How do you know if a pedigree is autosomal recessive?
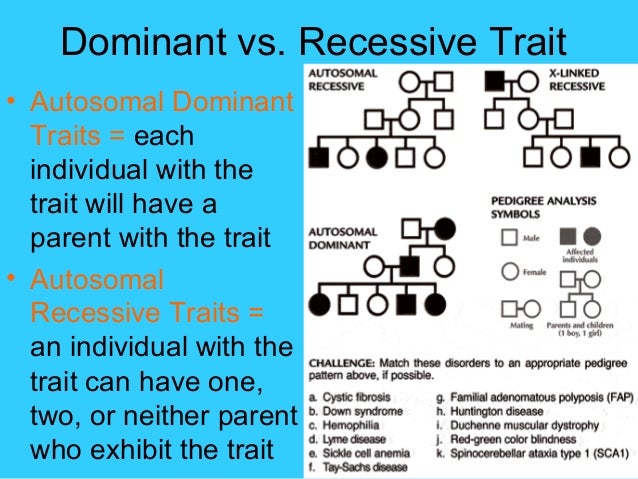
One trick for identifying a recessive trait is that if a trait skips a generation in a pedigree, it is often an autosomal recessive trait (although a trait can be autosomal recessive. and not skip generations). These traits appear with equal frequency in both sexes.
What does dominant pedigree mean?
Pedigrees are normally used to represent simple dominant and recessive traits. For example, having a widow's peak hairline is dominant.If an individual has that trait, their symbol on the pedigree will be shaded in. Certain traits like colorblindness are located on the X or Y chromosome and are called sex-linked.
What does autosomal dominant trait mean?
So an autosomal trait is one that occurs due to a mutation on Chromosomes 1 through 22. Dominant means that you only need one copy of a mutation in order to be effective. Some autosomal dominant traits that individuals may be familiar with are neourofibromitosis Type I, Huntington disease, and Marfan syndrome.
Do autosomal dominant traits skip generations?
Since autosomal dominant disorders involve autosomes or the non-sex chromosomes, the disorders affect males and females equally. Also, autosomal dominant disorders rarely skip generations because they only require the inheritance of one dominant allele to express the phenotype of the disorder.

How do you know if a pedigree is autosomal dominant?
Reading a pedigreeDetermine whether the trait is dominant or recessive. If the trait is dominant, one of the parents must have the trait. ... Determine if the chart shows an autosomal or sex-linked (usually X-linked) trait. For example, in X-linked recessive traits, males are much more commonly affected than females.
What is autosomal recessive pedigree?
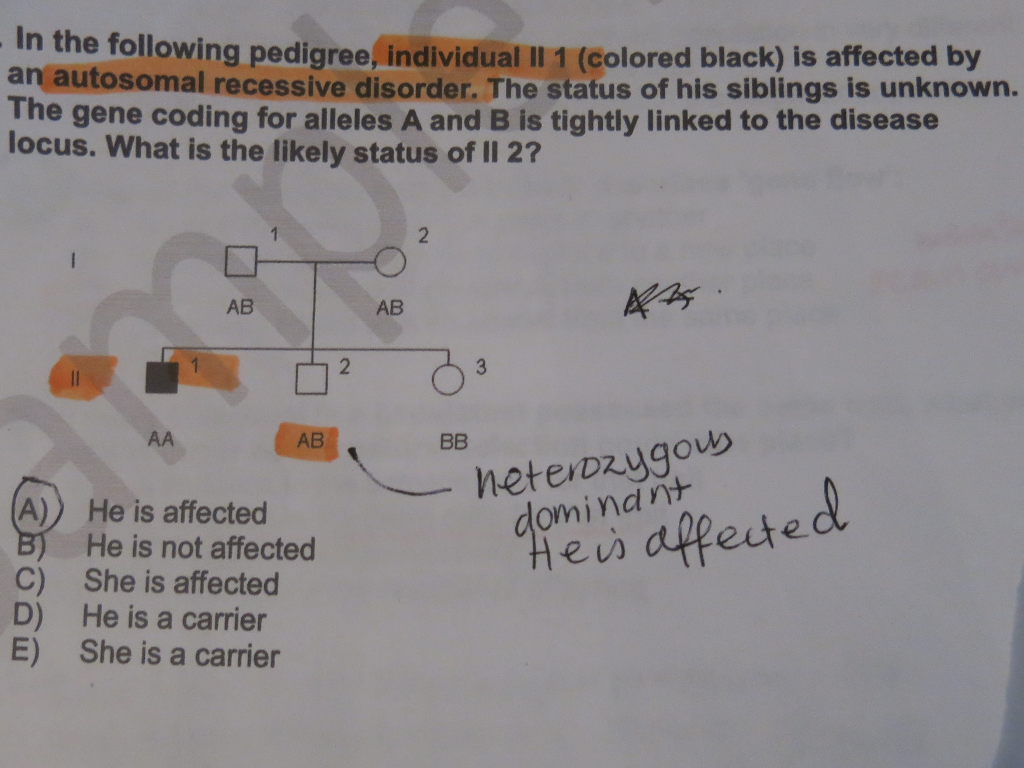
An autosomal recessive trait requires homozygosity or compound heterozygosity to manifest the disease phenotype. Features of autosomal recessive inheritance seen here include: Absence of family history of disease in prior generations. 25% affected status rate among siblings of the affected proband. Consanguinity.
What does autosomal dominant mean in genetics?
One of the ways a genetic trait or a genetic condition can be inherited. In autosomal dominant inheritance, a genetic condition occurs when a variant is present in only one allele (copy) of a given gene.
What is the difference between autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant pedigree?
Compared to pedigrees of dominant traits, autosomal recessive pedigrees tend to show fewer affected individuals and are often described as "skipping" generations. Thus, the major feature that distinguishes autosomal recessive from dominantly inherited traits is that unaffected individuals can have affected offspring.
