
What type of reaction do Alkenes undergo with hydrogen?
Alkenes undergo addition reactions, adding such substances as hydrogen, bromine, and water across the carbon-to-carbon double bond. What type of reaction do alkanes undergo? The main reaction that alkanes can undergo is combustion, that is, oxidation by (usually) atmospheric oxygen.
Why is an alkyne more acidic than an alkene?
Why is alkyne more acidic than alkene? Alkyne is more acidic than Alkene because the triple bond between the tow carbon atoms makes a very close distance (very short) between the carbon carbon bond and hence a great space between (C-H) , In the search of sincerity.
How does an alkene react with HBr?
HBr Addition Reaction: HBr adds to alkenes to create alkyl halides. A good way to think of the reaction is that the pi bond of the alkene acts as a weak nucleophile and reacts with the electrophilic proton of HBr. Alternatively, you can view the first step of the reaction as the protonation of the pi bond.
What is the mechanism of hydration of alkenes?
Acid-Catalyzed hydration is the addition of water to an alkene which forms an alcohol: The reaction goes through a stepwise mechanism which starts with the protonation of the double bond: The presence of an acid is necessary as the water by itself is a weak acid and cannot protonate the double bond. However, the hydronium ion, formed in acid ...
See more
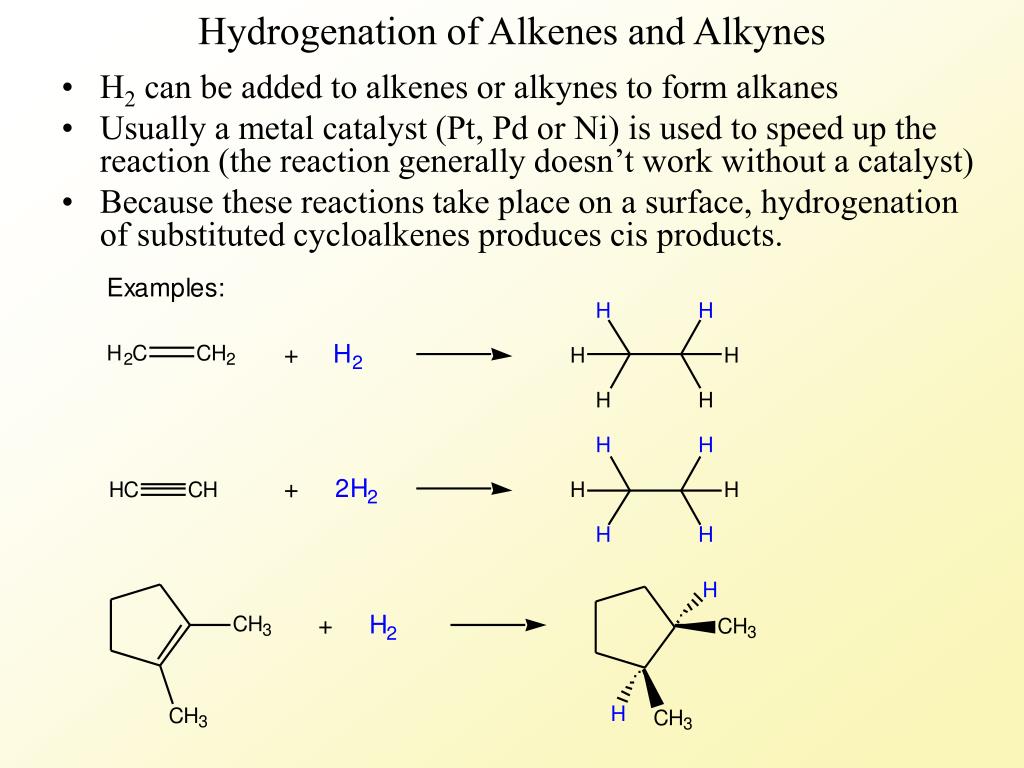
What is hydrogenation in simple words?
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds.
What is an example of hydrogenation?
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that adds hydrogen to a molecule. Hydrogenation is not thermodynamically favorable at ordinary temperatures, so a catalyst is needed. Usually this catalyst is a metal. Examples of hydrogenated products include margarine, mineral turpentine, and aniline.
What is hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes?
