Full Answer
How accurate is approximating the Earth as a sphere?
The assumption that the earth is a sphere is possible for small-scale maps (smaller than 1:5,000,000). At this scale, the difference between a sphere and a spheroid is not detectable on a map. However, to maintain accuracy for larger-scale maps (scales of 1:1,000,000 or larger), a spheroid is necessary to represent the shape of the earth.
What are celestial spheres?
What is the Celestial Sphere? In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with Earth. All objects in the observer’s sky can be thought of as projected upon the inside surface of the celestial sphere, as if it were the underside of a dome.
What are astronomical phenomena?
It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation.
Is the Earth an exact sphere?
earth, in geology and astronomy, 3rd planet of the solar system and the 5th largest, the only planet definitely known to support life. Gravitational forces have molded the earth, like all celestial bodies, into a spherical shape. However, the earth is not an exact sphere, being slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator.

How do you use an astronomical sphere?
1:1310:28How to Use an Armillary Sphere - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd it represents the midpoint of the sky if you're standing the northern hemisphere looking southMoreAnd it represents the midpoint of the sky if you're standing the northern hemisphere looking south or in the southern hemisphere looking due north. You're rotating inside of the meridian.
What is the astronomy sphere?
The sphere is a skeleton celestial globe, with circles divided into degrees for angular measurement.
What are the 4 celestial sphere?
The rising and setting points of celestial bodies (sun, moon, stars, and planets) are determined by their positions on the celestial sphere.
What is a celestial sphere why it is significant in astronomy?
celestial sphere, the apparent surface of the heavens, on which the stars seem to be fixed. For the purpose of establishing coordinate systems to mark the positions of heavenly bodies, it can be considered a real sphere at an infinite distance from the Earth.
How many celestial spheres are there?
The planetary spheres were arranged outwards from the spherical, stationary Earth at the centre of the universe in this order: the spheres of the Moon, Mercury, Venus, Sun, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. In more detailed models the seven planetary spheres contained other secondary spheres within them.
Is the celestial sphere another name for our universe?
In the celestial sphere model, Earth is placed at the center of the celestial sphere. a. The celestial sphere is just another name for our universe. Altair has a RA of 19.8 hours and a Dec of +9 degrees.
Is the moon in the celestial sphere?
The celestial sphere is an imaginary projection of the Sun, Moon, planets, stars, and all astronomical bodies upon an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth.
Does the celestial sphere rotate?
The celestial sphere is fixed. However, the Earth rotates inside the sphere, and so, from our point of view, the celestial sphere appears to rotate. The Earth rotates towards the east (counter-clockwise from a perspective looking down onto the north pole).
Why does the celestial sphere turns once around each day?
Because the Earth is tilted on an axis. Every celestial object appears to go around the Earth once a day. In addition to this motion, which celestial object has the fastest apparent motion in the sky? The Moon.
Which description best describes the celestial sphere?
The celestial sphere is a representation of how the entire sky looks as seen from Earth. Note that the celestial sphere is not meant to represent physical reality but rather the appearance of the sky from our planet.
What are the main features of the celestial sphere?
The celestial sphere has a north and south celestial pole as well as a celestial equator which are projected reference points to the same positions on the Earth surface. Right Ascension and Declination serve as an absolute coordinate system fixed on the sky, rather than a relative system like the zenith/horizon system.
Where is the celestial sphere?
the Earth's centerThe celestial sphere can be considered to be centered at the Earth's center, the Sun's center, or any other convenient location, and offsets from positions referred to these centers can be calculated.
What is the celestial sphere simple definition?
Definition of celestial sphere : an imaginary sphere of infinite radius against which the celestial bodies appear to be projected and of which the apparent dome of the visible sky forms half.
Where is the celestial sphere?
The celestial sphere can be considered to be centered at the Earth's center, the Sun's center, or any other convenient location, and offsets from positions referred to these centers can be calculated.
What are the main features of the celestial sphere?
The celestial sphere has a north and south celestial pole as well as a celestial equator which are projected reference points to the same positions on the Earth surface. Right Ascension and Declination serve as an absolute coordinate system fixed on the sky, rather than a relative system like the zenith/horizon system.
Where is the north celestial pole?