What is the difference between autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant?
Autosomal dominant traits pass from one parent onto their child. Autosomal recessive traits pass from both parents onto their child. Autosomal refers to the 22 numbered chromosomes as opposed to the sex chromosomes (X and Y).
What is an example of autosomal dominant?
Examples of autosomal dominant diseases include Huntington disease, neurofibromatosis, and polycystic kidney disease.
What are the characteristics of autosomal dominant inheritance?
The main features of autosomal dominant inheritance pattern include: Males and females are affected in roughly equal proportions. People in more than one generation are affected. Men and women are both able to pass on the condition to their sons and daughters.
How do you tell if a pedigree is autosomal or Sexlinked?
Explanation:In a pedigree displaying autosomal trait, affected individuals are of both sex: that is both male and female individuals could be affected in 1:1 ratio.In a pedigree displaying sex linked trait, an overwhelming number of males will be affected.
What is an example of an autosomal recessive trait?
Examples of autosomal recessive disorders include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease.
How do you tell if a pedigree is autosomal or Sexlinked?
Explanation:In a pedigree displaying autosomal trait, affected individuals are of both sex: that is both male and female individuals could be affected in 1:1 ratio.In a pedigree displaying sex linked trait, an overwhelming number of males will be affected.
Which feature is found among an autosomal recessive pedigree?
Which feature is found among an autosomal recessive pedigree? Heterozygotes have a normal phenotype. Affected children will have at least one affected parent.
How do you solve an autosomal recessive pedigree?
1:2414:23Pedigree analysis | How to solve pedigree problems? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOne way is autosomal dominant that means the disease gene is presenting the AutoZone. And the traitMoreOne way is autosomal dominant that means the disease gene is presenting the AutoZone. And the trait is dominant autosomal recessive that the disease-causing gene is present again in autism.
What is autosomal dominant?
Autosomal dominant or dominance is a pattern of genetic inheritance that occurs within an autosome (non-sex chromosome ). The way we look and function is most commonly the result of dominance of one parental gene over the other. In medical terms, an autosomal dominant disease describes a disorder caused by a single copy of a mutant gene or allele that is carried by one parent and can affect both male and female offspring. A single copy of the mutation from either parent is enough to cause an autosomal dominant disorder.
What are some examples of autosomal dominance?
