How to generate a sine wave?
- xlabel: x-axis label is generated.
- Ylabel: y-axis label is generated.
- Title: A title gets added to the sine wave plot
- Axis square: It enables the user to generate the sine wave in square form.
- Axis equal: User can create the sine wave plot with common scale factor and spaces for both the axes
- Grid on: gridlines gets enabled for the sine wave plot
Why do we use sine wave in AC circuits?
Sine waves are so important and so studied because the sine wave is the most basic and the most common waveform for AC Signal variations. A rotary generator is a very important device that allows us to have electricity in our homes. Most electricity is made by turbine blades rotating at speeds high enough to produce electricity in a generator.
What are the characteristics of a sine wave of voltage?
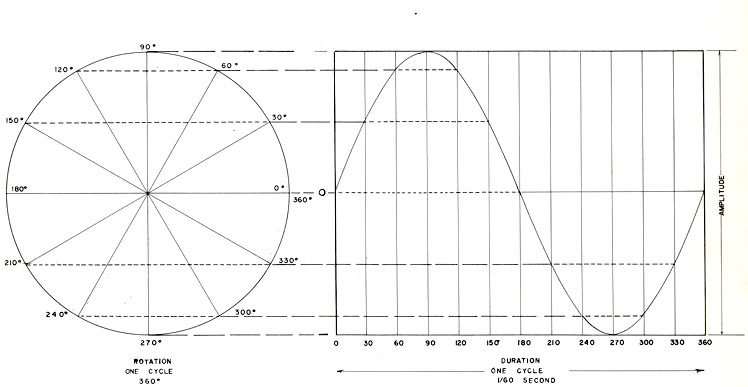
With a sine wave, the induced voltage increases to a maximum at 90 , when the loop is vertical, just as the sine of the angle of rotation increases to a maximum at 90°. The instantaneous value of a sine-wave voltage for any angle of rotation is expressed in the formula:
What is sine wave voltage?
Which is therefore given as the standard equation for the Average Voltage of a sine wave as: The average voltage ( VAV) of a sinusoidal waveform is determined by multiplying the peak voltage value by the constant 0.637, which is two divided by pi ( π ).

What produces a sine wave?
As the coil rotates the voltage decreases according to the sine of the angle until the conductor is parallel to the magnetic field. Further rotation then increases the voltage until once again it is at a maximum (but in the opposite direction). For each revolution a complete sine wave is generated.
Why is it called a sine wave?
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the sine trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function.
Is household electricity pure sine wave?
All AC appliances and equipment are designed to run off of a pure sine wave. Pure sine wave energy is the type of power that is produced by your local utility company.
What is sine wave in AC current?
The most familiar AC waveform is the sine wave, which derives its name from the fact that the current or voltage varies with the sine of the elapsed time. Other common AC waveforms are the square wave, the ramp, the sawtooth wave, and the triangular wave. Their general shapes are shown below.
What is sine in simple words?
In a right angled triangle, the sine of an angle is: The length of the side opposite the angle divided by the length of the hypotenuse. The abbreviation is sin. sin θ = opposite / hypotenuse. Well Done!
Is a sine wave AC or DC?
AC from a power supply This shape is called a sine wave. This triangular signal is AC because it changes between positive (+) and negative (-).
Can you run a fridge on a pure sine wave inverter?
Appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, and compressors that use AC motors won't run as efficiently on a modified sine wave as they would on a pure sine wave. In some cases, running an AC motor on a modified sine wave may lead to a buildup of excess waste heat that could damage the equipment.
Does a TV need a pure sine wave?
Do I need a pure sine wave inverter to run a television? In short, No. By using a modified sine wave inverter you will find that lines will appear across the screen (see above).
What appliances need pure sine wave?
What appliances need pure sine wave?Inductive loads like microwaves and motors.Laser printers.Newer TVs.Medical equipment such as CPAP machines.Audio-visual devices.
What is sine wave examples?
A sine wave is a repetitive change or motion which, when plotted as a graph, has the same shape as the sine function. For example, on the right is a weight suspended by a spring. As it bounces up and down, its motion, when graphed over time, is a sine wave.
What are the advantages of sine wave?