The north celestial pole is an imaginary projection of the Earth's axis into space. It is located directly above the Earth's North Pole. While it i...
What is the celestial sphere concept?
The celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere on which are projected objects in space. It is used to locate the positions of real and imaginary celes...
What is the celestial sphere used for?
The celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere encircling the Earth. It is used for pinpointing celestial objects, real and imaginary. Like a globe, t...
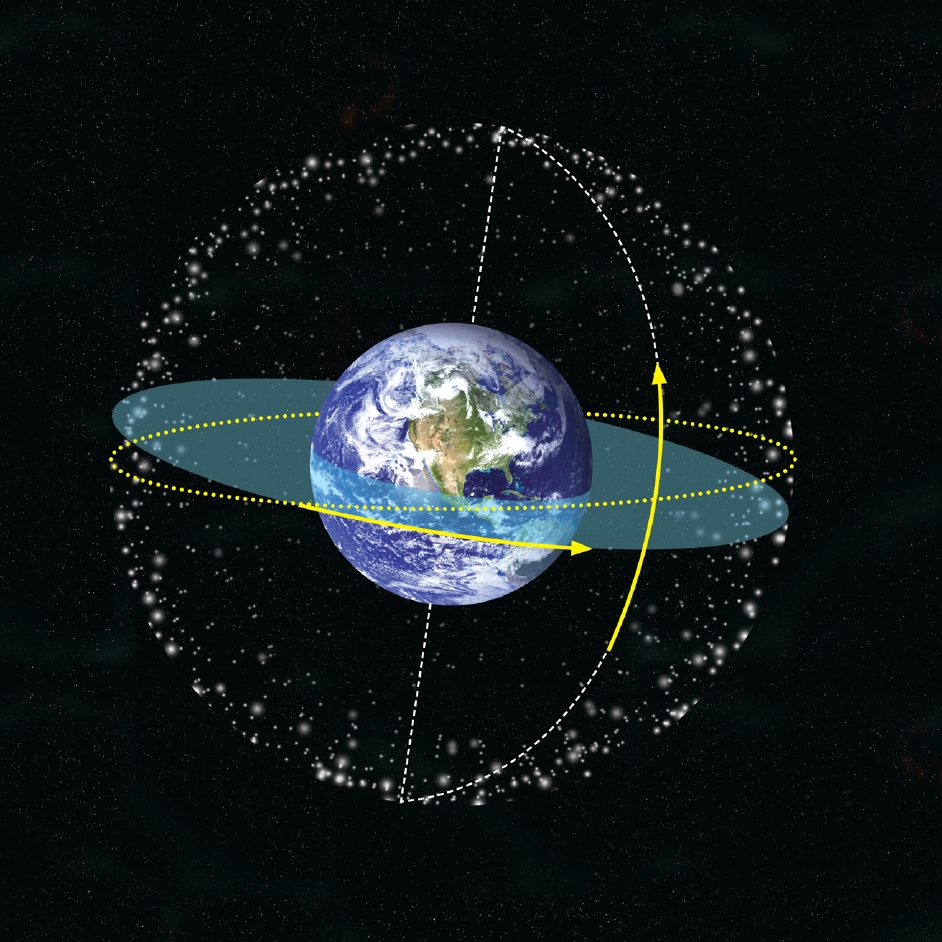
What is the celestial sphere?
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with Earth. All objects in the observer’s sky can be thought of as projected upon the inside surface of the celestial sphere, as if it were the underside of a dome. The celestial sphere is a practical tool for spherical astronomy, ...
Where is the celestial sphere located?
The celestial sphere can be considered to be centered at the Earth’s center, The Sun’s center, or any other convenient location , and offsets from positions referred to these centers can be calculated.
How to measure right ascension?
Right ascension (symbol α, abbreviated RA) measures the angular distance of an object eastward along the celestial equator from the vernal equinox to the hour circle passing through the object. The vernal equinox point is one of the two where the ecliptic intersects the celestial equator. Analogous to terrestrial longitude, right ascension is usually measured in sidereal hours, minutes and seconds instead of degrees, a result of the method of measuring right ascensions by timing the passage of objects across the meridian as the Earth rotates. There are (360° / 24h) = 15° in one hour of right ascension, 24h of right ascension around the entire celestial equator.
