What causes too much aldosterone?
Other causes include the following:
- Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia or growth on each adrenal gland
- A tumor outside the adrenal glands that release aldosterone
- Cancerous tumor that releases aldosterone
- A genetic disease called familial hyperaldosteronism type 1
What are the effects of increased aldosterone?
Hyperaldosteronism
- Hyperaldosteronism can be caused by a tumor in the adrenal gland or may be a response to some diseases.
- High aldosterone levels can cause high blood pressure and low potassium levels. ...
- Doctors measure the levels of sodium, potassium, and aldosterone in the blood.
- Sometimes, a tumor is removed, or people take drugs that block the action of aldosterone.
Do the kidneys secrete aldosterone?
Healthy kidneys produce a hormone called aldosterone to help the body regulate blood pressure. Kidney damage and uncontrolled high blood pressure each contribute to a negative spiral. As more arteries become blocked and stop functioning, the kidneys eventually fail. What is the main action in the kidneys that regulates BP?
Does aldosterone raise or lower blood pressure?
Aldosterone is a hormone that helps increase blood pressure by causing the kidneys to retain both salt and water, which over time increases the amount of fluid in the body. This increase, in turn, raises blood pressure.

What causes secretion of aldosterone?
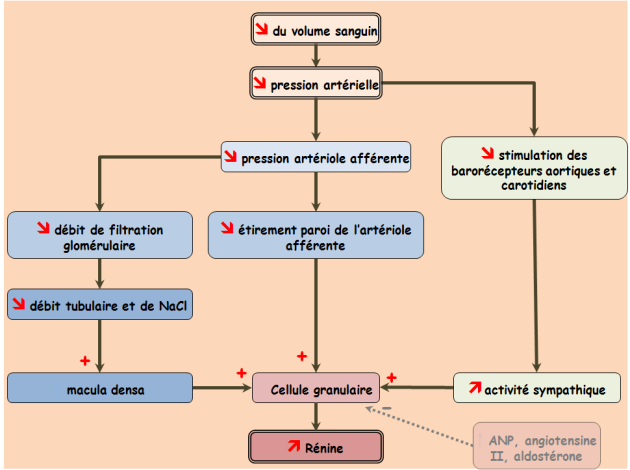
Aldosterone secretion is stimulated by an actual or apparent depletion in blood volume detected by stretch receptors and by an increase in serum potassium ion concentrations; it is suppressed by hypervolemia and hypokalemia.
What happens when aldosterone is secreted?
Aldosterone causes an increase in salt and water reabsorption into the bloodstream from the kidney thereby increasing the blood volume, restoring salt levels and blood pressure.
What is aldosterone and its function?
(al-DOS-teh-rone) A steroid hormone made by the adrenal cortex (the outer layer of the adrenal gland). It helps control the balance of water and salts in the kidney by keeping sodium in and releasing potassium from the body. Too much aldosterone can cause high blood pressure and a build-up of fluid in body tissues.
Does aldosterone increase or decrease blood pressure?
Aldosterone raises blood pressure and lowers potassium.
What regulates aldosterone secretion?
Aldosterone secretion by the zona glomerulosa cells of the adrenal gland is normally regulated by Ang II and potassium, which is mediated by an increase in intracellular calcium.
Why aldosterone is called life saving hormone?
Aldosterone of the adrenal cortex is life-saving hormone because it serves to retain sodium and water to maintain a sufficient blood volume for circulation.
Is aldosterone a diuretic?
Aldosterone antagonists are diuretics or “water pills.” They may also be called aldosterone receptor blockers. Aldosterone antagonists include: Eplerenone (Inspra) Spirinolactone (Aldactone)
Does aldosterone increase potassium?
Aldosterone causes sodium to be absorbed and potassium to be excreted into the lumen by principal cells. In alpha intercalated cells, located in the late distal tubule and collecting duct, hydrogen ions and potassium ions are exchanged. Hydrogen is excreted into the lumen, and the potassium is absorbed.
What is the effect of aldosterone on kidney and where is it produced?
Aldosterone causes sodium to be absorbed and potassium to be excreted into the lumen by principal cells. In alpha intercalated cells, located in the late distal tubule and collecting duct, hydrogen ions and potassium ions are exchanged. Hydrogen is excreted into the lumen, and the potassium is absorbed.
