the more deeply stalled wing. The difference in lift between the two wings causes the aircraft to roll, and the difference in drag causes the aircraft to continue yawing.
What aerodynamic condition will result in a spin entry?
Aerodynamics: All that is required is sufficient yaw rate while an aircraft is stalled. In a spin, one or both wings are in a stalled condition, if both are stalled one wing will be in a deeper stall condition than the other. The wing that stalls first will drop, increasing its angle of attack and deepening the stall.
Why does the f14 flat spin?
0:053:58F-14B Tomcat: Flat Spin Recovery Tutorial | DCS WORLD - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo what is a flat spin it's where the aircraft departs its flight envelope plummets. Down on theMoreSo what is a flat spin it's where the aircraft departs its flight envelope plummets. Down on the plumb spinning either left or right and it's going to be upright.
What causes a spin aviation?
The FAA defines a spin as “an aggravated stall that results in an airplane descending in a helical, or corkscrew path.” Since your high wing generates more lift than the low wing, it rolls your aircraft into the spin. And at the same time, your low wing produces more drag, because it’s at a higher angle-of-attack.
How do you do a flat spin?
To accomplish this manuever, first enter a conventional spin and as the spin developes, SLOWLY add in opposite aileron. As you do this slowly add throttle to about half. The plane *should* flatten out. Now to recover, release the sticks and add opposite rudder and a bit of down elevator.
What is spin maneuver?
deliberate, usually as a training rather than an operational. manoeuvre, or inadvertent, occurring usually during low. speed manoeuvres. A deliberate spin is initiated by slowing the aircraft towards. the stall speed and then applying full rudder deflection.
What are the 4 phases of a spin?
There are four phases of a spin: entry, incipient, developed, and recovery.
What is the difference between a slip and a skid?
A skid is where the rate of turn is too great for the angle of bank. Conversely, a slip is where the angle of bank is too great for the rate of turn.
Can you spin a Cessna 172?
The later model 172s will spin, and are approved, but they just don’t spin as nicely as the old ones.
Is a flat spin real?
Naturally stable flying wings never enter a flat spin ; their spin modes are all fairly steep due to the lack of a strong inertial moment from the lengthwise distribution of masses.
What causes a spin aviation?
The FAA defines a spin as “an aggravated stall that results in an airplane descending in a helical, or corkscrew path.” Since your high wing generates more lift than the low wing, it rolls your aircraft into the spin. And at the same time, your low wing produces more drag, because it’s at a higher angle-of-attack.
What is the difference between a spin and a spiral dive?
The difference between a spin and spiral dive is that a spin is a stalled condition and a spiral dive is an accerated condition. A spin is where you are stalled, then one wing gets more stalled than the rotation starts from that, the speed is low and stable.
What are the 4 phases of a spin?
There are four phases of a spin: entry, incipient, developed, and recovery.
Can you spin a Piper Warrior?
The Warrior had to meet basic requirements, including spin recovery, in order to be Part 23 certified. It may just be that Piper didn’t choose to spend the time and money to go through the entire protocol of testing necessary to get the Warrior FAA approved for intentional spins. Defiantly possible.
Is spin training required?
Spin Training Is Rarely Required Of all pilot certificates issued in the United States, only an initial CFI certificate requires spin training. Because of this, unless flying aerobatic aircraft or holding a CFI certificate, hundreds pilots have never performed a spin.
Can a Cirrus recover from a spin?
Normally a single-engine airplane has to be spun as part of the certification process. The Cirrus wasn’ t. That is the only way a pilot can recover from a spin in a Cirrus. The stall characteristics of the airplane are not bad when compared with some other airplanes but they aren’t real good, either.
Is a flat spin real?
Naturally stable flying wings never enter a flat spin ; their spin modes are all fairly steep due to the lack of a strong inertial moment from the lengthwise distribution of masses.
What is spin in airplanes?
A spin is simply an uncontrolled condition of flight for an airplane where in which it is also stalled. That seems sort of simple, so let’s break that down a little bit more and talk a little bit about some of the different elements of a spin. To start with, the first main element of a spin is that we have to be stalled.
What is the first element of a spin?
To start with, the first main element of a spin is that we have to be stalled. So, we need the airplane to be in a stalled condition. The second piece is what is known as an incipient phase. The third is a fully developed spin and the fourth is the recovery.