How do stars coordinate?
A star’s spherical coordinates are often expressed as a pair, right ascension and declination, without a distance coordinate. Because of the great distances to most celestial objects, astronomers often have little or no information on their exact distances, and hence use only the direction. The direction of sufficiently distant objects is the same for all observers, and it is convenient to specify this direction with the same coordinates for all. In contrast, in the horizontal coordinate system, a star’s position differs from observer to observer based on their positions on the Earth’s surface, and is continuously changing with the Earth’s rotation. Telescopes equipped with equatorial mounts and setting circles employ the equatorial coordinate system to find objects. Setting circles in conjunction with a star chart or ephemeris allow the telescope to be easily pointed at known objects on the celestial sphere.
Why does the sky seem to be standing still?
Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on the actual distances. All objects seem equally far away, as if fixed to the inside of a sphere of large but unknown radius, which rotates from east to west overhead while underfoot, the Earth seems to stand still. For purposes of spherical astronomy, which is concerned only with the directions to objects, it makes no difference whether this is actually the case, or if it is the Earth which rotates while the celestial sphere stands still.
What color is the right ascension?
Right ascension (blue) and declination (green) as seen from outside the celestial sphere. (Image Courtesy of Wikipedia)
Is the celestial sphere infinite in radius?
For purposes of spherical astronomy, which is concerned only with the directions to objects, it makes no difference whether this is actually the case, or if it is the Earth which rotates while the celestial sphere stands still. The celestial sphere can be considered to be infinite in radius. This means any point within it, including ...
What is the Celestial Sphere?
The celestial sphere definition in astronomy is an imaginary sphere surrounding the Earth. Another way of imagining the celestial sphere is to picture the Earth inside a transparent, celestial dome on which the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars are fixed. In this conception of the celestial sphere, the Earth is at the center of the universe.
North Celestial Pole
Several important points, also imaginary, are associated with the celestial sphere. One of them is the north celestial pole, an imaginary extension of the Earth's North Pole into space. It is a point on the celestial sphere directly above the Earth's North Pole. At night, the stars seem to turn around the north celestial pole.
South Celestial Pole
The other significant point on the celestial sphere is the south celestial pole. Like its counterpart in the north, the south celestial pole is the point on the celestial sphere directly above Earth's South Pole.
Celestial Sphere : Related Terminology
Other significant points on the celestial sphere include the celestial equator, the celestial meridian, zenith and nadir, and the celestial horizon. It is important to distinguish these points because they are terms used to describe events and objects in astronomy.
What Are Astronomical Sphere Rings?
These cool rings are popularly known as Gemma Rings as well that were created for an astronomical purpose. The history goes back to the ancient Greek astronomers that made small instruments, like these for multiple purposes. The most important factors of which are telling time or figuring out latitudes and even the season of the year.
What Purpose Do These Cool Rings Hold?
The main purpose as we mentioned previously was to check the latitudes and mainly to tell the time and season of the year. While, there were many types of astronomical sphere rings, at that time, fashion had taken a turn and converted these cool rings into fashionable rings to wear.
How many circles are there in an armillary sphere?
The earliest known complete armillary sphere with nine circles is believed to have been the meteōroskopion of the Alexandrine Greeks ( c. ad 140), but earlier and simpler types of ring instruments were also in general use. Ptolemy, in the Almagest, enumerates at least three.
What is the oldest known astronomical instrument?
The armillary sphere, the oldest known astronomical instrument, consisted essentially of a skeletal celestial globe whose rings represent the great circles of the heavens. The armillary sphere was known in ancient China; the ancient Greeks were also familiar with it and modified it to produce the…
What is the oldest instrument in the universe?
Learn More in these related Britannica articles: instrumentation. The armillary sphere, the oldest known astronomical instrument, consisted essentially of a skeletal celestial globe whose rings represent the great circles of the heavens.
What is the celestial sphere?
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer.
Where is the celestial sphere located?
The celestial sphere can be considered to be centered at the Earth's center, the Sun's center, or any other convenient location , and offsets from positions referred to these centers can be calculated.
How many spheres are there in the heavens?