Another popular example in the field of autosomal dominance is polycystic kidney disease, where multiple cysts develop in the kidneys and reduce their ability to filter waste products from the blood. Polycystic kidneys.
How many non-sex chromosomes are affected by autosomal dominance?
Autosomal dominance affects the twenty-two non-sex chromosomes or autosomes. Sex-linked dominance only affects the single sex chromosome or allosome. Dominant and recessive allele combinations control every aspect of the anatomy and physiology except for sex-linked traits.
What is the allele of a gene?
An allele is a very specific part of a gene or chromosome that is found at the same location. There are two alleles for each gene – one from each parent. While a gene may determine eye color, various alleles will determine the exact color. If one of your genes represents the trait of blood type, the alleles will decide which blood type this is. In the case of autosomal dominance we should really talk of dominant alleles because numerous alleles make up a single gene. Even if only one allele in tens of thousands is affected, it has the potential to affect the entire gene. An autosomal dominant (or recessive) disorder is commonly named after an affected gene, but the cause is due to one or more alleles associated with this gene.
How many repeats of the Huntington's disease gene are there?
Chromosome four hosts the huntingtin protein gene (HTT gene) that contains between 10 and 35 repetitions of a specific piece of code known as the CAG trinucleotide repeat. In patients with Huntington’s disease, these repetitions occur at least 40 times. This might be due to inheritance, but it has since been discovered that repeat expansions can change in size in the same or successive generations. Just because you have the HTT gene does not mean that you will develop Huntington’s disease. This particular disease has already be mentioned as being an autosomal dominant disorder with a twist; when researchers discover what triggers increased repeat expansions, they will be able to halt or even cure their associated illnesses. Repeat expansions cause many genetic disorders.
What is the difference between autosomal and sex-linked dominance?
The difference between autosomal and sex-linked dominance is purely to do with the type of chromosomes involved. Autosomal dominance affects the twenty-two non-sex chromosomes or autosomes.
How does autosomal dominance help?
Autosomal dominance and sex-linked dominance can help to predict how offspring will develop but concern different types of chromosomes. Human and mammal gender is determined by which sex-chromosome pair (X and Y) is present in a person’s genome. Females have two X chromosomes (XX); males one X and one Y (XY). Sex-chromosomes are also called allosomes.
What is the genotype of a non-shaded person?
When completing this pedigree with autosomal dominant inheritance, individuals that are non-shaded are expressing the recessive phenotype and have a genotype of “rr”. Use this knowledge and additional knowledge about how genes are passed from generation to generation to complete the remainder of the pedigree. Shaded individuals will either have a genotype of “Rr” or “R-“ (“RR” or “Rr”, not enough information to determine).
When are parents heterozygous?
The trait is present whenever the corresponding gene is present (generally). If both parents possess the trait, but it is absent in any of their offspring, then the parents are both heterozygous (“carriers”) of the recessive allele.
Which type of homozygotes have a more severe form of the condition?
Homozygotes for the dominant condition have a more severe form of the condition.
Do traits skip generations?
Traits do not skip generations (generally). If the trait is displayed in offspring, at least one parent must show the trait. If parents don’t have the trait, their children should not have the trait (except for situations of gene amplification).
What is autosomal dominant pedigree?
A pedigree analysis utilising Mendelian inheritance principles (autosomal dominant pedigree) could establish if a trait does have a dominant pedigree or recessive inheritance pattern. Autosomal Dominant Pedigrees are frequently created after a family member is diagnosed with a genetic illness.
How many copies of the gene are needed for autosomal dominant inheritance?
To be afflicted by an autosomal dominant inheritance, a person just needs one mutant copy of the gene. Each affected person typically contains a single parent who is also affected. A child has a 50% probability of inheriting the mutant gene. Reduced penetration is a feature of autosomal dominant trait diseases, which means that while only one mutant copy is required, not everyone who inherits that mutation develops the disease.
What are autosomal recessive disorders?
Certain autosomal recessive disorders are frequent as harbouring one of the defective genes formerly provided a little amount of protection against infectious diseases or toxins like tuberculosis or malaria. Cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria, sickle cell disease, and thalassaemia are such disorders.
What is the probability of inheriting a mutant gene?
