Price Efficiency
- Understanding Price Efficiency. Price efficiency theory posits that markets are efficient because all relevant information that impacts valuations is in the public domain.
- Example of Price Efficiency. Fictional company CDE currently trades at $20 a share. ...
- Limitations of Price Efficiency. ...
What is meant by price efficiency?
Price efficiency is the belief that asset prices reflect the possession of all available information by all market participants. The theory posits that markets are efficient because all relevant information that impacts valuations is in the public domain. Price efficiency is a shared article of faith for the adherents of all ...
What is market efficiency and why is it important?
Market efficiency refers to the degree to which market prices reflect all available, relevant information. If markets are efficient, then all information is already incorporated into prices, and so...
What is the theory of efficient market theory?
This theory considers that both prices and markets are efficient. As a result, the prices change when any new information is received. Further, past prices don’t serve as a basis for predicting future prices since prices already reflect all information available about the assets.
Is price efficiency flawed?
Price efficiency is a shared article of faith for the adherents of all of the three versions of the efficient market hypothesis (EMH). Critics point out price efficiency is flawed because not everyone thinks alike.

What is meant by an efficient market?
An efficient market is one where all information is transmitted perfectly, completely, instantly, and for no cost. Asset prices in an efficient market fully reflect all information available to market participants. As a result, it is impossible to ex-ante make money by trading assets in an efficient market.
Why is price taking efficient?
Price Takers in a Perfectly Competitive Market Price takers emerge in a perfectly competitive market because: All companies sell an identical product. There are a large number of sellers and buyers. Buyers can access information regarding the price charged by other companies.
How do you determine if a market is efficient?
We derive a measure to quantify the level of market efficiency (AMIM), analyze its theoretical properties and compute empirical estimates of the measure. AMIM is between zero and one if the market is inefficient, where closer to one means less efficient. When AMIM is smaller or equal to zero, the market is efficient.
What is the efficient market quantity?
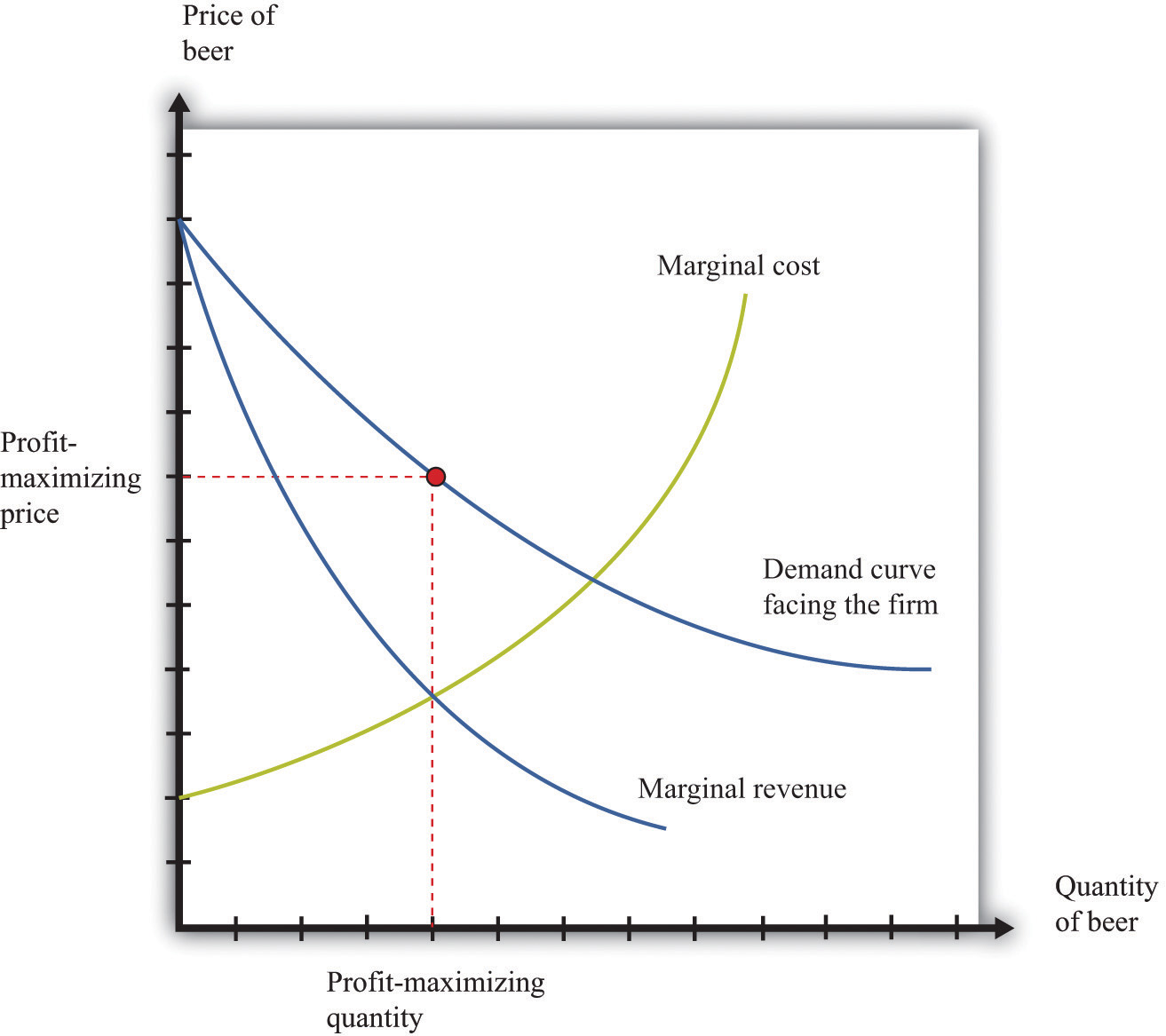
The efficient quantity of a good is the quantity that makes marginal benefit from the good equal to marginal cost of producing it. If marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost, resources use will be more efficiently if the quantity is increased.
