4.6 Addition, elimination and substitution reactions (ESCKY)
- An addition reaction occurs when two or more reactants combine to form a single product. This product will contain all the atoms that were present in the reactants. ...
- An elimination reaction occurs when a reactant is broken up into two products. ...
- A substitution reaction occurs when an exchange of elements in the reactants takes place. ...
What are addition reactions give two examples?
Addition Reactions. Imagine that you are given two sets of wooden planks and asked to make something out of them - anything you want. You get out your glue, saw, nails, and hammer and start building.
What is an addition reaction mechanism?
The addition reaction is the combination of two or more atoms or molecules in order to form a large molecule. This large molecule is known as an adduct. Most addition reactions are limited to molecules with unsaturation that have either double bonds or triple bonds. These addition reactions can be classified as follows.
What is an addition reaction?
In the simplest of terms of organic chemistry, we can say that an addition reaction is a chemical reaction wherein two or more reactants come together to form a larger single product.
What is a catalyst in organic chemistry?
- A catalyst does not initiate a chemical reaction.
- A catalyst does not be consumed in the reaction.
- Catalysts tend to react with reactants to form intermediates and at the same time facilitate the production of the final reaction product. After the whole process, a catalyst can regenerate.

What is addition organic reaction?
In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecules combine to generate a bigger one (the adduct). Molecules with carbon—hetero double bonds, such as carbonyl (C=O) or imine (C=N) groups, can be added because they have double-bond character as well.
What is addition reaction explain with example?
Addition reactions are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds, such as molecules with carbon-carbon double bonds (alkenes), with triple bonds (alkynes) or with carbonyl (C=O) groups can undergo addition as they too have double bond character. For example, CH2=CH2 + Cl2 → CH2Cl−CH2Cl. Chemistry.
How do you identify an addition reaction?
An addition reaction occurs when two or more reactants combine to form a single product. This product will contain all the atoms that were present in the reactants. Addition reactions occur with unsaturated compounds. Notice that C is the final product with no A or B remaining as a residue.
Which is an example of an addition reaction in organic compounds?
Perhaps the simplest addition reaction is hydrogenation. This is a reaction in which hydrogen gas reacts at a carbon-to-carbon double or triple bond or a carbon-to-oxygen double bond to add hydrogen atoms to carbon atoms.
What is the difference between addition and substitution reaction?
Solution : In addition reaction, product contains all the atoms present in the reactants whereas in substitution reaction, one type of atom/group of atom in a reactant is replaced by another atom/group of atoms.
What are the three types of addition reaction?
The different types of addition reactions are: Nucleophilic addition reaction. Electrophilic addition reaction. Free radical addition reaction.
What happens in addition reaction?
An addition reaction may be visualized as a process by which the double or triple bonds are fully or partially broken in order to accommodate additional atoms or groups of atoms in the molecule.
What does addition mean in chemistry?
An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one (the adduct).
How can you distinguish between electrophilic and addition?
A simple way to look if it's the electrophilic or a nucleophilic reaction is to look at the reactions and the species being added. Hence, nucleophilic and electrophilic addition reactions are differentiated.
Is synthesis and addition reaction the same?
Explanation: Addition reactions occur when two molecules combine to form a larger one, leading to a release of energy. Addition reactions result in the synthesis of a new molecule, giving them their second name: synthesis reactions.
Is addition reaction and combination reaction same?
Answer. in addition reaction, hydrogen in added in the presence of any catalyst to make a hydrocarbon saturated whereas in combination reaction two elements combine together to form a single compound.
Is Oxidation an addition reaction?
Oxidative addition is the reaction where the oxidation state of the metal center increases by two. This reaction cannot occur if the metal center of the complex doesn't have accessible two units higher than the initial oxidation state. Metal center in a complex is known to act as Lewis acid.
Which of the following will undergo addition reactions * 1 point ch4 c3h8 c2h6 C2H4?
C2H4 and C3H4 will give addition reaction because they connected by double or triple bond and are unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Is esterification an addition reaction?
Esterification is a subcategory of condensation reactions because a water molecule is produced in the reaction.
What are addition reactions of alkenes?
Addition reactions of alkenes The reaction is an 'addition' reaction because one molecule combines with another molecule, forming one larger molecule and no other products . Alkanes cannot take part in addition reactions. Propene, CH 3CH=CH 2, reacts with bromine. Predict the structure of the product formed.
What is addition reaction of hydrocarbons?
In addition reaction, an unsaturated hydrocarbon is converted to saturated hydrocarbon by the addition of hydrogen. Addition reactions are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds, such as molecules with carbon-carbon double bonds (alkenes), or with triple bonds (alkynes). Chemistry.
What is an addition reaction?
An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one (the adduct ).
What is the reverse of an elimination reaction?
An addition reaction is the reverse of an elimination reaction. For instance, the hydration of an alkene to an alcohol is reversed by dehydration. There are two main types of polar addition reactions : electrophilic addition and nucleophilic addition.
