What is a chronic apophyseal injury?
Chronic apophyseal injuries can occur in patients undergoing long programmes of intensive sport training. These injuries occur along a spectrum from apophysitis to avulsion fracture with significant displacement therefore, they can be very severe, resulting in growth disturbance.
What is the prevalence of apophyseal injuries during sport?
Apophyseal injuries occurring during sport are less common than overall rate of injuries affecting the adolescent population. Growth disturbance occurs only rarely after an apophyseal injury.
What is the relationship between apophyseal injury and growth deficit?
Growth deficit may occur in young athletes involved in intensive practice of sport following apophysitis. Apophyseal injuries occurring during sport are less common than overall rate of injuries affecting the adolescent population. Growth disturbance occurs only rarely after an apophyseal injury.
What causes apophyseal avulsion injuries?
Young athletes are at risk of apophyseal avulsion injuries, in particular during forceful and violent eccentric contractions, due to the inherent weakness across the unfused apophyseal growth plate. The cartilaginous growth plate is the most common structure involved in the injury mechanism.
What is a common Apophyseal injury?
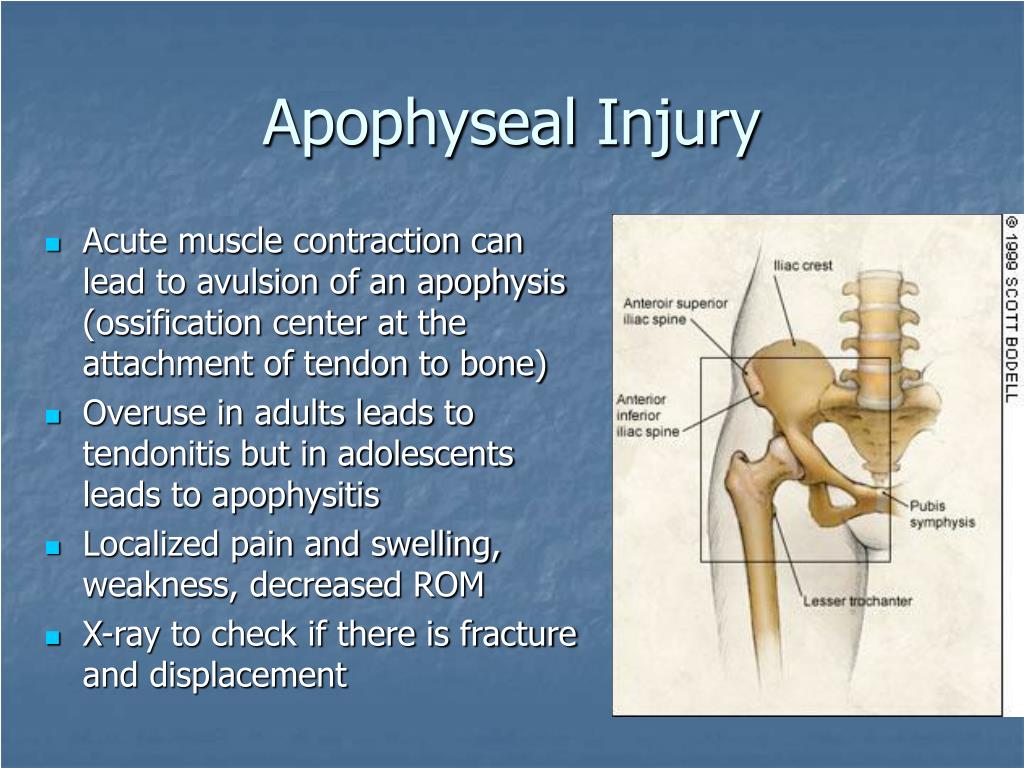
Common apophyseal injuries, and their sites, include Sever's disease (posterior calcaneus), Osgood-Schlatter disease (tibial tuberosity), Sindig-Larsen-Johansson syndrome (inferior patella), medial epicondylitis (humeral medial epicondyle) and apophysitis of the hip (iliac crest, ischial tuberosity).
