Full Answer
What are the basic parts of the embryonic plant?
embryo. What is the purpose of each part of a plant? The three main parts are: the roots, the leaves, and the stem. Each part has a set of jobs to do to keep the plant healthy. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. The stem supports the plant above ground, and carries the water and minerals to the ...
What is seed disperal embryo or young plant?
Seed Dispersal is an adaptive mechanism in all seed-bearing plants, participating in the movement or transport of seeds away from their parent plant to ensure the germination and survival of some of the seeds to adult plants. There are many vectors to transport the seed from one place to another. Also, read: Formation and Dispersal of Seeds.
What does the placenta provide with the embryo with?
The placenta is a complex organ consisting of a thick membrane and blood vessels that connect mother to baby via the umbilical cord. For the fetus, the placenta acts as a filter, delivering oxygen, glucose and other nutrients. It blocks out potentially harmful substances and removes carbon dioxide and waste from the baby’s blood.
What is an example of an embryo?
What does embryo mean? The developing young of an egg-laying animal before hatching. ... An example of an embryo is the draft of a series of new laws protecting human ...

What is a embryo on a plant?
A plant embryo is an undeveloped plant inside a seed. An animal embryo is the animal as it develops from the single cell of the zygote until birth.
Where is embryo in plant?
In both gymnosperms and angiosperms, the young plant contained in the seed, begins as a developing egg-cell formed after fertilization (sometimes without fertilization in a process called apomixis) and becomes a plant embryo. This embryonic condition also occurs in the buds that form on stems.
What is embryo of a seed?
The embryo is the fertilised ovule, an immature plant from which a new plant will grow under proper conditions. The embryo has one cotyledon or seed leaf in monocotyledons, two cotyledons in almost all dicotyledons and two or more in gymnosperms.
What is embryo short answer?
embryo, the early developmental stage of an animal while it is in the egg or within the uterus of the mother. In humans the term is applied to the unborn child until the end of the seventh week following conception; from the eighth week the unborn child is called a fetus.
What is embryo and its function?
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell.
How an embryo is formed?
From Egg to Embryo First, the zygote becomes a solid ball of cells. Then it becomes a hollow ball of cells called a blastocyst. Inside the uterus, the blastocyst implants in the wall of the uterus, where it develops into an embryo attached to a placenta and surrounded by fluid-filled membranes.
Are embryo and seed same?
An embryo is part of the seed which stores the food for the sustenance of the seed.
What is difference between embryo and a seed?
The embryo is a part of the seed from which a new plant develops....Complete answer:EmbryoSeedIt is the part of the seed that gives rise to the mature plantIt is the mature ovule formed after fertilization3 more rows
Is embryo a baby plant?
Seeds have a seed coat which protects them while they grow and develop, usually underground. Inside the seed there are is an embryo (the baby plant) and cotyledons. When the seed begins to grow, one part of the embryo becomes the plant while the other part becomes the root of the plant.
What is an embryo in plants Class 7?
Embryo is that part of a seed which develops into a new plant. An embryo is a kind of baby plant in dormant state.
What is zygote and embryo in plants?
In flowering plants, haploid gametes - an egg cell and a sperm cell fuse to form the first diploid cell - the zygote. The zygote is the progenitor stem cell that gives rise to all the embryonic and post embryonic tissues and organs.
What is an example of embryo?
The definition of an embryo is an unborn but developing child or animal, or something in the early stages that shows potential for development. An example of an embryo is when you have a viable female human egg that has been fertilized with a man's sperm.
Which part of the seed is the embryo?
The embryo or tiny plant is inside the bean's seed coat. This is the part of the bean that will grow into a big plant when the seed is put in the soil and watered. The cotyledon provides food for the tiny plant.
Which part of the fruit contains the embryo?
ovaryThe ovule becomes the seed; the ovary part of the carpel becomes the fruit. It is the egg, along with one sperm cell, that forms the embryo (A).
Where is the embryo sac?
ovuleThe embryo sac develops within the ovule surrounded by the nucellus, which is in turn surrounded by the integuments. One cell of the nucellus undergoes meiosis to produce four megaspores.
Do plants have embryos at some point?