Aristotle and Eudoxus claimed two different counts of spheres in the heavens. According to Eudoxus, there were only 27 spheres in the heavens while there are 55 spheres in Aristotle's model. Eudoxus attempts to mathematically construct his model from a treatise known as On the velocities (translated from Greek to English) and asserted the shape of the hippopede or lemniscate to be associated with the planetary retrogression. Aristotle emphasized the speed of the celestial orbs are unchanging like the heavens while Eudoxus emphasizes that the orbs are in a perfect geometrical shape. Eudoxus 's spheres would produce undesirable motions to the lower region of the planets while Aristotle introduced unrollers between each set of active spheres to counteract the motions of the outer set, or else the outer motions will be transferred to the outer planets. Aristotle would later observe "..the motions of the planets by using the combinations of nested spheres and circular motions in creative ways, but further observations kept undoing their work" (Olser pg. 15).
What would happen if the celestial sphere was centered on the observer?
If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a practical tool for spherical astronomy, allowing astronomers to specify the apparent positions of objects in the sky if their distances are unknown or irrelevant.
Why does Empedocles say the Earth is stationary?
Aside from Aristotle and Eudoxus, Empedocles gives an explanation that the motion of the heavens, moving about it at divine (relatively high) speed that puts Earth in a stationary position due to the circular motion preventing the downward movement from natural causes. Aristotle criticized Empedocles' case as he argued that all heavy objects go towards Earth and not the whirl itself coming to Earth. He ridiculed and claimed the Empedocles' statement to be extremely absurd. Anything that defies the motion of natural place and the unchanging heavens (including the celestial spheres would be immediately be criticized from Aristotle).
What objects change their position against the celestial sphere?
For some objects, this is over-simplified. Objects which are relatively near to the observer (for instance, the Moon) will seem to change position against the distant celestial sphere if the observer moves far enough, say, from one side of planet Earth to the other.
What is the difference between observers looking at the same point on an infinite-radius celestial sphere?
Conversely, observers looking toward the same point on an infinite-radius celestial sphere will be looking along parallel lines, and observers looking toward the same great circle, along parallel planes. On an infinite-radius celestial sphere, all observers see the same things in the same direction. For some objects, this is over-simplified.
Who was the first person to use a sphere?
The use of such a device may be traced to the astronomer Zhang Heng , who lived during the second half of the Han Dynasty, i.e. the Eastern Han Dynasty (25 AD– 220 AD). Originally, the structure of these spheres was very simple, consisting of three rings and a metal axis that was orientated towards the North and South Poles .
When was the armillary sphere discovered?
Interestingly, the armillary sphere was also being developed independently in another civilization – China (albeit possibly at a later date.) The armillary sphere is said to have appeared in China during the Han dynasty 206 BC – 220 AD.)
What was the role of armillary spheres in the 17th century?
As My Modern Met reports , “During the 16th and 17th centuries, these astronomy tools were sized down to become fashionable finger rings that moved just like regular armillary spheres .”
What are the two main categories of armillary spheres?
Armillary spheres may be divided into two main categories based on their function – demonstrational armillary spheres and observational armillary spheres . The former is used to demonstrate and explain the movement of celestial objects , whilst the latter is used to observe the celestial objects themselves. Therefore, observational armillary spheres are generally larger in size when compared to their demonstrational counterparts. The observational armillary spheres also had fewer rings, which made them more accurate and easier to use.
What instrument was invented to aid the important science of astronomy?
Therefore, various instruments were invented to aid the important science of astronomy. One of these instruments was called the armillary sphere .
Why were rings added to spheres?
However, over the centuries, more rings were added to the spheres so that different measurements could be taken. In the courtyard of the Ancient Observatory in Beijing, for example, one can see a full sized replica of an elaborate armillary sphere produced during the reign of a 15th century Ming emperor, Zhengtong.
Where did the armillary sphere originate?
The armillary sphere is believed to have originated in the ancient Greek world. The inventor of this device, however, is less than certain. Some, for instance, claim that the armillary sphere was invented sometime during the 6th century BC by the Greek philosopher Anaximander of Miletus . Others credit the 2nd century BC astronomer, Hipparchus, with the invention of this device.
History
In Greek antiquity the ideas of celestial spheres and rings first appeared in the cosmology of Anaximander in the early 6th century BC.
