What does Weber's theory explain?
The Max Weber Theory of Bureaucracy proposes that all business tasks must be divided among the employees. The basis for the division of tasks should be competencies and functional specializations. In this way, the workers will be well aware of their role and worth in the organization and what is expected of them.
What are the three categories of Weber's least cost theory?
According to Weber, three main factors influence industrial location; transport costs, labor costs, and agglomeration economies.
What are the three points of the least cost theory?
Manufacturing plants will be located, in response to three forces: relative transport costs, labor costs, and agglomeration (a collection of industries, factories, etc., in one location).
Who created Weber's least cost theory?
Weber's Least-Cost Theory. ... Alfred Weber formulated a theory of. ... In one the weight of the final product is less than the weight of the raw material going into making the product. ... In the other the final product is heavier than the raw. ... Usually this is a case of a raw material such as water being.More items...
What is an example of the least cost theory?
A company that could be an example of the least cost theory is the google industry because they are located in a place with agglomeration,causing a lot of customers to emerge.
What are the basic assumptions of Weber's theory?
His first assumption is known as the isotropic plain assumption. This means the model is operative in a single country with a uniform topography, climate, technology, economic system. His second assumption is that only one finished product is considered at a time, and the product is shipped to a single market.
When was Weber's least cost theory created?
Developed by Alfred Weber in 1909 In Weber's Theory is mainly focused on the transportation cost, but it also takes the labor cost and agglomeration into account as well.
What are criticisms of Weber's least cost theory?
According to critics of this theory, Weber has unrealistically over-simplified the theory of industrial location. Many assumptions in the theory are unrealistic. According to them Weber has taken only two elements for determining the cost of transportation namely weight and distance.
When was the least cost theory developed?
1909Proposed by : Alfred Weber of Germany Year: 1909 In his Book: “Theory of the Location of Industries” (Uber den Standort der Industrien) His book is translated in English in 1929 and after that this concept became popular.
What is Weber's primary focus?
Weber would primarily be concerned with the question of objectivity and subjectivity, going on to distinguish social action from social behavior, noting that social action must be understood through how individuals subjectively relate to one another.
What is Weber's least cost theory AP Human geography?
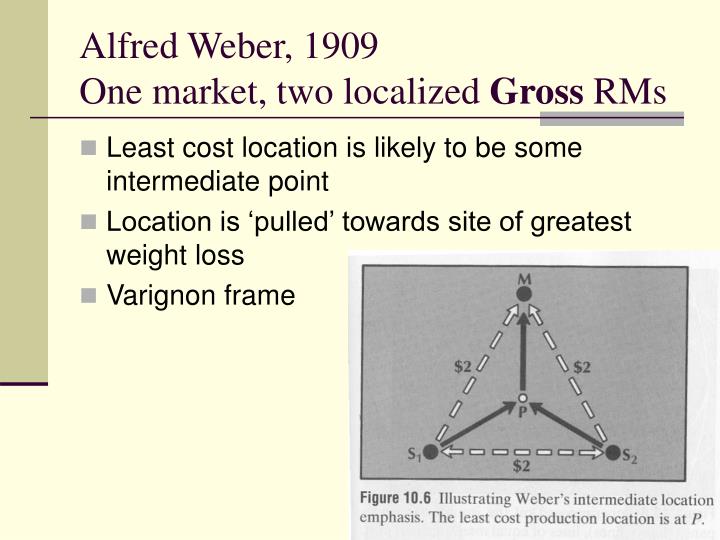
Weber's least cost theory suggests that a production point must be located within a “triangle,” with raw materials coming from at least two sources. Weight-gaining industries must have their production point closer to the market.
What is the importance of least cost by planning to establish an industry?
Solution : Least cost is the key factor that determines the location of an industry because industry tends to be located at a place where factors of production are either available or can be arranged at low cost.
What is Weber's least cost theory AP Human Geography?
Weber's least cost theory suggests that a production point must be located within a “triangle,” with raw materials coming from at least two sources. Weight-gaining industries must have their production point closer to the market.
What is Weber's primary focus?
Weber would primarily be concerned with the question of objectivity and subjectivity, going on to distinguish social action from social behavior, noting that social action must be understood through how individuals subjectively relate to one another.
When was Weber's least cost theory created?
Developed by Alfred Weber in 1909 In Weber's Theory is mainly focused on the transportation cost, but it also takes the labor cost and agglomeration into account as well.
What are the main theories of industrial location?
Central theme of Industrial location theory has been the concept of optimum location i.e. finding out best location where profit is maximum and cost is minimum. Where the cost of manufacturing is least due to the presence of Raw Material, Market, etc.
How did Weber come to know that there were certain costs in the total cost of production?
Through the process of cost analysis, Weber came to know that there were certain costs in the total cost of production which are directly influenced by geographical factors. Geographical conditions vary from place to place and influence the cost of production. There are certain costs which are not all influenced by geographical factors such as interest and depreciation.
What is Weber's theory?
Weber has used index numbers and coefficient in his theory which has made it complicated. In fact, the theory is based on technical analysis and has become mathematical in character. This has made it more difficult to understand.
How do transportation costs affect the location of an industry?
Transportation costs play an important part in the location of an industry. Transportation costs are influenced by the weight to be transported and the distance to be covered. Generally, industries will have a tendency to localize at a place where material and fuel are not difficult to obtain. Weber has further given that the basic factors for location of an industry are the nature or type of material used and the nature of their transformation into products.
What are some examples of decentralization?
Examples of such factors are: local taxes cost of land, residence, labor costs and transportation costs. Such factors decentralization because the cost of production stands reduced due to decentralization of shift in location. Weber has indicated two more possibilities. One is split in location.
What is Weber's raw material?
Weber has divided raw material into two categories: iniquities and specific local raw material. The former is generally available at all places whereas the latter is found only in a few. Likewise, material may be pure raw material and gross raw material.
What are the two factors that Weber considers in his analysis of transportation costs?
Inadequate analysis of transportation costs: Weber considers only two factors in transportation costs— the weight to be transported and the distances to be covered.
What are the salient features of Weber's theory?
Salient Features of Weber’s Theory: The first and perhaps the most important feature of the theory given by Weber is its division into two parts: Pure theory and Realistic theory. Other features of his theory are that it is based on the deductive method and incorporates all those general factors which attract of localize in some areas ...