A child has a 50% probability of inheriting the mutant gene. Reduced penetration is a feature of autosomal dominant trait diseases, which means that while only one mutant copy is required, not everyone who inherits that mutation develops the disease.
What is X linked dominant inheritance?
Mutations in genes on the X chromosome produce X linked dominant inheritance. Such an inheritance pattern is found in just a few illnesses, one of which being X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Both males and females are impacted by these illnesses, with men suffering from them more seriously than females.
What is genetic disorder?
VIEW MORE. Genetic Disease:- A genetic disorder is a medical condition caused by one or even more genetic defects. A chromosomal anomaly or a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) could be the reason for the same. Although polygenic illnesses are the most frequent, the term is typically applied to conditions ...
How many people are affected by genetic mutations?
Because of the large variety of genetic abnormalities, roughly one in every twenty-one people is affected by a "rare" genetic disorder.
What are some examples of autosomal dominant disorder?
Unaffected parents do not transmit the trait. Examples of Autosomal Dominant Disorders. Examples: Huntington disease, Marfan syndrome.
Do affected offspring have affected parents?
Affected offspring must have an affected parent, unless they possess a new mutation.
What is autosomal dominant?
Autosomal Dominant. This pedigree shows an autosomal dominant trait or disorder. Autosomal means the gene is on a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome (X or Y). Not all of the offspring inherited the trait because their parents were heterozygous and passed on two recessive genes to those that do not show the trait.
How are pedigrees represented?
Pedigrees use a standard set of symbols to make them easier to understand. Males are represented by squares, while females are represented by circles. Parents are connected by horizontal lines, and vertical lines stemming from horizontal lines lead to the symbols for their offspring. The generations are also clearly marked with numbers, with I being the first generation, II being the children of the first generation, and III being the grandchildren, for example.
What does the red square on a pedigree mean?
This pedigree is of an autosomal recessive trait or disorder. The completely red square represents a male that is homozygous recessive and has the trait. All of the half-shaded individuals are carriers; they do not exhibit the trait because it is recessive, but they could pass it on to their offspring if their partner is also a heterozygote. Autosomal recessive disorders include cystic fibrosis and Tay-Sachs disease.
Why do two people with a dominant trait have a child that shows the recessive trait?
Why is it that two people with a dominant trait can sometimes have a child that shows the recessive trait? This can occur because people have two copies of each gene, one from their mother and one from their father. Different forms of a gene—such as widow’s peak or no widow’s peak—are called alleles. In genetics, the dominant allele is represented by a capital letter, like W, while the recessive allele is represented by a lowercase letter, like w. There are three different genotypes (genetic makeups):
How to understand pedigrees?
To be able to understand pedigrees, one must understand dominant and recessive genes. Some characteristics, such as height, are influenced by a variety of genes and an individual’s environment. Height cannot be easily represented by a pedigree. Pedigrees are normally used to represent simple dominant and recessive traits. For example, having a widow’s peak hairline is dominant. If an individual has that trait, their symbol on the pedigree will be shaded in. If they have no widow’s peak, their symbol will not be shaded in because having no widow’s peak is recessive.
What is the purpose of a pedigree?
The purpose of a pedigree is to have an easy-to-read chart that depicts a certain characteristic or disorder in an individual. It can be used for a characteristic like having a widow’s peak or attached earlobes, or a genetic disorder like colorblindness or Huntington’s disease. Besides being used to represent familial characteristics in humans, pedigrees are also important in animals that are selectively bred for certain characteristics. They visually represent the ancestors of an animal and make it easier to understand whether that animal will pass on certain characteristics to its offspring.
What are the different forms of a gene?
Different forms of a gene—such as widow’s peak or no widow’s peak —are called alleles. In genetics, the dominant allele is represented by a capital letter, like W, while the recessive allele is represented by a lowercase letter, like w. There are three different genotypes (genetic makeups): WW = dominant. Ww = dominant.
How to determine if a disorder is dominant or recessive?
Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. If non-affected parent transmit the disease, it is Recessive disorder. If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous.
Why does neither parent have to have the disorder if the disorder is recessive?
If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous.