Definition : An artifact is a structure or an appearance that is not normally present on the radiograph and is produced by artificial means. Radiographic errors may be due to technical errors [ errors related to the technique of taking the radiograph] or processing errors [related to all aspects of processing]
What is an X-ray artifact?
X-ray artifacts | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org X-ray artifacts can present in a variety of ways including abnormal shadows noted on a radiograph or degraded image quality, and have been produced by artificial means from hardware failure, operator error and software (post-processing) artifacts...
What are common imaging artifacts in radiology?
Common artifacts (film and computed/digital radiography) motion artifact due to patient movement resulting in a distorted image. image compositing (or twin/double exposure) superimposition of two structures from different locations due to double exposure of same film/plate.
What is a stitching artifact in radiography?
stitching artifacts occur when two separate DR or CR (computed radiography) images are merged into a single image (see case 3)
What is an artifact in the background of an image?
faint radiopaque striping (often vertical) in the background of an image, yet not evident on the anatomy this artifact should be carefully examined, if it does not interfere with the anatomy, it is not a detector failure/grid cut off, rather a limitation of the detector calibration
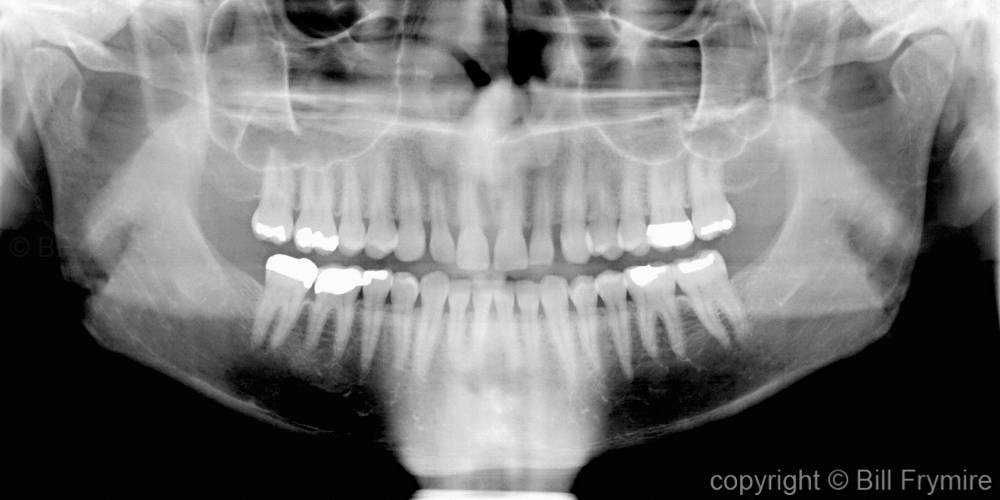
What does artifact mean in dentistry?
Artifacts are undesired alterations in data introduced by improper technique, a technological glitch or a combination of the two. The issue can become critical to a patient's health, and in veterinary dentistry it frequently means the difference between tooth extraction or no treatment.
What do you mean by artifact in radiology?
In radiologic imaging, the term artifact is used to describe any part of an image that does not accurately represent the anatomic structures present within the subject being evaluated.
What causes artifacts in radiography?
Artifacts in this image are caused by filters in the collimator assembly of the x-ray tube becoming loose and mispositioned in the x-ray beam, attenuating the x-ray beam non-uniformly and resulting in the attenuation pattern shown in the image.
What causes film artifacts?
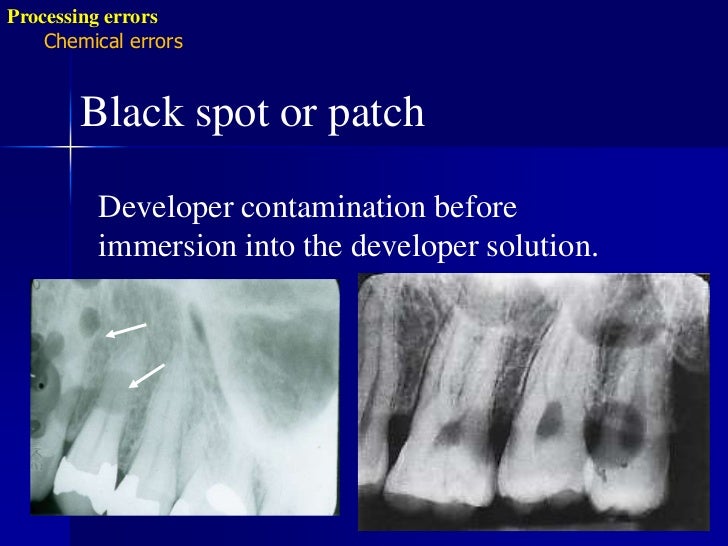
A number of artifacts may occur in the darkroom during handling, developing, fixing and drying of the film. White to shiny artifacts are caused by the contamination of films with fixer, inability of developer to reach parts of the film or loss of emulsion from the developed film.
