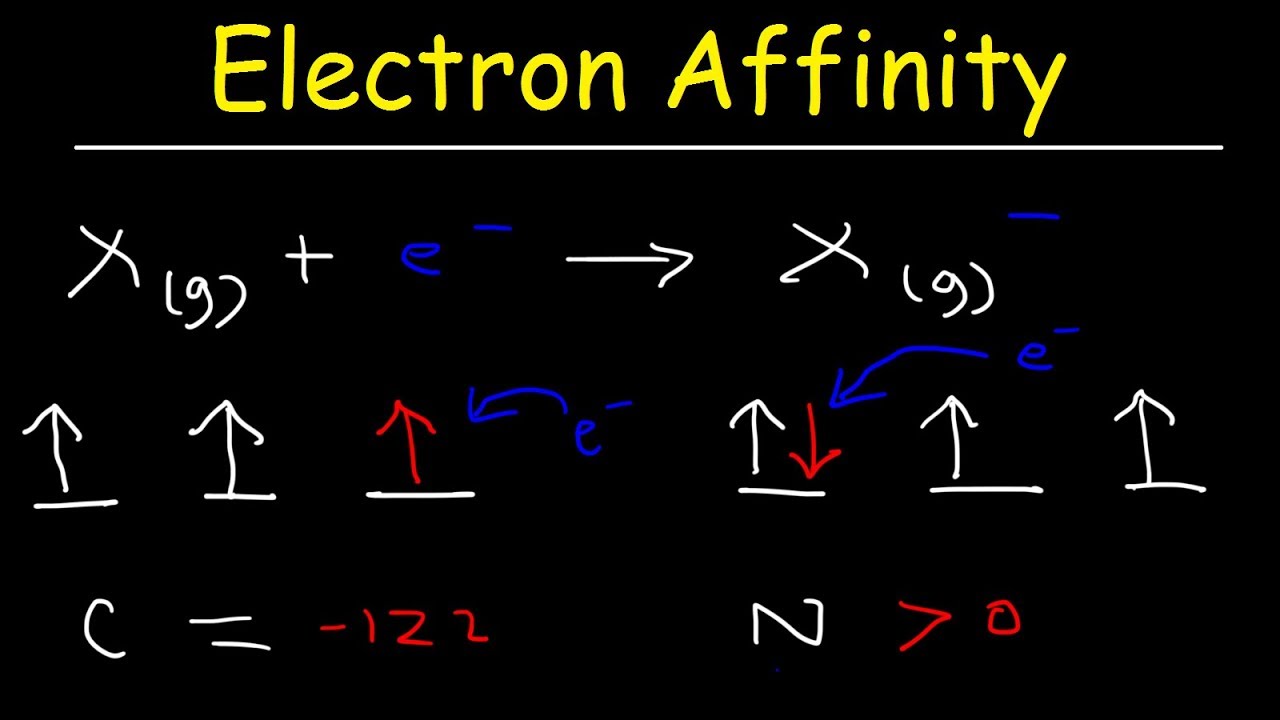
What are the essential characteristics of an electron?
What are the essential characteristics of an electron ? Electron is a negatively charged particles having very small mass. Mass and charge of an electron are given below. (i) Mass of an electron (m e ): The mass of a electron is about 1/1840 times that of a hydrogen atom. Its absolute mass is ,
What is the job of an electron?
Electrons play an essential role in numerous physical phenomena, such as electricity, magnetism, chemistry and thermal conductivity, and they also participate in gravitational, electromagnetic and weak interactions.
Does an electron determine what element it is?
Electron configurations provide insight into the chemical behaviour of elements by helping determine the valence electrons of an atom. It also helps classify elements into different blocks (such as the s-block elements, the p-block elements, the d-block elements, and the f-block elements).
What exactly is an electron?
What exactly is an electron? Even in classical electrodynamics one can describe the electron as an orbiting massless charge embedded in its synchrotron radiation and obtains the fundamental properties, also the mass and the de Broglie wave.
See more
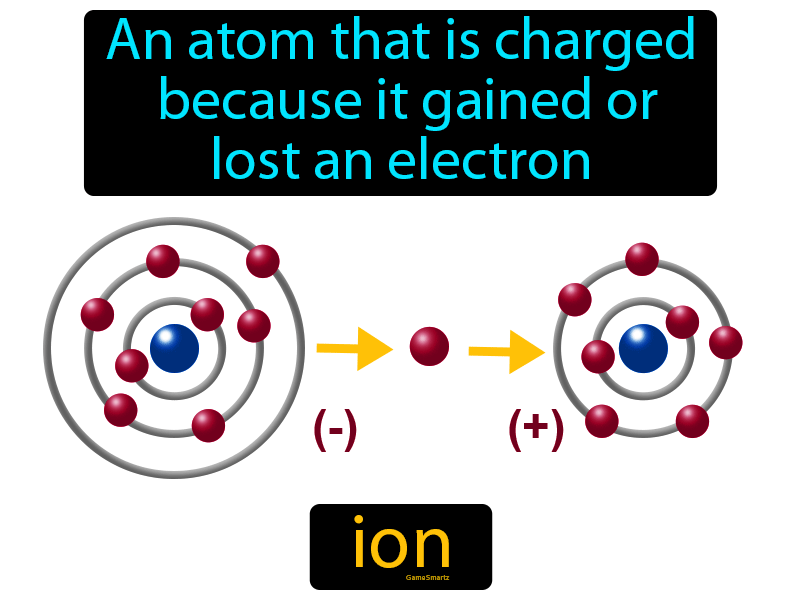
What is an electron definition for kids?