What is Apophyseal?
An apophyseal joint is a point where two or more bones join in the spine. The spinal joint is encapsulated by connective tissues, coated with cartilage and lubricated with synovial fluid to enable smooth joint articulation. Each vertebra has a pair of apophyseal joints- one on the left and one on the right.
Where do Apophyseal injuries occur?
The apophysis is the location of a growth plate with a muscle attachment - there are several in the pelvis where the various thigh muscles attach. Apophysitis involves inflammation of one of these with associated dull pain, and is typically associated with muscle overuse.
How long does it take to recover from apophysitis?
How is apophysitis treated? Rest and physical therapy are required to completely heal an inflamed apophysis and return back to sport successfully. Usually this process takes anywhere from 4-8 weeks depending on the stage of injury, but every athlete is different.
Does facet joint pain go away?
While facet joint arthritis can't be reversed, there is evidence that exercise, lifestyle changes and careful management of your back pain can contribute to better quality of life. If conservative therapies fail to help you manage and control the pain, your doctor may recommend injections, ablations or surgery.
What aggravates facet joint pain?
Things like aging (wear and tear), obesity (extra weight creates a greater burden), a previous injury or trauma to the spine, and weight-bearing jobs are risk factors for facet joint damage.
How do you recover from apophysitis?
Ice should be applied to the painful area for 15-20 minutes as often as every 2-3 hours until the pain goes away. Once you can tolerate daily activities without pain, you can start gently stretching and strengthening the muscles that attach to the affected apophysis (the hip flexors and abdominal muscles).
What are the symptoms of apophysitis?
Symptoms of apophysitis can vary but there are a few key things to watch for: Pain that worsens during or after repetitive sports activities such as running, jumping, and throwing. Pain, swelling, and/or tenderness to the touch over growth plate areas at the heel, knee, elbow, shoulder, hip, or foot.
What is the difference between epiphysis and apophysis?
An apophysis is a growing center which, as its name indicates, grows (physis) upon (apo) the mother bone. It differs from the epiphysis in that with the development of the ossification center all growth is completed.
How do you say apophysitis?
0:051:01How To Say Apophysitis - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipA veces a veces apophis antes apophis antes apophis antes a veces.MoreA veces a veces apophis antes apophis antes apophis antes a veces.
What is apophysitis knee?
Apophysitis relates to inflammation of an apophysis usually secondary to bony trauma. It is most commonly found in the immature skeleton where contraction force at the point of tendon insertion causes detachment of the ossification center from the parent bone as seen with Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease.
What is a traction apophysitis?
A Traction Apophysitis is an injury to the cartilage and bony attachment of tendons in children and adolescents. Commonly, this is an overuse injury associated with inflexible muscles and muscular tendon junction (Achar & Yamanaka, 2019).
What is the difference between epiphysis and apophysis?
An apophysis is a growing center which, as its name indicates, grows (physis) upon (apo) the mother bone. It differs from the epiphysis in that with the development of the ossification center all growth is completed.
What is the Apophyseal ring?
The ring apophysis is a secondary ossification center of the vertebral endplate connected to the intervertebral disc. It is firmly attached to disc fibrous annulus through Sharpey fibers and its ossification occurs at 4-6 years old.
How do you say Apophyseal?
0:051:01How To Say Apophyseal - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipA profesión a profesión aprecio a profesión aprecio a profesión.MoreA profesión a profesión aprecio a profesión aprecio a profesión.
What is Apophyseal avulsion?
Iliac crest apophyseal avulsion injury is relatively rare and occurs with pulling of one or more of the muscles that have their attachment to the iliac crest (the external and internal abdominal oblique muscles, transverse abdominis muscle, gluteus medius muscle, and tensor fascia latae).
Who is the doctor who treats apophyseal injuries?from muirortho.com
Dr. George Tischenko of Muir Or thopaedic Specialists describes an apophyseal injury and explains the time it takes to heal.