2.0 advantages of sine Wave inverters Inductive loads like microwaves and motors run faster, quieter and cooler. Reduces audible and electrical noise in fans, fluorescent lights, audio amplifiers, TV, fax and answering machines. Prevents crashes in computers, weird print outs and glitches in monitors.
Can a sine wave be DC?
DC circuits have a unidirectional flow of current and like AC it is not changing the direction periodically. Waveform of DC is a pure sine wave. As you can see, the voltage is constant with respect to time.
Why sine bar is called sine bar?
The sine bar is based on trigonometry. The distance between the two setting rollers of the Sine Bar is given by L. From this we can write θ = sin^-1 (h / L). This is the formula for sine bar for calculating the angle or setting the workpiece to the required angle. This device is called “Sine Bar”.
Does sine mean sin?
The sine of one of the angles of a right triangle (often abbreviated “sin”) is the ratio of the length of the side of the triangle opposite the angle to the length of the triangle's hypotenuse.
What is the sum of two sinusoids of a given frequency?
A similar result may be established if the sine and cosine terms have phase angles other than zero, indicating that, in general, the sum of two sinusoids of a given frequency is another sinusoid of the same frequency.
What is a solid curve in a sketch of (6)?
A sketch of (6) is shown in figure (2) by the solid line, along with a sketch of (1), shown dashed. The solid curve is simply the dashed curve displaced ϕ/ω seconds, or ϕ radians to the left. Therefore, points on the solid curve, such as its peaks, occur ϕ radians, or ϕ/ω seconds earlier than corresponding points on the dashed curve.
What is the amplitude of a sinusoid?
Which is sketched in figure (1). The amplitude of the sinusoid is Vm, which is the maximum value that the function attains. The radian frequency, or angular frequency, is ω, measured in radian per second (rad/s).
What is the difference between sines and cosines?
The only difference between sines and cosines is thus the phase angles. For example, we may write (6) as
How many cycles does a function go through in 1 second?
As may be seen from (1) and (2). Thus in 1 second the function goes through 1/T cycles, or periods. Its frequency f is then
Is a sine wave a sinusoid?
The sum of a sine wave and a cosine wave of the same frequency is another sinusoid of that frequency . To show this, consider
Is sine a cosine function?
Thus far we have considered sine functions rather than cosine functions in defining sinusoids. It does not matter which form we use since
Why is a sound different from a note?
To the human ear, a sound that is made of more than one sine wave will have perceptible harmonics; addition of different sine waves results in a different waveform and thus changes the timbre of the sound. Presence of higher harmonics in addition to the fundamental causes variation in the timbre, which is the reason why the same musical note (the same frequency) played on different instruments sounds different. On the other hand, if the sound contains aperiodic waves along with sine waves (which are periodic), then the sound will be perceived to be noisy, as noise is characterized as being aperiodic or having a non-repetitive pattern.
Why is the sine wave important?
The sine wave is important in physics because it retains its wave shape when added to another sine wave of the same frequency and arbitrary phase and magnitude. It is the only periodic waveform that has this property. This property leads to its importance in Fourier analysis and makes it acoustically unique.
What is sine wave?
A sine wave is a continuous wave. It is named after the function sine, of which it is the graph. It occurs often in both pure and applied mathematics, as well as physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Its most basic form as a function of time ( t) is: y ( t ) = A sin ( 2 π f t + φ ) = A sin ( ω t + φ ) ...
What is the Fourier series?
Fourier series. Sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waveforms. Main article: Fourier analysis. In 1822, French mathematician Joseph Fourier discovered that sinusoidal waves can be used as simple building blocks to describe and approximate any periodic waveform, including square waves.
How many seconds of a 220 Hz wave?
2 seconds of a 220 Hz sine wave. This is the sound wave described by a sine function with f = 220 oscillations per second.
What type of waves are found in nature?
This wave pattern occurs often in nature, including wind waves, sound waves, and light waves.
What is the spatial variable of a wave?
a spatial variable x that represents the position on the dimension on which the wave propagates, and a characteristic parameter k called wave number (or angular wave number), which represents the proportionality between the angular frequency ω and the linear speed ( speed of propagation) ν;
What is special about sine waves?
One way to describe what is special about a sine wave is that it is a "pure" frequency. Any analytic repeating function can be described as a combination of sine wave. Sine waves are the building blocks that such functions can be decomposed into. Sines are also the "natural" waveform that something oscillating produces.