Kids Definition of electron : a very small particle that has a negative charge of electricity and travels around the nucleus of an atom.
What is a electron in science?
(ee-LEK-tron) A small particle with a negative charge that is found in all atoms. Streams of electrons made by special equipment can be used for radiation treatment.
What is electrons example?
Electrons are the smallest of the particles that make up an atom, and they carry a negative charge. The number of protons and electrons is equal in a neutral atom. The hydrogen atom, for example, has just one electron and one proton. The uranium atom, on the other hand, has 92 protons, and therefore, 92 electrons.
What is in an electron?
4:4710:51What is an Electron? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThese shapes are called orbitals. So while the electron. Itself has zero volume in another sense itMoreThese shapes are called orbitals. So while the electron. Itself has zero volume in another sense it takes up a relatively.
What is electron and proton?
Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge. Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge. Protons are bound together in an atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. Neutrons are a type of subatomic particle with no charge (they are neutral).
Where are the electrons?
Where Are Electrons? Unlike protons and neutrons, which are located inside the nucleus at the center of the atom, electrons are found outside the nucleus. Because opposite electric charges attract each other, negative electrons are attracted to the positive nucleus.
Is electron a charge?
electron, lightest stable subatomic particle known. It carries a negative charge of 1.602176634 × 10−19 coulomb, which is considered the basic unit of electric charge.
How big is an electron?
It is concluded that the diameter of the electron is comparable in magnitude with the wave-length of the shortest γ-rays. Using the best available values for the wave-length and the scattering by matter of hard X-rays and γ-rays, the radius of the electron is estimated as about 2 × 10−10 cm.
Are electrons positive or negative?
Because a proton has a positive charge (+) and an electron has a negative charge (-), element atoms are neutral, with all positive charges cancelli...
Who named Electron?
G. Johnstone Stoney invented the term “electron” in 1891 to describe the unit of charge discovered in tests that conveyed electric current through...
Do protons and electrons have the same mass?
Electrons are a sort of negative-charged subatomic particle. Protons and neutrons have about the same mass as electrons, yet they are both signific...
Are protons and electrons equal?
Protons and electrons are in equal proportions in an atom. Because protons and electrons have equal and opposing charges, atoms are generally neutral.
Why do electrons repel each other?
A free electron will flow in the opposite direction of the force lines since it has the opposite charge qualities as a positive charge. As a result...
What are Electrons?
Electrons are subatomic particles that hold an elementary charge of magnitude -1. The charge of an electron is equal in magnitude to the charge held by a proton (but has an opposite sign). Therefore, electrically neutral atoms/molecules must have an equal number of electrons and protons. Although the magnitude of the charges held by protons and electrons are the same, the size and mass of an electron are much smaller than that of a proton (the mass of an electron is roughly 1/1836 the mass of a proton).
Who invented the term "electron"?
G. Johnstone Stoney invented the term “electron” in 1891 to describe the unit of charge discovered in tests that conveyed electric current through chemicals. J.J. Thomson’s Cambridge classmate Joseph Larmor used the phrase in this context.
Why are protons and electrons in equal proportions?
Protons and electrons are in equal proportions in an atom. Because protons and electrons have equal and opposing charges, atoms are generally neutral.
Why are element atoms neutral?
Because a proton has a positive charge (+) and an electron has a negative charge (-), element atoms are neutral, with all positive charges cancelling out all negative charges. The number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom varies from one to the next.
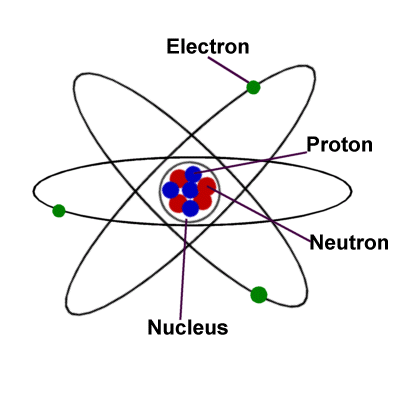
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The nucleus contains the protons and the neutrons. Considering the solar system, it has been observed that the sun is at its centre, and the planets revolve around it. Similarly, in an atom, the nucleus is at the centre, and the electrons revolve around the nucleus. Electron structure.