What is the reaction in which hydrogen gas reacts with carbon?
This is a reaction in which hydrogen gas reacts at a carbon-to-carbon double or triple bond or a carbon-to-oxy gen double bond to add hydrogen atoms to carbon atoms. In the laboratory this reaction can be facilitated with hydrogen (H 2) in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel (Ni) or platinum (Pt). Note that the name ‘addition’ is apt here, ...
What is the reaction between water and alkene?
Another important addition reaction occurs between an alkene and water to form an alcohol. This reaction is called hydration, and represents t he addition of water to a substance.
How do alkenes undergo halogenation?
Alkenes also readily undergo halogenation through addition, a reaction in which a halogen reacts at a carbon-to-carbon double or triple bond to add halogen atoms to carbon atoms. Indeed, the addition reaction with bromine (Br 2) can be used to test for alkenes in an uncharacterized sample of material. Bromine solutions are brownish red.
Why is hydrogenation important in cooking?
Hydrogenating foods in this way has several benefits: it removes a functional group on the fats that could react by oxidation to make products with off flavors. It also raises the melting points of the fats, changing the texture in ways that might be pleasing to consumers. It allows for higher temperature cooking for baked products, which can increase browning and improve flavor.
What is the reaction in which hydrogen gas reacts with a carbon-to-carbon double or triple bond?
Perhaps the simplest addition reaction is hydrogenation. This is a reaction in which hydrogen gas reacts at a carbon-to-carbon double or triple bond ...
What is hydrogenation used for?
In one important application of this chemistry, hydrogenation is used to convert unsaturated vegetable oils to saturated fats. Hydrogenated fats, or partially-hydrogenated fats often appear on nutrition labels for processed foods such as crackers or chips.
What are the most common addition reactions in organic chemistry?
In organic chemistry, the most common use of addition reactions involves alkenes. Alkenes are molecules consisting of hydrocarbons (hydrogen + carbon) and double bonds. As alkenes have double bonds, can you guess what kind of compounds they are? If you just said, 'unsaturated compound,' you're correct!
When do addition reactions occur?
Addition reactions occur when an atom is added to a compound that has a double or triple bond.
What happens when atoms are combined using double and triple bonds to create a compound that retains all components in?
An addition reaction happens when atoms are combined using double and triple bonds to create a compound that retains all components in the reaction. Learn the rules of addition reactions and see examples of how they function. Updated: 11/02/2021
What is the product of addition reactions?
This is a very important point, as the product of addition reactions contains all the atoms and elements originally present in the reactants being combined. Now, let's go over some basic rules for performing addition reactions.
What happens when a compound with multiple bonds is transformed to a compound with single bonds?
When a compound with multiple bonds is transformed to a compound with single bonds, this directly affects stability. The relationship between addition reactions and bond stability is known as Markovnikov's rule, which states that the outcome of some (not all) addition reactions will result in a more stable product.
What happens when an alkene reacts with a molecule?
As shown in this diagram, when an alkene reacts with a molecule - in this case hydrogen chloride, or HCL - it undergoes a chemical transformation and changes to a single product with no double bond present. This chemical transformation just means that bonds were broken and formed, something very characteristic of addition reactions.
When can atoms be added to a compound?
Atoms can only be added to molecules when forming a product; nothing is eliminated or taken away. Remember that addition reactions involve the addition of an atom to a compound containing a single or double bond.
What are the forms of addition reactions?
Other forms of addition reactions include: catalyzed addition reactions, such as the self-addition of alkenes (catalyzed by acids) or the hydrogenationof alkenes, aldehydes, and ketones (catalyzed by metals); addition reactions in which cyclic compoundsare formed; and addition reactions that proceed by chain mechanisms.
What is the addition of one molecule to another to give a single new molecule?
The addition of one molecule to another to give a single new molecule constitutes an important class of reactions. Illustrative is the addition of chlorine to ethylene to give the dichloroethane used for the industrial production of vinyl chloride. Alcohols are commonly made….
What is the reaction of propene?
The hydrochlorination of propene or, in general, the addition to alkenes is said to be initiated by electron-seeking (electrophilic) reagents, while the additions to alkynes, aldehydes, and ketones are said to be initiated by electron-rich (nucleophilic) reagents. Other forms of addition reactions include: catalyzed addition reactions, such as the self-addition of alkenes (catalyzed by acids) or the hydrogenationof alkenes, aldehydes, and ketones (catalyzed by metals); addition reactions in which cyclic compoundsare formed; and addition reactions that proceed by chain mechanisms.
Why is the addition reaction called saturation?
Addition reactions to alkenes and alkynes are sometimes called saturation reactions because the reaction causes the carbon atoms to become saturated ...
What is a reaction in which a bond between two atoms becomes partly or fully saturated by covalent attachment?
Reactions in which a multiple bond between two atoms becomes partly or fully saturated by covalent attachments at both centres are called addition reactions. Many mechanisms are known for such reactions; most of them are variants of four basic mechanisms, which differ chiefly…. chemical compound: Addition reactions.