What is sine wave?
A sine wave is a repetitive change or motion which, when plotted as a graph, has the same shape as the sine function. A quote more directed to electronics: The electrical power in your house is AC or Alternating Current. The direction of current flow reverses 50 or 60 times per second depending on where you live.
What is the general solution of sine function?
You could define the sine function as f, the general solution to this equation. It is possible to show that it is the only general solution to this problem.
What is the only real periodic function?
Sinewaves are the only real periodic functions for which this holds true. All other real periodic functions will change shape when they are differentiated or integrated. So we can say. "a sinewave is a periodic signal that keeps it's shape and frequency when differentiated or integrated".
How to describe sine wave?
One way would be to describe a sinewave with respect to the unit circle. The radius obviously draws a circle BUT the x and y co-ordinates trace out the familiar waveforms.
Why is the piston on the other side of the sine wave?
For instance look at the linkage at 3:00 and 9:00 positions (90 and 270 on the sinewave, where it is flat) and you see where the piston has a problem: it can't apply any force. That's why the mechanism is duplicated on the other side, 90 degrees out of phase. That piston is at the peak of its leverage.
How many degrees out of phase is a steam locomotive?
The concept works even better with 3 (60 degrees out of phase), which steam locomotives did when they could (UK, Shay) and that concept is used today in 3-phase power.
Why do modified sine wave inverters consume more power?
Modified Sine Wave Inverters consume more power because of its low efficiency as compared to other ones. Cost Factor: Sine Wave Inverters are costlier than Modified Sine Wave Inverters. But this is because of its higher efficiency. The low cost of the Modified Sine Wave Inverters may have an edge, but it also reduces the life and durability ...
Why are sine wave inverters more preferred?
Compatibility With Various Appliances: Sine Wave Inverters are more preferred in today’s era because of its quality and efficiency. Thus we why many appliances are made with keeping in mind it’s compatibility with Pure Sine Wave Inverters. Modified Sine Wave Inverters, on ...
What is sine wave inverter?
A sine wave refers to a continuous wave that works based on a smooth repetitive oscillation. Pure sine waves tend to produce power that works better than the power at home- with state of the art, intricate technology to ensure the protection ...
What is the difference between a pure sine wave and a modified sine wave?
Here are some the basic points of distinctions to understand the difference between a best Pure Sine Wave Inverter and a Modified Sine Wave inverter clearly: 1 Efficiency: Sine Wave Inverters are more efficient and effective in the smooth functioning of electronic equipment and appliances. This ensures the durability and long life of the appliances.#N#Modified Sine Wave Inverters, on the other hand, is not much effective in the smooth functioning of some of the appliances. Appliances are worn out fast with this kind of inverters. 2 Compatibility With Various Appliances: Sine Wave Inverters are more preferred in today’s era because of its quality and efficiency. Thus we why many appliances are made with keeping in mind it’s compatibility with Pure Sine Wave Inverters.#N#Modified Sine Wave Inverters, on the other hand, is not much compatible with the latest appliances. This may create some problems with the smooth functioning of the appliances. 3 Power Consumption: Sine Wave Inverters are more effective in the utilization of power for the efficient working of the appliances that ensure less power consumption.#N#Modified Sine Wave Inverters consume more power because of its low efficiency as compared to other ones. 4 Cost Factor: Sine Wave Inverters are costlier than Modified Sine Wave Inverters. But this is because of its higher efficiency.#N#The low cost of the Modified Sine Wave Inverters may have an edge, but it also reduces the life and durability of the appliances.
Why use a pure sine inverter?
Many factors like the input voltage, frequency, and output voltage are dependent on the design of the design- now a pure sine inverter comes in amidst these to ensure that you have a reliable source of electricity for various applications.
What appliances do you target with an inverter?
For instance, some are ideal for sensitive electrical appliances, like – computers, laptops, etc. while others may provide support for a wide range of products, like – refrigerators, car vacuum, phones, PC, truck, semi-truck, etc.
Which is better: sine wave or modified wave inverters?
This ensures the durability and long life of the appliances. Modified Sine Wave Inverters , on the other hand, is not much effective in the smooth functioning of some of the appliances.