Hydrogenation of an Alkyne to a Trans-Alkene Alkynes can be reduced to trans-alkenes with the use of sodium dissolved in an ammonia solvent. An Na radical donates an electron to one of the P bonds in a carbon-carbon triple bond. This forms an anion, which can be protonated by a hydrogen in an ammonia solvent.
What is the meaning of hydrogenation reaction?
hydrogenation, chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen and an element or compound, ordinarily in the presence of a catalyst.
What is the purpose of hydrogenation?
Purpose of hydrogenation To convert a liquid oil into a solid fat. When solid fats of the right consistency are expensive or not available, hydrogenation, sometimes in combination with other processes such as interesterification or fractionation, may provide a way to produce the desired fat.
What is hydrogenation and why is it used?
Hydrogenation is used to solidify, preserve or purify many products, raw materials, or ingredients. Ammonia, fuels (hydrocarbons), alcohols, pharmaceuticals, margarine, polyols, various polymers and chemicals (hydrogen chloride and hydrogen peroxide) are products treated using a hydrogenation process.
How do you find the hydrogenation of an alkene?
0:3610:52Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes - Heterogeneous Catalysts - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn order for you to get a reaction with this alkene and hydrogen gas you need to break the bondMoreIn order for you to get a reaction with this alkene and hydrogen gas you need to break the bond between the two hydrogen atoms and that's very difficult to do.
Is hydrogenation of alkenes oxidation?
The reaction of the hydrogenation of alkenes is an oxidation-reduction reaction, as it is accompanied by a change in oxidation states: CH₃-CH=CH₂ + H₂ = CH₃-CH₂-CH₃ (in propylene, in the carbon atoms from left to right the oxidation states are equal to -3, -1 and -2, and in propane - -3, -2 and -3).
Why catalyst is used in hydrogenation?
During hydrogenation, vegetable oils react with hydrogen gas at about 60ºC. This catalyst is used to speed up the reaction. In this process, double bonds are converted to single bonds in the reaction.
What is the difference between hydrogenation and hydrogenation?
The main difference between hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis is that hydrogenation includes the formation of a saturated compound from an unsaturated compound whereas hydrogenolysis includes the formation of two small compounds from a large molecule.
What are three examples of hydrogen?
Examples of Hydrogen Bondswater (H2O): Water is an excellent example of hydrogen bonding. ... chloroform (CHCl3): Hydrogen bonding occurs between hydrogen of one molecule and carbon of another molecule.ammonia (NH3): Hydrogen bonds form between hydrogen of one molecule and nitrogen of another.More items...•
What are the two types of hydrogenation?
Hydrogenation can be either partial hydrogenation or full hydrogenation. While full hydrogenation converts the vegetable oils into fully saturated fats, vegetable oils being partially hydrogenated are partially saturated so the melting point increases to the point where solid fat is present at room temperature.
What is hydrogenation of oil give example?
In the food industry, hydrogen is added to oils (in a process called hydrogenation) to make them more solid, or 'spreadable'. Hydrogenated oils can be sold directly as 'spreads', but are also used in the food industry in the manufacture of many foodstuffs such as biscuits and cakes.
What kind of reaction is hydrogenation?
An example of an alkene addition reaction is a process called hydrogenation.In a hydrogenation reaction, two hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of an alkene, resulting in a saturated alkane.
What is the reaction of alkenes with hydrogen?
The reaction of alkenes with hydrogen (hydrogenation), including the manufacture of margarine
What happens if you don't hydrogenate carbon?
If these particular bonds aren't hydrogenated during the process, they will still be present in the final margarine in molecules of trans fats.
How is margarine made?
Some margarine is made by hydrogenating carbon-carbon double bonds in animal or vegetable fats and oils. You can recognise the presence of this in foods because the ingredients list will include words showing that it contains "hydrogenated vegetable oils" or "hydrogenated fats". The impression is sometimes given that allmargarine is made by ...
How to harden oil?
You can "harden" (raise the melting point of) the oil by hydrogenating it in the presence of a nickel catalyst. Conditions (like the precise temperature, or the length of time the hydrogen is passed through the oil) are carefully controlled so that some, but not necessarily all, of the carbon-carbon double bonds are hydrogenated.
Which type of bond is found in unsaturated fats and oils?
The double bonds in unsaturated fats and oils tend to have the groups around them arranged in the "cis" form.
Is hydrogenation bad for you?
The downside of hydrogenation as a means of hardening fats and oils. There are some probable health risks from eating hydrogenated fats or oils. Consumers are becoming more aware of this, and manufacturers are increasingly finding alternative ways of converting oils into spreadable solids.