How long does it take for an apophyseal fracture to heal?from muirortho.com
But an apophyseal fracture can take 6-8 weeks to heal properly and it is important to monitor the progression of the healing so the athlete can return at an appropriate time without reaggravating the injury. L earn More. Categories. General.
When does apophyseal stress occur?
Apophyseal stress injuries occur in skeletally immature patients, usually in the 2 nd decade of life , but they may affect younger children as well. It is postulated that the physeal closure may be delayed in the female athletes due to low estrogen levels - in such a case apophyseal injury may occur in a slightly older age group.
How to treat apophyseal stress?
Apophyseal stress injuries are treated conservatively with NSAIDs, activity modification and physiotherapy. The outcome is generally favorable. If not diagnosed and treated early, the injury may progress to apophyseal fragmentation or result in deformities.
Which modality is most sensitive for detecting apophyseal stress injuries?
MRI is the most sensitive modality for detecting apophyseal stress injuries, showing: physeal widening without displacement. increased signal of the physis on fluid-sensitive sequences. bone marrow edema of the apophysis. soft-tissue edema.
Which vertebrae have apophyseal joints?
Each vertebra has a pair of apophyseal joints- one on the left and one on the right. Each joint is composed of a superior articular facet joint that faces up and an inferior articular facet that faces down.
What is the point where two or more bones join in the spine?
An apophyseal joint is a point where two or more bones join in the spine.
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Syndrome
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome is an apophyseal injury to the inferior pole of the patella. The condition is thought to result from multiple episodes of traction-induced microtrauma at an immature, inferior patellar pole, with resultant calcification and ossification at this junction.
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease, the most common apophyseal disorder, was independently described in 1903.38 The condition is found most commonly in boys age 10 to 15 years and in girls 2 years earlier; it is often bilateral (20-30% of cases).
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is characterized by separation of a fragment of bone with overlying articular cartilage from the sur rounding normal bone. OCD most commonly affects the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle, but is also seen in the talar dome and humeral capitellum (Fig 7.9). OCD can occur in all large joints.
What is the iliac crest apophyseal avulsion injury?
Iliac crest apophyseal avulsion injury is relatively rare and occurs with pulling of one or more of the muscles that have their attachment to the iliac crest ( the external and internal abdominal oblique muscles, transverse abdominis muscle, gluteus medius muscle, and tensor fascia latae). Ossification of the iliac crest apophysis starts along the anterolateral aspect of the iliac crest between the ages of 13-15 years, and continues posteromedially. The fusion of the ossified apophysis usually starts at the age of 15 years and continues to the age of 25 years.
What is avulsed apophysis?
The most commonly avulsed apophysis is the ischial tuberosity, followed by the AIIS and the ASIS. Radiographs may be interpreted as negative when an apophyseal avulsion is nondisplaced or when the apophysis is unossified. Alternatively, exuberant callus formation may mimic neoplasm or osteomyelitis, confusing the clinical picture. Knowledge of anatomy allows the experienced interpreter of MRI to correctly identify the characteristic appearance and location of apophyseal avulsion injuries. MRI allows evaluation of the extent of injury and osseous displacement, both of which are important factors in treatment decisions. Associated muscle and tendon strain injuries are also well demonstrated.
What is the name of the fracture that occurs when the hip is hyperextended and the knee is in flexion?
AIIS avulsion , also known as sprinter’s fracture, occurs from overpull of the straight head of the rectus femoris when the hip is hyperextended and the knee is in flexion. The AIIS apophysis starts to ossify between the ages of 13 to 14 years and fuses with the ilium between the ages of 16 and 18 years.
What is the most common avulsion injury in adolescent athletes?