What is the first step in the hydrogen ion reaction?
The reaction proceeds in two stages: first, the hydrogen ion, H+, of hydrogen chloride(the positively charged component) adds to one of the pair of carbon atoms joined by double bonds—in this case, the less alkylated carbon atom—followed by addition of the chloride ion, Cl−(the negatively charged component), to the other carbon atom.
When a hydrogen halide adds to the carbon-carbon triple bond of an alkyne, the?
When a hydrogen halide adds to the carbon-carbon triple bond of an alkyne, addition of the first molecule is faster than the second, and a vinylic halide can be isolated. …
What is the reaction of addition?
The addition reaction is the inverse of the elimination reaction.
What is the main phenomenon that causes the addition reaction?
The main phenomenon that causes the addition reaction is called the Electromeric effect. No byproducts are formed in addition reaction.
Why is the positive charge on carbonyl carbon more in aldehydes than in ketones?
Due to the smaller +1 effect of one alkyl group in aldehydes, as compared to the larger +1 effect of two alkyl groups , the magnitude of positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is more in aldehydes than in ketones. As a result, nucleophilic addition reactions occur more readily in aldehydes than in ketones.
Which step of carbocation undergoes nucleophilic addition?
In the second step, the most stable carbocation undergoes nucleophilic addition by the bromide ion.
Which species undergo electrophilic addition reactions?
Alkenes and Alkynes are the main species that undergo electrophilic addition reactions.
Where are nucleophilic addition reactions found?
Nucleophilic addition reactions are generally found in Aldehydes and Ketones. The Presence of an electrophilic centre triggers the nucleophilic addition reaction.
What happens to the carbon atom in a nucleophile?
In the presence of a nucleophile, the pi bond is shifted towards the Oxygen atom and the carbon atom becomes the electrophilic centre. As a result of nucleophilic addition, an intermediate tetrahedral product is formed which on hydrogenation gives the end product.
What is the major product of a reaction?
The major product of a reaction is the product that is most likely to form. Minor products are those that are less likely to form. The hydrohalogenation of 2-methylpropene to form 2-fluoro-2-methylpropane (major product) and 1-fluoro-2-methylpropane (minor product). Reaction conditions:
What is the process of adding hydrogen to an alkene?
Hydrogenation. Hydrogenation involves adding hydrogen (H2) ( H 2) to an alkene. During hydrogenation the double bond is broken (as with hydrohalogenation and halogenation) and more hydrogen atoms are added to the molecule. A specific example is shown in the figure below. The hydrogenation of ethene to ethane.
What is the name of the compound that is added to an unsaturated compound?
Hydrohalogenation involves the addition of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom to an unsaturated compound (containing a carbon-carbon double bond). An example is given in the figure below. X can be fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br) or iodine (I).
How to tell if a compound is saturated or unsaturated?
If bromine water or potassium permanganate are decolourised by a compound the compound is unsaturated, if they are not decolourised the compound is saturated.
What is the reaction of H2O and H2O?
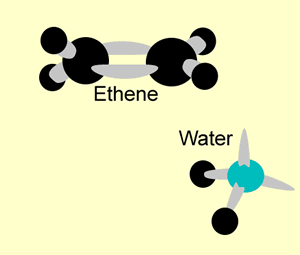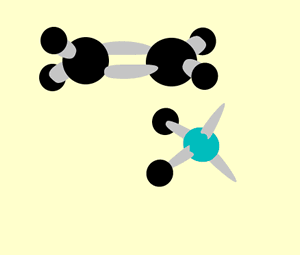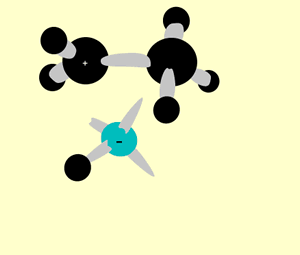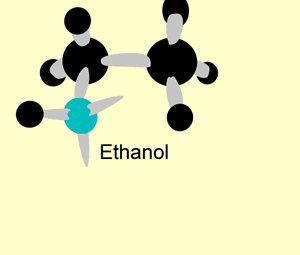
A hydration reaction involves the addition of water ( H2O H 2 O) to an unsaturated compound. This is one way of preparing an alcohol from the corresponding alkene (see figure below).
How does polymerization occur?
When these monomers are added together, they form a polymer. One way for polymerisation to occur is through an addition reaction. More details are given later on. The polymerisation of vinyl chloride monomers to form a polyvinyl chloride polymer.
Which atom is added to the least substituted carbon atom?
the hydrogen atom hydrogen atom is added to least substituted carbon atom least substituted carbon atom. i.e. the carbon atom with the least number of carbon atoms bonded to it. the halogen atom halogen atom is added to the more substituted carbon atom more substituted carbon atom. i.e. the carbon atom with the most number ...