What is the function of pitching down?
Next is pitch down. Well pitching down, what is the function of this? We’re once again attempting to try to break the airplane out of a stalled condition. If the airplane isn’t stalled, then we’re not in a spin, we’re just simply in a steep spiraling turn, but it’s not a spin condition. So, pitching down is ideally there to, once again, try to break the stall or reduce our angle of attack.
Which side of an airplane has more drag?
Additionally, the right wing of the airplane has more drag than the left wing . What does that mean?
Which aileron will go down?
Well first, let’s think about the movement of the ailerons. As we move the yoke to the left, we know the left aileron will go up, the right aileron will go down, ideally then that means that the right aileron would have a greater angle of attack.
Is it normal to roll to the right when spinning?
Let’s roll to the right. Okay, theoretically that may help in breaking the stal led condition, but this is not a normal reaction. If you’re spinning to the right, your reaction is not to roll even more right so it’s easier to just simply remember to keep the ailerons neutral.
What is spin in flight?
In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation (uncommanded roll) about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis. Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.
How do airplanes spin?
Many types of airplanes spin only if the pilot simultaneously yaws and stalls the airplane (intentionally or unintentionally). Under these circumstances, one wing stalls, or stalls more deeply than the other. The wing that stalls first drops, increasing its angle of attack and deepening the stall. At least one wing must be stalled for a spin to occur. The other wing rises, decreasing its angle of attack, and the aircraft yaws towards the more deeply stalled wing. The difference in lift between the two wings causes the aircraft to roll, and the difference in drag causes the aircraft to continue yawing.
What are the different types of spins?
Spins can be classified using the following descriptors: 1 Incipient – With the inside wing stalled more deeply than the advancing wing, both the roll and yaw motions dominate. 2 Developed – The aircraft's rotation rate, airspeed, and vertical speed are stabilized. One wing is stalled more deeply than the other as the aircraft spins downward along a corkscrew path. 3 Recovery – With appropriate control inputs, the yaw rotation is slowed or stopped and the aircraft nose attitude is lowered, thus decreasing the wing's angle of attack and breaking the stall. Airspeed increases quickly in a nose low attitude and the aircraft is no longer in a spin. The controls respond conventionally and the airplane can be returned to normal flight.
What can lead to an unintentional spin?
One common scenario that can lead to an unintentional spin is a skidding uncoordinated turn toward the runway during the landing sequence. A pilot who is overshooting the turn to final approach may be tempted to apply more rudder to increase the rate of turn.
How many phases of spin are there in an aircraft?
In aircraft that are capable of recovering from a spin, the spin has four phases. Some aircraft are difficult or impossible to recover from a spin, especially a flat spin. At low altitude, spin recovery may also be impossible before impacting terrain, making low and slow aircraft especially vulnerable to spin-related accidents.
How does a spiral dive differ from a spin dive?
A spin differs from a spiral dive in which neither wing is stalled and which is characterized by a low angle of attack and high airspeed. A spiral dive is not a type of spin because neither wing is stalled. In a spiral dive, the aircraft responds conventionally to the pilot's inputs to the flight controls and recovery from a spiral dive requires a different set of actions from those required to recover from a spin.
What causes an aircraft to yaw?
The other wing rises, decreasing its angle of attack, and the aircraft yaws towards the more deeply stalled wing. The difference in lift between the two wings causes the aircraft to roll, and the difference in drag causes the aircraft to continue yawing.
What does it mean when an airplane spins?
A spin occurs when the aircraft is stalled, but one wing is more severely stalled than the other. To understand precisely what this means, you’ll need to understand a few basic terms and some aerodynamics.
What happens to the aircraft when it spins?
During a spin, the aircraft usually pitches down and begins spinning in a corkscrew-shaped spiral toward the ground. The forward airspeed is very slow since the aircraft is stalled. But the sink rate towards the ground can be very fast, and the rotation rate can be violent and disorienting to the pilot.
What Causes a Flat Spin?
The type of spin a plane enters depends on what happened when the condition started and how the aircraft was loaded. Weight and balance plays a pivotal role in stalls and spins.
What is flat spin training?