What is an example of a price taker?
What is a Price Taker? A price taker is a business that sells such commoditized products that it must accept the prevailing market price for its products. For example, a farmer produces wheat, which is a commodity; the farmer can only sell at the prevailing market price.
What is price taking?
Key Takeaways. A price-taker is an individual or company that must accept prevailing prices in a market, lacking the market share to influence market price on its own. Due to market competition, most producers are also price-takers.
What are the 3 forms of market efficiency?
Three common types of market efficiency are allocative, operational and informational.
What makes an economy efficient?
Economic efficiency implies an economic state in which every resource is optimally allocated to serve each individual or entity in the best way while minimizing waste and inefficiency. When an economy is economically efficient, any changes made to assist one entity would harm another.
How do you find the efficient price and quantity?
10:5111:47Efficiency and Equilibrium in Competitive Markets - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe market is set to be efficient meaning that resources are allocated in the best possible wayMoreThe market is set to be efficient meaning that resources are allocated in the best possible way towards the production of this good at any other price quantity combination.
What is an efficient market outcome?
An important characteristic of the marketplace is that in certain circumstances it produces what we call an efficient outcome, or an efficient market. Such an outcome yields the highest possible sum of surpluses. An efficient market maximizes the sum of producer and consumer surpluses.
Is the market efficient or inefficient?
Markets are efficient in that prices generally reflect available information, and it is difficult to profit from active management. However, the market is ultimately inefficient enough to incentivise some active management that exploits profit opportunities.
What is the relationship between price supply and demand?
It's a fundamental economic principle that when supply exceeds demand for a good or service, prices fall. When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged.
What is price discovery in stock market?
Price discovery is the result of the interaction between sellers and buyers, or in other words, between supply and demand and occurs thousands of times per day in the futures markets. This auction type environment means that a trader can find trades that they feel are fair and efficient.
What is the cost of time?
"The opportunity cost of time is usually measured by wage," explains Hurst. "If you take an hour that could be spent working and devote that hour to another activity, you give up potential income.
What is price efficiency?
Price efficiency is a theory that advocates prices for the assets in a market reflects the fact that all information about the assets is available to all market participants. The theory further suggests that the market is efficient since all the information about the assets that could influence price is available in the public domain and hence accessible by all and no investor is in a position to derive excess returns on account of extra information available to him or her.
What happens if price efficiency theory doesn't hold?
If price efficiency theory doesn’t hold i.e., if the prices of the assets do not reflect the entire information available about the asset, then prices of the assets can be over-valued or under-valued. This gives rise to an inefficient market.
Why are past prices not a basis for future prices?
Further, the past prices don’t serve as a basis for predicting future prices since prices already reflect all information available about the assets. The theory is sometimes criticized because the same information can’t be expected to be perceived by everyone in the same manner.
What are the advantages of equal access to information?
Advantages. Everyone has equal access to information , and everyone is free to use the same for their analysis. No one remains in a position to gain excess profits due to equal access to information, and thus, all are placed in an equal position. The assets are priced at their fair value and reflect the information available in the market.
What is Price Efficiency?
Price efficiency is the concept that the price at which an asset sells should already reflect all public supply and demand information pertaining to it. A variation on the concept states that changes in this information are reflected instantly in the market price, while yet another version states that the price already reflects information that is both publicly and privately available. The concept implies that it should not be possible for an investor to consistently earn excess returns.
Why is price efficiency skewed?
Thus, it seems likely that price efficiency can be skewed by such factors as: The relative need of the parties to a transaction to buy or sell an asset. For example, the seller may be desperate for cash, and so will pay a price lower than the market would indicate is reasonable.
Is price efficiency an imperfect concept?
The concept implies that it should not be possible for an investor to consistently earn excess returns. Realistically, buyers and sellers may agree to prices that are different from what perfect information about an asset would state that the price should be , which suggests that price efficiency is an imperfect concept.
What is market efficiency?
Market efficiency refers to how well current prices reflect all available, relevant information about the actual value of the underlying assets. A truly efficient market eliminates the possibility of beating the market, because any information available to any trader is already incorporated into the market price.