What is it called when there are two or more carbon-carbon double bonds in each chain?
If there are two or more carbon-carbon double bonds in each chain, then it is said to be polyunsaturated.
What is an example of an alkene addition reaction?
Introduction. An example of an alkene addition reaction is a process called hydrogenation. In a hydrogenation reaction, two hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of an alkene, resulting in a saturated alkane. Hydrogenation of a double bond is a thermodynamically favorable reaction because it forms a more stable (lower energy) product.
How does a metal catalyst absorb an alkene?
The metal catalyst also absorbs the alkene onto its surface. A hydrogen atom is then transferred to the alkene, forming a new C-H bond. A second hydrogen atom is transferred forming another C-H bond. At this point, two hydrogens have added to the carbons across the double bond.
What is the process of making coal into a liquid?
This process also increases the chemical stability of products and yields semi-solid products like margarine. Hydrogenation is also used in coal processing. Solid coal is converted to a liquid through the addition of hydrogen. Liquefying coal makes it available to be used as fuel.
What is the heat released by an alkene?
The heat released is called the heat of hydrogenation, which is an indicator of a molecule’s stability. Although the hydrogenation of an alkene is a thermodynamically favorable reaction, it will not proceed without the addition of a catalyst.
What is hydrogenation used for?
Hydrogenation reactions are extensively used to create commercial goods. Hydrogenation is used in the food industry to make a large variety of manufactured goods, like spreads and shortenings, from liquid oils. This process also increases the chemical stability of products and yields semi-solid products like margarine.
What are the metals that are used in catalysts?
Common catalysts used are insoluble metals such as palladium in the form Pd-C, platinum in the form PtO2, and nickel in the form Ra-Ni. With the presence of a metal catalyst, the H-H bond in H2 cleaves, and each hydrogen attaches to the metal catalyst surface, forming metal-hydrogen bonds.
Why is carbon-carbon bond so weak?
Because the carbon-carbon π bond is relatively weak, it is quite reactive and can be easily broken and reagents can be added to carbon. Reagents are added through the formation of single bonds to carbon in an addition reaction.
What is an example of an alkene addition reaction?
An example of an alkene addition reaction is a process called hydrogenation. In a hydrogenation reaction, two hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of an alkene, resulting in a saturated alkane. Hydrogenation of a double bond is a thermodynamically favorable reaction because it forms a more stable (lower energy) product.
What is the reaction between carbon and hydrogen?
The reaction between carbon-carbon double bonds and hydrogen provides a method of determining the number of double bonds present in a compound. For example, one mole of cyclohexene reacts with one mole of hydrogen to produce one mole of cyclohexane: but one mole of 1,4-cyclohexadiene reacts with two moles of hydrogen to form one mole of cyclohexane:
How many moles of hydrogen react with 1,4-cyclohexadiene?
but one mole of 1,4-cyclohexadiene reacts with two moles of hydrogen to form one mole of cyclohexane:
What metals are used in chemistry?
Three metals—nickel, platinum and palladium —are commonly used, but a chemist cannot simply place a piece of one of these metals in a mixture of the alkene and hydrogen and get a reaction. Each metal catalyst must be prepared in a special way: nickel is usually used in a finely divided form called “Raney nickel.”.
What is the effect of adding hydrogen to a double bond?
The overall effect of such an addition is the reductive removal of the double bond functional group. Regioselectivity is not an issue, since the same group (a hydrogen atom) is bonded to each of the double bond carbons.
What is the addition of hydrogen to a carbon-carbon double bond?
Addition of hydrogen to a carbon-carbon double bond is called hydrogenation.
How is palladium prepared?
It is prepared by reacting a Ni-Al alloy with NaOH. palladium is obtained commercially “supported” on an inert substance, such as charcoal, (Pd/C). The alkene is usually dissolved in ethanol when Pd/C is used as the catalyst.
What is the process of reducing or saturating organic compounds?
The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures.
How is hydrogenation done?
The original and still a commonly practised form of hydrogenation in teaching laboratories, this process is usually effected by adding solid catalyst to a round bottom flask of dissolved reactant which has been evacuated using nitrogen or argon gas and sealing the mixture with a penetrable rubber seal. Hydrogen gas is then supplied from a H 2 -filled balloon. The resulting three phase mixture is agitated to promote mixing. Hydrogen uptake can be monitored, which can be useful for monitoring progress of a hydrogenation. This is achieved by either using a graduated tube containing a coloured liquid, usually aqueous copper sulfate or with gauges for each reaction vessel.