How does aldosterone increase sodium reabsorption?
If decreased blood pressure is detected, the adrenal gland is stimulated by these stretch receptors to release aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorption from the urine, sweat, and the gut. This causes increased osmolarity in the extracellular fluid, which will eventually return blood pressure toward normal.
How does aldosterone increase water reabsorption?
Aldosterone increases sodium transport by binding to the MR, translocating to the nucleus, and increasing the transcription of sodium channels and transporters, thereby indirectly promoting water reabsorption in the renal distal tubule.
Why aldosterone is called life saving hormone?
Aldosterone of the adrenal cortex is life-saving hormone because it serves to retain sodium and water to maintain a sufficient blood volume for circulation.
What is aldosterone?
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal glands.It is categorized as a mineralocorticoid.
What is aldosterone's role in the body?
Aldosterone regulates the salt and water balance of the body by increasing the retention of sodium and water and the excretion of potassium by the...
What regulates the production of aldosterone?
Production of aldosterone (in adult humans, about 20–200 micrograms per day) in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex is regulated by the reni...
How does aldosterone act in the body?
Aldosterone acts in the body by binding to and activating a receptor in the cytoplasm of renal tubular cells. The activated receptor then stimulate...
What hormone is secreted by the adrenal glands?
Last Updated: May 26, 2021 See Article History. aldosterone, a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal glands. Aldosterone serves as the principal regulator of the salt and water balance of the body and thus is categorized as a mineralocorticoid. It also has a small effect on the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
How does aldosterone work?
Aldosterone acts in the body by binding to and activating a receptor in the cytoplasm of renal tubular cells. The activated receptor then stimulates the production of ion channels in the renal tubular cells. It thus increases sodium reabsorption into the blood and increases potassium excretion into the urine.
How does aldosterone affect the body?
It also has a limited effect on the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins .
What is the function of renin?
Renin acts on a protein circulating in the plasma called angiotensinogen, cleaving this substance into angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is subsequently converted to angiotensin II, which stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. pathways in the biosynthesis of steroid hormones.
Where is aldosterone synthesized?
Aldosterone is synthesized in the body from corticosterone, a steroid derived from cholesterol. Production of aldosterone (in adult humans, about 20–200 micrograms per day) in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex is regulated by the renin-angiotensin system. Renin is secreted from the kidneys in response to variations in blood pressure ...
Where did aldosterone come from?
Pure aldosterone was isolated from beef adrenal glands in 1953 by research groups in England and Switzerland. By 1956 its structure was established, and it was synthesized from other steroids. The availability of other mineralocorticoids as therapeutic agents greatly restricts the use of aldosterone in therapy.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
What is aldosterone?
Aldosterone is a hormone produced in the outer section (cortex) of the adrenal glands, which sit above the kidneys . It plays a central role in the regulation of blood pressure mainly by acting on organs such as the kidney and the colon to increase the amount of salt ( sodium) reabsorbed into the bloodstream and to increase the amount of potassium excreted in the urine. Aldosterone also causes water to be reabsorbed along with sodium; this increases blood volume and therefore blood pressure.
What happens if I have too much aldosterone?
The symptoms include high blood pressure, low blood levels of potassium and an abnormal increase in blood volume.
What enzymes are involved in the production of angiotensin II?
Renin is an enzyme that leads to a series of chemical reactions resulting in the production of angiotensin II, which in turn stimulate aldosterone release. Aldosterone causes an increase in salt and water reabsorption into the bloodstream from the kidney thereby increasing the blood volume, restoring salt levels and blood pressure.
What is the role of aldosterone in the kidneys?
Aldosterone is part of a group of linked hormones, which form the renin– angiotensin –aldosterone system. Activation of this system occurs when there is decrease in blood flow to the kidneys following loss of blood volume or a drop in blood pressure (e.g. due to a haemorrhage ).
What is the condition where aldosterone levels are low?
Low aldosterone levels are found in a rare condition called Addison's disease . In Addison's disease, there is a general loss of adrenal function resulting in low blood pressure, lethargy and an increase in potassium levels in the blood (see the article on Addison's disease for further information). Last reviewed: Jan 2018.