In the adolescent competitive athlete the pelvis is a common location of apophyseal avulsion injury. In a study of 203 avulsion fractures seen on radiographs, 3 the most commonly affected apophyses were: (1) the ischial tuberosity (the origin of the hamstrings); (2) the anterior inferior iliac spine, AIIS (the origin of the straight head of the rectus femoris); (3) the anterior superior iliac spine, ASIS (the origin of the sartorius and some fibers of the tensor fascia lata); and (4) a portion of the pubic symphysis (the origin of the adductor brevis and longus as well as the gracilis) (4a).
What are the most common injuries to the hip and pelvis?
Apophyseal avulsion injuries to the hip and pelvis account for 10 to 24 % of athletic injuries in children.1 The most commonly implicated sports and physical activities are soccer, running and ballet dancing. 1 Similar injuries also occur in football, baseball and track. 2 In skeletally immature individuals, injuries caused by excessive tensile force on the muscle-tendon-bone unit tend to result in apophyseal avulsion fractures, because the weakest biomechanical point is the growth plate. When an apophyseal avulsion is nondisplaced or when the apophysis is not yet ossified, radiographs may be interpreted as negative. MRI may be extremely helpful for diagnosis and clinical management in such cases.
How long does it take for a nondisplaced avulsion to heal?
6 After resolution of clinical symptoms, which usually takes 4-6 weeks, the patient can gradually return to athletic activity. Surgery is considered for recent apophyseal avulsion fractures displaced more than 2 cm. In cases of malunited or hypertrophied fragments, surgery may also be beneficial. 7 Permanent disability and limitation of sporting activity have been reported. 8
What causes avulsions in the apophysis?
The mechanism of injury in apophyseal avulsions is sudden forceful concentric or eccentric muscle contraction during running, jumping or kicking a ball, which results in traction on the unfused apophysis. Extreme passive stretching and chronic repetitive microtrauma have also been implicated in the development of apophyseal avulsion. When a strain-type injury occurs it is the patient’s age that tends to determine where the disruption occurs in the chain of bone, tendon and muscle. In a young adult, the failure usually involves the myotendinous junction. In an older adult, the failure tends to target the tendon, which is often weakened by tendinosis. The weak link in the muscle-tendon-bone chain in children and adolescents is the physis (growth plate), especially at times of growth acceleration. 4,5
What are the most common apophyseal injuries?
Apophyseal injuries occur most commonly during sport activities. 17, 22 Acute apophyseal injuries lack of a systematic classification in literature. The severity of injury can be very different, ranging from pain (apophysistis) to avulsion of the secondary growth centre. Young athletes are at risk of apophyseal avulsion injuries, in particular during forceful and violent eccentric contractions, due to the inherent weakness across the unfused apophyseal growth plate. The cartilaginous growth plate is the most common structure involved in the injury mechanism. Separation and retraction of the partially ossified apophysis occurs. Chronic repetitive stress is a risk factor for acute and traction injuries. Pain and swelling of the involved area are usually observed after injury. Discomfort often worsen with passive stretching and activity, and is relieved when the patients rest. 28 Short periods of rest and exercise programmes of muscle conditioning, are usually sufficient to return to sport. 26
Why should apophyseal injuries be considered analytical?
Further studies should consider analytical as well as descriptive components of apophyseal injuries, to allow the identification of new possible risk factors and preventive measures and to help early detection and proper treatment as well.
What is the purpose of the apophyseal injury review?
The authors reviewed the current English literature regarding apophyseal injuries affecting young athletes, to highlight the frequency and characteristics of these injuries, to clarify risk factors and specific prevention measures, and to identify future research objectives.
Is the apophysis susceptible to repetitive physical loading?
Concerns have been raised for the tolerance limits of the apophysis. The apophysis is particularly susceptible to repetitive physical loading, as may be seen in different sports (e.g. distance running, baseball, gymnastics, etc.), and to mechanical stresses of high demand sports (e.g. football, hockey, etc.). 14 – 16 Nevertheless, length discrepancy, angular deformity, or altered joint mechanics are uncommon after apophyseal injuries, but long-term disability may persist, especially if the injury goes unrecognized. 4