What equipment can be damaged when running on modified sine waves?
Equipment that can be damaged when running on modified sine waves such as laser printers, rechargeable battery powered devices and pellet stoves run perfectly when operated from a pure sine wave inverter. Telecommunications equipment run with less noise and hum. Motors run at their intended speed and with less heat.
Why use a sine wave?
The benefits of running your equipment and appliances on a pure sine wave include: Generates less electrical noise in your equipment. Means no lines on your TV set and no hum in your sound system. Microwave ovens cook faster. Equipment and appliances lasts longer.
Can AC run on a sine wave?
In fact, some equipment will operate properly only from a true sine wave source: Some examples include laser and motor driven printers, variable speed motors, medical equipment, and any equipment deriving timing signals from the input. All AC appliances and equipment are designed to run off of a pure sine wave.
What type of equipment runs with less noise and hum?
Telecommunications equipment run with less noise and hum.
Can you run a laser from a sine wave?
In fact, some equipment will operate properly only from a true sine wave source: Some examples include laser and motor driven printers, variable speed motors, medical equipment, and any equipment deriving timing signals from the input.
What Is A Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
Let’s start by understanding what a pure sine wave inverter is and why you would need one for your electrical system.
What Appliances Need A Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
For example, electric heaters or water pumps. However, their efficiency will be reduced and they might overheat.
How Do Pure Sine Wave Inverters Increase Voltage?
The second step is to increase the voltage of the pure sine wave current. DC is usually 12V, 24V or 48V. Whereas AC is 230V.
What Is The Difference Between A Modified And Pure Sine Wave Inverters?
Looking into the inverters available on the market, you probably found out two models:
Why Are Pure Sine Wave Inverters So Expensive?
Pure sine wave inverters provide a clean and reliable electric current, the same quality the utility grid delivers. To achieve this high quality, they use high-end electronic components, unlike modified sine wave inverters that contain only cheap electronics.
How many volts does a sine wave inverter output?
Previously, we saw that pure sine wave inverters first convert DC into AC, and then increase the input voltage (12V, 24V, 48V…) to reach an output voltage of 230V (transformer), usable by all our household appliances.
How much more expensive is a pure sine wave inverter than a modified sine wave inverter?
Pure sine wave inverters are up to 2 times more expensive than a modified sine wave inverter. You might then ask yourself, are they any good? And what exactly is a pure sine wave inverter?
Overview
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the sine trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields.
Formulation
Its most basic form as a function of time (t) is:
• A, amplitude, the peak deviation of the function from zero.
• f, ordinary frequency, the number of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time.
• ω = 2πf, angular frequency, the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second.
General form
In general, the function may also have:
• a spatial variable x that represents the position on the dimension on which the wave propagates, and a characteristic parameter k called wave number (or angular wave number), which represents the proportionality between the angular frequency ω and the linear speed (speed of propagation) ν;
• a non-zero center amplitude, D
Cosine
The term sinusoid describes any wave with characteristics of a sine wave. Thus, a cosine wave is also said to be sinusoidal, because , which is also a sine wave with a phase-shift of π/2 radians. Because of this head start, it is often said that the cosine function leads the sine function or the sine lags the cosine. The term sinusoidal thereby collectively refers to both sine waves and cosine waves with any phase offset.
Occurrence
This wave pattern occurs often in nature, including wind waves, sound waves, and light waves.
The human ear can recognize single sine waves as sounding clear because sine waves are representations of a single frequency with no harmonics.
To the human ear, a sound that is made of more than one sine wave will have …
Fourier series
In 1822, French mathematician Joseph Fourier discovered that sinusoidal waves can be used as simple building blocks to describe and approximate any periodic waveform, including square waves. Fourier used it as an analytical tool in the study of waves and heat flow. It is frequently used in signal processing and the statistical analysis of time series.
Traveling and standing waves
Since sine waves propagate without changing form in distributed linear systems, they are often used to analyze wave propagation. Sine waves traveling in two directions in space can be represented as
When two waves having the same amplitude and frequency, and traveling in opposite directions, superpose each other, then a standing wave pattern is created. Note that, on a plucked string, th…
See also
• Crest (physics)
• Damped sine wave
• Fourier transform
• Harmonic analysis
• Harmonic series (mathematics)