Why is aldosterone important?
Because of the significance of aldosterone to the physiology and pathophysiology of the cardiovascular system, it is important to understand the regulation of its biosynthesis and secretion from the adrenal cortex. Herein, the mechanisms regulating aldosterone production in zona glomerulosa cells are discussed, ...
What is the role of aldosterone in the body?
Aldosterone is responsible for regulating sodium homeostasis, thereby helping to control blood volume and blood pressure.
Where is aldosterone secreted?
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone synthesized in and secreted from the outer layer of the adrenal cortex, the zona glomerulosa. Aldosterone is responsible for regulating sodium homeostasis, thereby helping to control blood volume and blood pressure. Insufficient aldosterone secretion can lead to hypo ….
Can aldosterone cause hypertension?
On the other hand, excessive aldosterone levels, or those too high for sodium status, can cause hypertension and exacerbate the effects of high blood pressure on multiple organs, contributing to renal disease, stroke, visual loss, and congestive heart failure.
What is aldosterone?from yourhormones.info
Aldosterone is a hormone produced in the outer section (cortex) of the adrenal glands, which sit above the kidneys . It plays a central role in the regulation of blood pressure mainly by acting on organs such as the kidney and the colon to increase the amount of salt ( sodium) reabsorbed into the bloodstream and to increase the amount of potassium excreted in the urine. Aldosterone also causes water to be reabsorbed along with sodium; this increases blood volume and therefore blood pressure.
What happens if I have too much aldosterone?from yourhormones.info
The symptoms include high blood pressure, low blood levels of potassium and an abnormal increase in blood volume.
What hormone is secreted by the adrenal glands?from britannica.com
Last Updated: May 26, 2021 See Article History. aldosterone, a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal glands. Aldosterone serves as the principal regulator of the salt and water balance of the body and thus is categorized as a mineralocorticoid. It also has a small effect on the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
How does aldosterone work?from britannica.com
Aldosterone acts in the body by binding to and activating a receptor in the cytoplasm of renal tubular cells. The activated receptor then stimulates the production of ion channels in the renal tubular cells. It thus increases sodium reabsorption into the blood and increases potassium excretion into the urine.
What is the function of renin?from britannica.com
Renin acts on a protein circulating in the plasma called angiotensinogen, cleaving this substance into angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is subsequently converted to angiotensin II, which stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. pathways in the biosynthesis of steroid hormones.
Where is aldosterone synthesized?from britannica.com
Aldosterone is synthesized in the body from corticosterone, a steroid derived from cholesterol. Production of aldosterone (in adult humans, about 20–200 micrograms per day) in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex is regulated by the renin-angiotensin system. Renin is secreted from the kidneys in response to variations in blood pressure ...
Where did aldosterone come from?from britannica.com
Pure aldosterone was isolated from beef adrenal glands in 1953 by research groups in England and Switzerland. By 1956 its structure was established, and it was synthesized from other steroids. The availability of other mineralocorticoids as therapeutic agents greatly restricts the use of aldosterone in therapy.
Why Is Aldosterone Important?
It's a hormone that plays a big role in keeping your blood pressure in check.
What does it mean when you feel exhaustion?
An overall feeling of exhaustion. It can happen when there is damage to your adrenal glands. Secondary hyperaldosteronism: It happens when your body makes more aldosterone in response to problems with other organs, like your kidneys, heart, or liver. It can cause things like: High blood pressure. Low potassium.
What happens if your aldosterone levels are out of whack?
When the level of aldosterone in your body is out of whack, it could lead to other health issues, including damage to your heart, brain, and kidneys.
What happens if you have high levels of aldosterone?
If your aldosterone and cortisol levels are lower than normal, and your renin level is high, you may be diagnosed with Addison’s disease.
What is the best test for blood pressure?
If you’re having trouble with your blood pressure, your doctor might order an aldosterone test to help them figure out what’s going on. When you get this test, a lab tech takes a small sample of your blood to measure how much of the hormone aldosterone is in your system. That result will help your doctor figure out what’s going on ...
What is the name of the condition where the body makes too much aldosterone?
Conn’s syndrome: Also called primary hyperaldosteronism, this happens when your body makes too much aldosterone. Conn's syndrome is usually the result of benign hyperplasia (enlargement) of both adrenals or small, benign tumors forming on your adrenal glands, which make aldosterone.