How much heat does hydrogenation release?
In the hydrogenation of vegetable oils and fatty acids, for example, the heat released, about 25 kcal per mole (105 kJ/mol), is sufficient to raise the temperature of the oil by 1.6–1.7 °C per iodine number drop. However, the reaction rate for most hydrogenation reactions is negligible in the absence of catalysts.
What is the name of the chemical reaction that occurs when a compound is dissolved in a catalyst?
Year of invention. 1897. Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H 2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds.
When was hydrogenation first used?
In 1922, Voorhees and Adams described an apparatus for performing hydrogenation under pressures above one atmosphere. The Parr shaker, the first product to allow hydrogenation using elevated pressures and temperatures, was commercialized in 1926 based on Voorhees and Adams' research and remains in widespread use. In 1924 Murray Raney developed a finely powdered form of nickel, which is widely used to catalyze hydrogenation reactions such as conversion of nitriles to amines or the production of margarine.
Where does hydrogen come from?
For hydrogenation, the obvious source of hydrogen is H 2 gas itself, which is typically available commercially within the storage medium of a pressurized cylinder. The hydrogenation process often uses greater than 1 atmosphere of H 2, usually conveyed from the cylinders and sometimes augmented by "booster pumps". Gaseous hydrogen is produced industrially from hydrocarbons by the process known as steam reforming. For many applications, hydrogen is transferred from donor molecules such as formic acid, isopropanol, and dihydroanthracene. These hydrogen donors undergo dehydrogenation to, respectively, carbon dioxide, acetone, and anthracene. These processes are called transfer hydrogenations .
What are the components of hydrogenation?
Hydrogenation has three components, the unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst.
How to name an alkene?
For straight-chain alkenes with 4 or more carbon atoms, that name does not completely identify the compound. For those cases, and for branched acyclic alkenes, the following rules apply: 1 Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule. If that chain does not contain the double bond, name the compound according to the alkane naming rules. Otherwise: 2 Number the carbons in that chain starting from the end that is closest to the double bond. 3 Define the location k of the double bond as being the number of its first carbon. 4 Name the side groups (other than hydrogen) according to the appropriate rules. 5 Define the position of each side group as the number of the chain carbon it is attached to. 6 Write the position and name of each side group. 7 Write the names of the alkane with the same chain, replacing the "-ane" suffix by " k -ene".
What is terminal alkene?
Terminal alkenes are precursors to polymers via processes termed polymerization. Some polymerizations are of great economic significance, as they generate as the plastics polyethylene and polypropylene. Polymers from alkene are usually referred to as polyolefins although they contain no olefins. Polymerization can proceed via diverse mechanisms. conjugated dienes such as buta-1,3-diene and isoprene (2-methylbuta-1,3-diene) also produce polymers, one example being natural rubber.
What are alkenes used for?
Alkenes are ligands in transition metal alkene complexes. The two carbon centres bond to the metal using the C–C pi- and pi*-orbitals. Mono- and diolefins are often used as ligands in stable complexes. Cyclooctadiene and norbornadiene are popular chelating agents, and even ethylene itself is sometimes used as a ligand, for example, in Zeise's salt. In addition, metal–alkene complexes are intermediates in many metal-catalyzed reactions including hydrogenation, hydroformylation, and polymerization.
How many carbon atoms are in an alkene?
Alkenes having four or more carbon atoms can form diverse structural isomers. Most alkenes are also isomers of cycloalkanes. Acyclic alkene structural isomers with only one double bond follow:
What is an alkene compound?
Chemical compound. A 3D model of ethylene, the simplest alkene. In chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon that contains a carbon –carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal.
What is the method of synthesis of alkene?
Another important method for alkene synthesis involves construction of a new carbon–carbon double bond by coupling of a carbonyl compound (such as an aldehyde or ketone) to a carbanion equivalent. Such reactions are sometimes called olefinations. The most well-known of these methods is the Wittig reaction, but other related methods are known, including the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction .
What is transition metal catalyzed hydrovinylation?
It involves the addition of a hydrogen and a vinyl group (or an alkenyl group) across a double bond.
