
What is a J curve in trading?
Key Takeaways 1 A J-curve depicts a trend that starts with a sharp drop and is followed by a dramatic rise. 2 The trendline ends in an improvement from the starting point. 3 In economics, the J-curve shows how a currency depreciation causes a severe worsening of a trade imbalance followed by a substantial improvement.
What does a U-shaped curve mean?
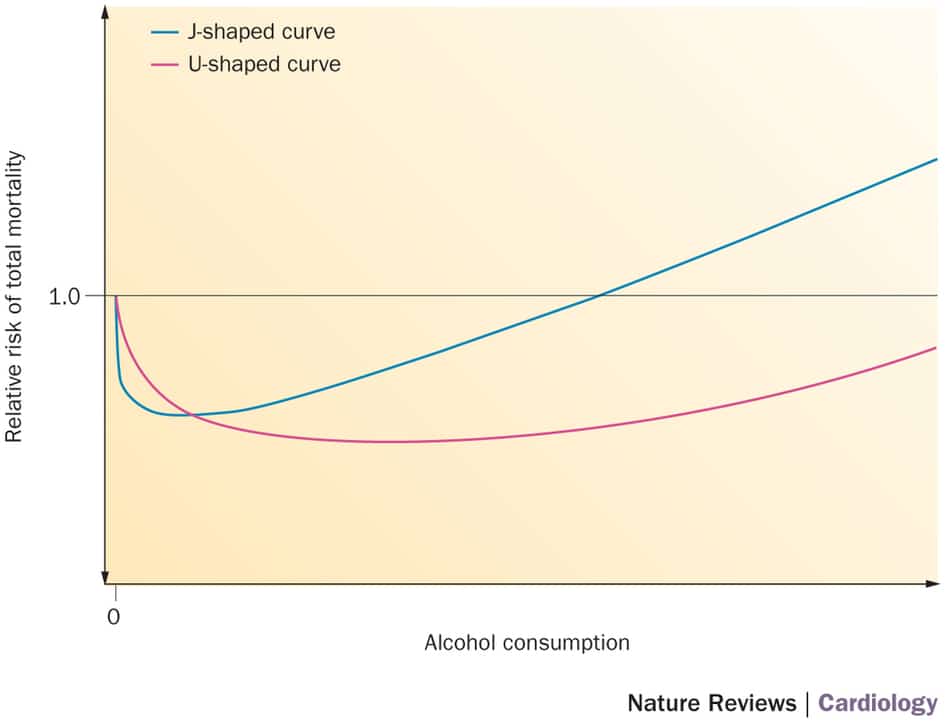
Today we are going to explore a bit about what that means. What is a U-shaped or a J-shaped curve? When a study reports a U-shaped curve it means that there is the lowest incidence of disease in the middle ranges, with peaks in both the lower and upper ranges. A graph of the outcomes would look something like the image on the right.
What is an example of a backwards J graph?
On the right is an example of a backwards-J shaped graph. A study published in 2015 by Durup et al. reported “ A reverse J-shaped association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cardiovascular disease mortality – the CopD-study .”
What is the J-curve and why is it useful?
The J-curve is useful to demonstrate the effects of an event or action over a set period of time. Put bluntly, it shows that things are going to get worse before they get better.
What does a J shape population growth curve indicate?
The J-shaped of growth curve for the population growth in a species indicates the exponential form of growth. There is rapid increase in the growth rate due to the favorable factors.
Are there J curves?
A J-curve is defined as the combination of a negative short-run derivative with a positive long-run derivative. The question posed - under what circum- stances does a real depreciation improve the real trade balance in the long run but worsen it in the short run? - is distinctly partial equilibrium in nature.
What do you mean by J-curve effect?
This refers to a phenomenon wherein the trade balance of a country worsens following the depreciation of its currency before it improves. Generally, any depreciation in the value of a currency is expected to improve the economy's overall trade balance by encouraging exports and discouraging imports.
Who gave the concept of J-curve?
The J-curve hypothesis was introduced in 1962 by American sociologist James C. Davies, who believed that social and political unrest was precipitated by a brief period of sharp decline in economic development after a prolonged period of economic growth and improvement.
When did the J-curve start?
The J CurveAuthorIan BremmerLanguageEnglishGenrePolitics, International AffairsPublisherSimon & SchusterPublication dateSeptember 12, 20068 more rows
What Is a J-Curve?
A J-curve is a trendline that shows an initial loss immediately followed by a dramatic gain. In a chart, this pattern of activity would follow the shape of a capital "J".
What is the J curve effect?
The J-curve effect is often cited in economics to describe, for instance, the way that a country’s balance of trade initially worsens following a devaluation of its currency, then quickly recovers and finally surpasses its previous performance.
Why is the J curve useful?
The J-curve is useful to demonstrate the effects of an event or action over a set period of time. Put bluntly, it shows that things are going to get worse before they get better.
What is the J curve in private equity?
The J-Curve in Private Equity. The term J-curve is used to describe the typical trajectory of investments made by a private equity firm. The J-curve is a visual representation of the plain fact that sometimes things will get worse before they get better.