What happens when you don't make enough cortisol?
When this happens, you can have: Low blood pressure. Higher potassium levels. An overall feeling of exhaustion. It can happen when there is damage to your adrenal glands.
What is the condition where one adrenal gland produces too much of the hormone aldosterone?
Hyperaldosteronism. Hyperaldosteronism is a condition in which one or both adrenal glands produce too much of the hormone aldosterone. This can lower potassium levels, which can cause weakness and muscle spasms. Hyperaldosteronism can be treated with medication, or if necessary, surgery. Appointments & Access.
How to check for hyperplasia?
To check for hyperplasia (overactivity) of the adrenal glands, the doctor may order a test in which blood samples are taken directly from both adrenal glands. If one gland has a higher level of aldosterone, the cause is likely a tumor; if both glands have a high aldosterone level, then it is probably hyperplasia.
What causes hyperaldosteronism?
Hyperaldosteronism can be caused by a benign (noncancerous) tumor on the adrenal gland. Another possible cause of hyperaldosteronism is hyperplasia (overactivity) of the adrenal glands. In some cases, hyperaldosteronism is an inherited condition.
What is the adrenal gland?
The adrenal glands are part of the endocrine system. They produce hormones the body needs to carry out daily functions, including testosterone, aldosterone and adrenaline. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney and are about the size of your thumb. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is the best treatment for hyperaldosteronism?
These drugs include spironolactone (Aldactone®), eplerenone (Inspra®), or amiloride (Midamor®).
Can adrenal glands be removed?
If the cause is a tumor on one of the adrenal glands, the gland can be removed with surgery, or the same medications can be used. Those should improve the blood pressure control, and may reduce the number of medications you need to control your blood pressure.
Which is more likely to be at risk for hyperaldosteronism?
People who are at the greatest risk for hyperaldosteronism are those who have hypertension (high blood pressure) that is difficult to control even if the patient is taking several medications at the same time. Hyperaldosteronism is also more likely in people who: Have hypertension and low potassium levels.
What factors affect aldosterone secretion?
Of these factors, potassium ion concentration and the renin-angiotensin system are by far the most potent in regulating aldosterone secretion. A small percentage increase in potassium concentration can cause a severalfold increase in aldosterone secretion. Likewise, activation of the renin-angiotensin system, usually in response to diminished blood flow to the kidneys or to sodium loss, can cause a severalfold increase in aldosterone secretion. In turn, the aldos-terone acts on the kidneys (1) to help them excrete the excess potassium ions and (2) to increase the blood volume and arterial pressure, thus returning the renin-angiotensin system toward its normal level of activity. These feedback control mechanisms are essential for maintaining life, and the reader is referred again to Chapters 27 and 29 for a full understanding of their functions.
Which cells regulate aldosterone secretion?
The regulation of aldosterone secretion by the zona glomerulosa cells is almost entirely independent of the regulation of cortisol and androgens by the zona fas-ciculata and zona reticularis.
Does sodium ion concentration affect aldosterone secretion?
By contrast, the effects of so dium ion concentration per se and of ACTH in controlling aldosterone secretion are usually minor. Nevertheless, a 10 to 20 per cent decrease in extracellular fluid sodium ion concentration, which occurs on rare occasions, can perhaps double aldosterone secretion. In the case of ACTH, if there is even a small amount of ACTH secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, it is usually enough to permit the adrenal glands to secrete whatever amount of aldosterone is required, but total absence of ACTH can significantly reduce aldosterone secretion.
Does angiotensin increase aldosterone?
2. Increased activity of the renin-angiotensin system (increased levels of angiotensin II) also greatly increases aldosterone secretion.
Is aldosterone secretion a regulation of extracellular fluid?
The regulation of aldosterone secretion is so deeply intertwined with the regulation of extracellular fluid electrolyte concentrations, extracellular fluid volume, blood volume, arterial pressure, and many special aspects of renal function that it is difficult to discuss the regulation of aldosterone secretion independently of all these other factors. This subject is presented in detail in Chapters 28 and 29, to which the reader is referred. However, it is important to list here some of the more important points of aldosterone secretion control.