Stall and Spin Training. A flat spin is a dangerous flight condition that can be impossible to recover from. Thankfully, it’s not likely to happen on any routine flight. It occurs when the plane has no forward airspeed as it spins towards the ground around its vertical axis.
Why do pilots use the acronym "PARE"?
The FAA teaches the acronym “PARE” to help pilots remember how to recover from a spin and spin recovery technique.
How do ailerons work?
Ailerons work by changing the angle of attack at the plane’s wingtips. In the middle of a spin, any use of the ailerons will make the spin worse. Remember, a spin occurs when one wing is more severely stalled than the other. Ailerons will make it even more stalled.
How does a flat spin work?
To get a flat spin’s look and feel, power is used to flatten out the aircraft’s flight attitude during a normal upright spin. Even still, the forces that are put on the airframe, engine, and pilot are extreme during such a maneuver.
What is a spin in an air show?
Typically, you'll see the prop-driven plane soar upward in a steep ascension, only to stall out and fall into a dramatic spin.
What is stall and spin?
Stalls and Spins. As we covered earlier, an aircraft's flight is a careful balance of thrust, drag, weight and lift. Should lift decrease and drag increase suddenly, such as when an aircraft's angle of attack surpasses that for maximum lift, a stall occurs. The airframe shakes and the plane falls, at least for a few feet.
What happens if you uncorrect a spin?
If uncorrected, an incipient spin degrades into a fully developed spin composed of a near-vertical helical flight path -- as if the plane is descending an invisible spiral stair. Such a spin can cost an aircraft hundreds of feet with every turn.
How does a pilot correct a stall?
The airframe shakes and the plane falls, at least for a few feet. In most cases the pilot merely corrects for the stall by lowering the plane's angle of attack. However, an improperly corrected stall can result in a secondary stall, or degrade into a spin.
Do pilots take passengers for a spin?
Most pilots aren't looking to take their passengers for a spin though. They're too busy manning the flight instruments we'll talk about next.
Is a plane level or level?
In other words, the plane is mostly level as it falls in an extremely dangerous spin. Spin recovery techniques vary depending on the design of a given aircraft and where its center of gravity is situated.
How long does the spin phase last?
This phase may last for as little as a quarter turn or up to several turns depending upon the airplane and the type of spin
Why do airplanes yaw?
The other wing will rise, decreasing its angle of attack, and the aircraft will yaw toward the more deeply-stalled wing. The difference in lift between the two wings causes the aircraft to roll, and the difference in drag causes the aircraft to yaw.
What happens when both wings are stalled?
In a spin, one or both wings are in a stalled condition, if both are stalled one wing will be in a deeper stall condition than the other. The wing that stalls first will drop, increasing its angle of attack and deepening the stall. Both wings must be stalled for a spin to occur.
Why do you need to hold the rudder after the rotation stops?
You want to stabilize the aircraft's directional control. Holding the rudder after the rotation stops could induce a spin in the opposite direction. Roll wings level. Level wins ensures you are not climbing in a turn. Climbing in a turn decreases vertical lift, and causes unnecessary load factors.
What is the entry phase of a pilot?
In the entry phase, the pilot intentionally or accidentally provides the necessary elements for the spin
How many steps are required for spin recovery?
In the absence of the manufacturer’s recommended spin recovery procedures and techniques, use the six-step spin recovery procedure in Figure 5-17
What is auto rotation?
Auto-rotation occurs from an asymmetrical stall (think skid) There is an abrupt loss of control when leaving the stall and entering the spin.
First Off, What Exactly Is A Spin?
Before we jump into the spin recovery steps, let's take a quick look at what's happening in a spin. The FAA defines a spin as "an aggravated stall that results in an airplane descending in a helical, or corkscrew path."
So How Do You Recover With "PARE"?
Spin recovery is pretty simple: break the stall on both your wings. When you do, your plane with fly itself out of the spin. And that's where the "PARE" acronym comes into play.
Finish Your Spin Recovery
Once you've completed these 4 steps, your plane will fly itself out of the spin. When it does, bring your rudder to neutral, and raise the nose, and slowly add power to get as you get back to level flight.
Watch A Spin From The Air
Want to try a spin? Grab an instructor and a spin-approved airplane. It's a great experience, no matter how much flying time you have.