Literary and visual expressions
"Because the medieval universe is finite, it has a shape, the perfect spherical shape, containing within itself an ordered variety....
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Celestial spheres (cosmological model).
Who invented the astronomical ring?
Parts of the instrument go back to instruments made and used by ancient Greek astronomers. Gemma Frisius combined several of the instruments into a small, portable, astronomical-ring instrument. He first published the design in 1534, and in Petrus Apianus 's Cosmographia in 1539.
What are the rings in the sun called?
Astronomical rings ( Latin: annuli astronomici ), also known as Gemma's rings, are an early astronomical instrument. The instrument consists of three rings, representing the celestial equator, declination, and the meridian . It can be used as a sun dial to tell time, if the approximate latitude and season is known, or to tell latitude, ...
What is the inner ring on a traveller's sundial?
Often equipped with a graduated scale, it can be used to measure right ascension. On the traveller's sundial shown above, it is the inner ring. This ring is sometimes engraved with the months on one side and corresponding zodiac signs on the outside; very similar to an astrolabe.
What is the outermost ring of an instrument?
Because the instrument is often supported by the meridional ring , it is often the outermost ring, as it is in the traveller's rings illustrated above. There, a sliding suspension shackle is attached to the top of the meridional ring, from which the whole device can be suspended. The meridional ring is marked in degrees of latitude (0–90, for each hemisphere). When properly used, the pointer on the support points to the latitude of the instrument's location. This tilts the equatorial ring so that it lies at the same angle to the vertical as the local equator.
What is the instrument used to determine the time of year?
When the solar time is exactly noon, or known from another clock, the instrument can be used to determine the time of year. The meridional ring can function as the gnomon, when the rings are used as a sundial. A horizontal line aligned on a meridian with a gnomon facing the noon-sun is termed a meridian line and does not indicate the time, ...
What is the sun dial used for?
It can be used as a sun dial to tell time, if the approximate latitude and season is known, or to tell latitude, if the time is known or observed (at solar noon ). It may be considered to be a simplified, portable armillary sphere, or a more complex form of astrolabe .
When the shadow of the rings are aligned so that they appear to be in the same, or nearly the same?
When the shadow of the rings are aligned so that they appear to be in the same, or nearly the same, place, the meridian identifies itself .

Overview
History
Throughout Chinese history, astronomers have created celestial globes (Chinese: 渾象) to assist the observation of the stars. The Chinese also used the armillary sphere in aiding calendrical computations and calculations.
According to Needham, the earliest development of the armillary sphere in China goes back to the astronomers Shi Shen and Gan De in the 4th century BC, as th…
Description and use
The exterior parts of this machine are a compages [or framework] of brass rings, which represent the principal circles of the heavens.
1. The equinoctial A, which is divided into 360 degrees (beginning at its intersection with the ecliptic in Aries) for showing the sun's right ascension in degrees; and also into 24 hours, for showing its right ascension in time.
Paralympic Games
An artwork-based model of an Armillary sphere has been used since the March 1, 2014 to light the Paralympic heritage flame at Stoke Mandeville Stadium, United Kingdom. The sphere includes a wheelchair that the user can rotate to spark the flame as part of a ceremony to celebrate the past, present and future of the Paralympic Movement in the UK. The Armillary Sphere was created by artist Jon Bausor and will be used for future Heritage Flame events. The flame in the first-ever cer…
Heraldry and vexillology
The armillary sphere is commonly used in heraldry and vexillology, being mainly known as a symbol associated with Portugal, the Portuguese Empire and the Portuguese discoveries.
In the end of the 15th century, the armillary sphere became the personal heraldic badge of the future King Manuel I of Portugal, when he was still a Prince. The in…
See also
• Antikythera mechanism – Ancient analogue astronomical computer
• Chinese constellations – Groupings used in Chinese astrology
• De sphaera mundi – Book by Sacrobosco, describes the late medieval (Ptolemaic) cosmos
External links
• Starry Messenger Archived 2014-10-12 at the Wayback Machine
• Armillary Spheres and Teaching Astronomy | Whipple Museum
• AstroMedia* Verlag in Germany offers a cardboard construction kit for an armillary sphere ("Das Kleine Tischplanetarium")