Which subatomic particle has the same mass as an electron?
Electrons are a sort of negative-charged subatomic particle. Protons and neutrons have about the same mass as electrons, yet they are both significantly more massive (approximately 2,000 times as massive as an electron). A proton’s positive charge is the same magnitude as an electron’s negative charge.
Why is the mass of an electron negligible?
This is because matter behaves differently at the quantum scale. For example, the uncertainty associated ...
What is an electron?
Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated July 24, 2019. An electron is a stable negatively charged component of an atom. Electrons exist outside of and surrounding the atom nucleus. Each electron carries one unit of negative charge (1.602 x 10 -19 coulomb) and has a small mass as compared with that of a neutron or proton.
Where did the term "electron" come from?
The words "electron" and "electricity" trace their origins to the ancient Greeks. The ancient Greek word for amber was elektron.
How much does an electron weigh?
Electrons are much less massive than protons or neutrons. The mass of an electron is 9.10938 x 10 -31 kg. This is about 1/1836 the mass of a proton. In solids, electrons are the primary means of conducting current (since protons are larger, typically bound to a nucleus, and thus more difficult to move).
Why do we have chemical bonds?
Chemical bonds are the result of transfers or sharing of electrons between atoms.
What happens when there are more electrons than positive charges?
If there are more electrons than positive charges, a material is said to be negatively charged. If there is an excess of protons, the object is considered to be positively charged. If the number of electrons and protons is balanced, a material is said to be electrically neutral. Electrons can exist free in a vacuum.
Why are electrons considered elementary particles?
Electrons are considered to be a type of elementary particle because they are not made up of smaller components. They are a type of particle belonging to the lepton family and have the smallest mass of any charged lepton or other charged particle. In quantum mechanics, electrons are considered to be identical to each other because no intrinsic ...
What is the symbol for an electron?
A common symbol for an electron is e -. The electron's antiparticle, which carries a positive electric charge, is called a positron or antielectron and is denoted using the symbol β -. When an electron and a positron collide, both particles are annihilated and gamma rays are released.
What Does Electron Configuration Mean?
Electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals; for example, the electron configuration of a neon atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. From electron configuration, an atoms' reactivity and potential for corrosion can be determined.
What is the principle of electron configuration?
The electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, ...
Who proposed the electron configuration theory?
The electron configuration theory was proposed by Uhlig and is an extension of the adsorption theory of passivity. Uhlig noted that a number of transition metals become passive at certain critical compositions when alloyed with a second metal.
What are the physical and chemical properties of elements?
Many of the physical and chemical properties of elements can be correlated to their unique electron configurations. The most widespread application of electron configurations is in the rationalization of chemical properties, in both inorganic and organic chemistry. In effect, electron configurations, along with some simplified form ...
What is the order of electrons in a semiregular process?
Electrons fill in shell and subshell levels in a semiregular process, as indicated by the arrows above. After filling the first shell level (with just an s subshell), electrons move into the second-level s subshell and then into the p subshell before starting on another shell level. Because of its lower energy state, the 4 s orbital fills before the 3 d, and later s orbitals fill similarly (for example, 6 s fills before 4 f ).
What is the quantum number of electrons in Bohr's atomic model?
In the quantum mechanical version of the Bohr atomic model, each of the allowed electron orbits is assigned a quantum number n that runs from 1 (for the orbit closest to the nucleus) to infinity (for orbits very far from the nucleus). All…
How many valence electrons are in the outermost electron shell?
…valence electrons in their outermost electron shell. These seven outermost electrons are in two different kinds of orbitals, designated s (with two electrons) and p (with five). Potentially, a halogen atom could hold one more electron (in a p orbital), which would give the resulting halide ion the same arrangement…
Which shell contains the electrons that are involved in bond formation?
Each shell can contain a characteristic maximum number of electrons. The outermost shell contains the electrons that are involved in bond formation, for they are the least tightly bound to the nucleus and…. Sodium donates one electron to chlorine, forming a sodium ion (Na +) and a chlorine ion (Cl − ).
How many electrons does sodium donate to chlorine?
Sodium donates one electron to chlorine, forming a sodium ion (Na +) and a chlorine ion (Cl − ). Each ion thus attains a closed outer shell of electrons and takes on a spherical shape. In addition to having filled shells and a spherical shape, the ions of an ionic solid…. Read More.
What is a valence electron?
: a single electron or one of two or more electrons in the outer shell of an atom that is responsible for the chemical properties of the atom. Comments on valence electron. What made you want to look up valence electron?
Where are valence electrons located?
Recent Examples on the Web The scientists at Tokyo Tech want to do something similar with valence electrons, which reside on the outer shell of an atom and are responsible for each atom's chemical properties. — David Grossman, Popular Mechanics, 10 Sep. 2019