What is the weak form of market efficiency?
The weak form of market efficiency is that past price movements are not useful for predicting future prices. If all available, relevant information is incorporated into current prices, then any information relevant information that can be gleaned from past prices is already incorporated into current prices. Therefore future price changes can only ...
How do value investors make money?
Successful value investors make their money by purchasing stocks when they are undervalued and selling them when their price rises to meet or exceed their intrinsic worth. People who do not believe in an efficient market point to the fact that active traders exist.
What is value investing?
For example, at the other end of the spectrum from Fama and his followers are the value investors, who believe stocks can become undervalued, or priced below what they are worth. Successful value investors make their money by purchasing stocks when they are undervalued and selling them when their price rises to meet or exceed their intrinsic worth.
Who invented the efficient market hypothesis?
The term was taken from a paper written in 1970 by economist Eugene Fama, however Fama himself acknowledges that the term is a bit misleading because no one has a clear definition of how to perfectly define or precisely measure this thing called market efficiency. Despite such limitations, the term is used in referring to what Fama is best known for, the efficient market hypothesis (EMH) .
What happens to the market as the quality of information increases?
As the quality and amount of information increases, the market becomes more efficient reducing opportunities for arbitrage and above market returns.
Key Takeaways
The market efficiency occurs when current market prices reflect all relevant financial information about an underlying asset or security.
Features
Investors cannot use any new information about a security or asset for their benefit.
Market Efficiency Forms
You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked For eg: Source: Market Efficiency (wallstreetmojo.com)
Examples of Market Efficiency
Let us consider the following market efficiency examples to understand the concept well:
Market Efficiency And Market Failure
Market efficiency also plays a crucial role in allocating resources to produce consumer-friendly goods. Resource allocation efficiency refers to a market where the value obtained for goods is equivalent to the predicted value.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Market Efficiency and its definition. Here we discuss how market efficiency theory works along with forms, features, and examples. You may also learn more about financing from the following articles –
What year was the first cost efficient?
M-W gives 1970 as the “first known use of cost-efficient.”
When was cost effective first used?
The OED and M-W date the terms from 1967 and 1970, but the Ngram Viewer shows that cost-effective was present in printed sources as early as 1836. Both terms are documented in works printed in 1887. Cost-effective shows a bump on the graph in the 1940s, but then both terms remain more or less even until the 1960s, when cost-effective soars ahead.
When was the first OED citation given for cost effective?
The first OED citation given for cost-effective is dated 1967. I find no entry for cost-efficient.

Explanation
Examples of Price Efficiency
- Consider an example of a company’s stock, XYZ Ltd., which is currently trading at $10. The company publishes its quarterly results on its website, which anyone can view. The results showed great pr...
- In this case, this news is available in the public domain, and all investors have access to the information. The investors will trade, keeping in mind that the prices may increase. It is know…
- Consider an example of a company’s stock, XYZ Ltd., which is currently trading at $10. The company publishes its quarterly results on its website, which anyone can view. The results showed great pr...
- In this case, this news is available in the public domain, and all investors have access to the information. The investors will trade, keeping in mind that the prices may increase. It is known as p...
Price Efficiency in Natural Monopoly
- Natural monopoly refers to a monopoly created on its own due to market forces. It is created when it is better to have a single organization as a service producer in the entire industry because it can provide low-priced products. The theory of price efficiency is not expected to operate in the case of a natural monopoly since the single service provider is in a position to manage or contro…
Price Efficiency Variance
- If price efficiency theory doesn’t hold, i.e., if the prices of the assets do not reflect the complete information available about the asset, then prices can be overvalued or under-valued. It gives rise to an inefficient marketInefficient MarketAn inefficient market represents the one which fails to exhibit the actual value of the assets. Such a market doesn't provide transparent information an…
Advantages
- Everyone has equal access to information, and everyone is free to use the same for their analysis.
- No one remains in a position to gain excess profits due to equal access to information, and thus, all are placed in an equal position.
- The assets are priced at their fair value and reflect the information available in the market.
Disadvantages
- The theory assumes that all individuals will react similarly to the information available about the asset. In reality, people can differ in opinion and arrive at different conclusions based on the...
- Since people can perceive information differently, there are high chances of anomalies in the prices of the assets. As a result, assets can be under-valued or overvalued, and there is a cha…
- The theory assumes that all individuals will react similarly to the information available about the asset. In reality, people can differ in opinion and arrive at different conclusions based on the...
- Since people can perceive information differently, there are high chances of anomalies in the prices of the assets. As a result, assets can be under-valued or overvalued, and there is a chance for...
- The theory states that the prices reflect the information available and change when new information is received. It doesn’t stand true when human emotions also influence prices. Take an example of...
Recommended Articles
- This has been a guide to What is Price Efficiency & its Definition. Here we discuss the examples of price efficiency and variance and advantages and disadvantages. You can learn more about from the following articles – 1. Value Stock 2. Overvalued Stocks 3. Stock Market Bubble 4. How does the Stock Market Work?