What does artifact mean in medical terms?
In medical imaging, artifacts are misrepresentations of tissue structures produced by imaging techniques such as ultrasound, X-ray, CT scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What causes artefacts in images?
A compression artifact (or artefact) is a noticeable distortion of media (including images, audio, and video) caused by the application of lossy compression.
What are the most common radiographic artifacts?
Common artifacts (all forms of radiography)motion artifact. ... image compositing (or twin/double exposure) ... grid cut-off.radiopaque objects on/external to the patient (e.g. jewelry (e.g. necklaces, piercings), clothing (e.g. buttons), hair (e.g. ponytail, hair braids etc.)debris in the housing.
What are the different types of artifacts?
Examples include stone tools, pottery vessels, metal objects such as weapons and items of personal adornment such as buttons, jewelry and clothing. Bones that show signs of human modification are also examples.
What are artifacts?
An artifact is an object made by a human being. Artifacts include art, tools, and clothing made by people of any time and place. The term can also be used to refer to the remains of an object, such as a shard of broken pottery or glassware. Artifacts are immensely useful to scholars who want to learn about a culture.
How can we reduce artifacts in radiology?
It is known that metal artifacts can be reduced by modifying standard acquisition and reconstruction, by modifying projection data and/or image data and by using virtual monochromatic imaging extracted from dual-energy CT.
How can Radiology prevent artifacts?
Adherence to detail, especially in patient preparation, factor selection, positioning, and darkroom technique, using state-of-the-art equipment, will reduce the chances for producing artifacts.
How do glasses affect dental images?
With respect to whether or not the presence of the eyeglasses would have caused any unwanted radiation results (presumably meaning higher radiation exposure to the patient), while there might be some small amount of scattering of the x rays from the eyeglasses, it would be very low and not considered significant.
What are X-ray artifacts?
X-ray artifacts can present in a variety of ways including abnormal shadows noted on a radiograph or degraded image quality, and have been produced by artificial means from hardware failure, operator error and software (post-processing) artifacts.
What causes trapezoidal areas in a collimator?
debris in the housing caused by the colli mator tube can cause small trapezoidal regions, indicative of lead shavings
What is an artifact in X-rays?
An artifact is a false image or part of an image on an X-ray.
What are X-ray artifacts?
X-ray artifacts can present in a variety of ways including abnormal shadows noted on a radiograph or degraded image quality, and have been produced by artificial means from hardware failure, operator error and software (post-processing) artifacts.
What is radiographic artifact?
Radiographic artifact is spurious or unclear appearance of an anatomical structure due to radiographic technique. Other radiographic artifact includes clothing or jewelry not removed.
What is an artifact on a radiograph?
An artifact on a radiograph is nothing more than a negligible finding. Pressure marks from a fingernail are examples of a radiographic artifact. Any artifact *may* hide or distort information useful to the radiologist or attending physician BUT the artifact itself means nothing.
What are the three main types of artifacts?
The three main types of artifact are radiographic, patient, or medical/surgical.
What is an artifact in medical imaging?
In medical imaging, artifacts are misrepresentations of tissue structures produced by imaging techniques such as ultrasound, X-ray, CT scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Physicians typically learn to recognize some of these artifacts to avoid mistaking them for actual pathology.
What does it mean when an image is an artifact?
Artifact pretty much means something showing in the image where it shouldn’t. It can be caused by the equipment (if a digital detector is damaged it creates an artifact like a white line through the image, or maybe “dead pixels” which are little blank spots on the picture. It can also be something like clothing, hair or piercings showing. Sometimes an artifact doesn’t reduce the diagnostic quality of the image - especially if it doesn’t overlap any anatomy, but if it does overlap anatomy results can be affected - it may be hard to rule pathology in or out if artifact obscures or mimics the app
Why do teeth elongate on xrays?
Cause of Elongation of few teeth: Due to excessive bending of the film while placing the x-ray in the patient mouth. The region in which the x-ray is where the teeth or supporting structures are elongated. To prevent this from happening the film should not bent excessively only a gentle bend must be given to the film just for confirming to the anatomical contour of the intraoral structures such as the palate and the floor of the mouth. There is also a chance for bending of the film when canine -premolar areas are radiographed due to the contour of the palate.
What is the name of the phalanx on a radiograph?
Phalangioma. The term phalangioma was used by Dr. David F Mitchell. It refers to the image of phalanx or fingers (plural -phalanges) appearing in the film. Cause: Phalangioma occurs when the patient holds the film in the mouth in an incorrect way which results in exposing the image of fingers on the radiograph.
Why does my xray tube elongate?
Cause of Elongation: Due to decreased vertical angulation of the x-ray tube while capturing the x-ray. As seen in Foreshortening it will be leading to difficulty in getting the correct working length during Endodontic Treatment and other diagnostic procedures.
Why is a good radiograph important?
A good radiograph is an essential part of any Dental Diagnosis involving the hard tissue (Tooth or Bone) and getting an ideal radiograph is important to get a proper diagnosis. For an ideal Radiograph the following things should be satisfied – Good Density, Good Sharpness, Accurate positioning and Good Contrast, when all the above criteria are not fulfilled it results in a faulty radiograph which deters the diagnosis of the condition and can in turn result in the inability to decide on a proper treatment plan.
What is the density of a radiograph?
Density: This is the darkness or the black areas seen on the radiograph, the soft tissue or the lack of hard tissue can be identified by Black regions on the radiograph. The changes in kV alters the density of the radiograph – decrease in kV decreases the density making the radiograph lighter, while increase in kV increases the density making the radiograph darker.
What does "foreshortening" mean in x-rays?
Foreshortening as the name suggests refers to images of teeth and other structures in the x-ray appear too short.
What is cone cut on dental radiograph?
Cone cut appearance refers to a clear, unexposed area in a dental radiograph. The other region of the X-ray is clear with the structures seen clearly.
What are radiographic artifacts?
Radiographic artifacts. Radiographic artifacts commonly occur, particularly with hand processing. The artifacts may originate between the X-ray tube and the cassette as extraneous material on the patient or contamination of positioning aids, or result from debris within the cassette, or damage to, or staining of the screen ….
Why are there black marks on film?
Black artifacts result from improper handling or storage of films, resulting in exposure to light, or from pressure marks or static electricity discharges. Dropped levels of hand-processing chemicals may result in a variety of tide-marks on films.
What is the artifact on a radiograph?
Lateral Lumbar. The artifact on the radiograph represents an area where two radiographs became attached to each other in the manual developing process ( arrows ). This has been called a kissing defect. (Courtesy of Felix G. Bauer, DC, DACBR (Hon), Sydney, Australia.)
Why is the gray area on the lower portion of this oblique radiograph not developed?
The gray area on the lower portion of this oblique radiograph was not developed because of the low level of developer solutions in the manual developing tank.
What causes dark spots on a lumbar radiograph?
Figure 16-9 DEVELOPMENT PROBLEMS. Oblique Lumbar. The darkened area over this oblique lumbar radiograph is caused by two films overlapping in the development procedure. COMMENT: This may occur if insufficient time is allowed between feeding film through the automatic processor.
What causes the washed out image in Figure 16-13?
Figure 16-13 DEVELOPMENT PROBLEMS. AP Thoracic. The washed-out image was caused by exhausted developer solution. COMMENT: This occurs when the developer oxidizes or has been replenished with water rather than with fresh chemicals. (Courtesy of Felix G. Bauer, DC, DACBR (Hon), Sydney, Australia.)
What is the black area on a lumbar radiograph?
Figure 16-7 DEVELOPMENT PROBLEMS. Oblique Lumbar. The black area represents light exposure on the radiograph, which occurred sometime during the development process.
What does the lightning-like black densities represent?
Figure 16-5 STATIC ELECTRICITY. Lateral Cervical Skull. The lightning-like black densities represent static electric ity. COMMENT: This might make quite an advertisement for headaches. The metallic devices are earrings, which should always be removed when doing an x-ray examination of the skull or cervical spine.
Why do radiographs repeat?
Artifacts are a common cause of repeat radiographs; they often occur in unexpected places, with many peculiar internal objects being detected. Without a complete history, many unusual artifactual shadows cannot be adequately identified.
Common Causes
Common Artifacts
- motion artifact
- image compositing (or twin/double exposure)
- grid cut-off
- radiopaque objects on/external to the patient (e.g. jewelry (e.g. necklaces, piercings), clothing (e.g. buttons), hair(e.g. ponytail, hair braids etc.)
Film Radiography Artifacts
- finger marks
- clear film
- static electricity
- crescent-shaped black lines
Computed/Digital Radiography Artifacts
- detector image lag or ghosting
- incorrect detector orientation i.e. upside-down cassette
- backscatter
- stitching artifacts