In addition, embryos contain the meristems that give rise to post-embryonically generated structures. However common, flowering plant embryos are an evolutionary derived state. Flowering plants are part of a much larger group of embryo-bearing plants, aptly termed Embryophyta.
Where is the embryo located in a plant?
The embryo, variously located in the seed, may be very small (as in buttercups) or may fill the seed almost completely (as in roses and plants of the mustard family). It consists of a root part, or radicle, a prospective shoot (plumule or epicotyl), one or…
How does an embryo develop?
The embryo develops and is fed by the nutritive tissue of the female gametophyte. The embryo rapidly enlarges at the expense of the maternal tissue and initiates typical sporophytic organization, consisting at maturity of a single axis with a root apex at one end and a…
What is the term for a multicellular embryo?
In plant: Life histories. …mitotically to form a multicellular embryo (embryogenesis), which is protected by either gametophytic tissues (such as remnants of archegonia in the nonseed land plants) or sporophytic tissues (the seed in the seed plants). An embryo, which is actually an immature sporophyte, is universally found among ...
What are the two major parts of an embryo?
Following fertilization, the embryo is on its way to becoming a…. …two major parts, endosperm and embryo. Endosperm is a starchy, storage tissue (popcorn is exploded endosperm). The embryo lies between the endosperm and fruit wall with the large scutellum facing the endosperm.
What is the axis of an embryo?
The embryo consists of a bipolar axis that bears one or two cotyledons, or seed leaves; in most dicots the cotyledons contain…. Read More. In angiosperm: Fertilization and embryogenesis. …to form a multicellular, undifferentiated embryo.
What is angiosperm in biology?
angiosperms. In angiosperm: Vegetative structures. …cell division to form an embryo—a simple multicellular structure of undifferentiated cells (i.e., those that have not developed into cells of a specific type)—and eventually a mature plant.
What is the differentiation of an embryo?
Differentiation of the embryo—e.g., the development…. …egg cell, which becomes an embryo, and the other joins with two polar nuclei to form the endosperm. (Normally many pollen grains fall on a stigma; they all may germinate, but only one pollen tube enters any one ovule.)
What is the embryo?
An embryo refers to the early developmental stage of eukaryotic organisms following the fertilization of an egg (derived from a female) by sperm (derived from a male) as a method of sexual reproduction. In animals, the initial diploid cell that results from the fusion of the egg and the sperm contains half ...
How does embryogenesis occur in plants?
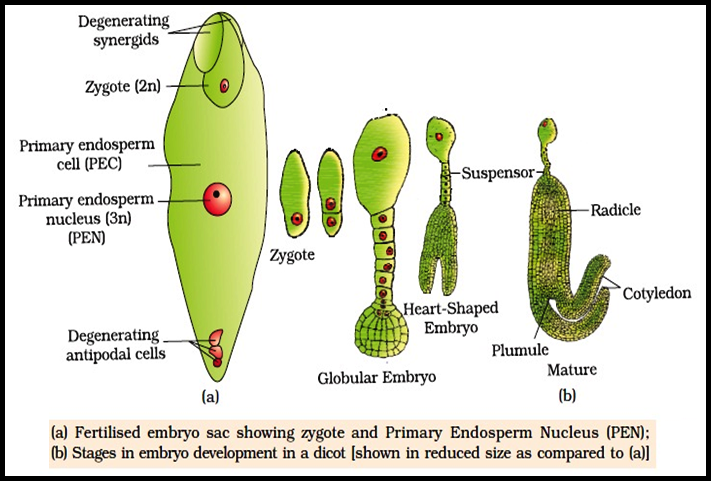
Similar to animals, plant embryogenesis occurs as the result of sexual reproduction via the fertilization of the ovule via pollination. The resulting diploid zygote is accompanied by an endosperm, which together form the seed (shown below). The endosperm consists of dense nutrients which will supply the growing embryo. After undergoing asymmetrical cell division, a small apical cell, which forms the embryo, and a larger basal cell which supplies nutrients to the embryo via the endosperm are formed. At the eight-cell stage, the embryo begins to flatten, forming the axis of the structures which will eventually form the shoot meristem, cotyledons, hypocotyl, roots, and root meristem. In plants, the embryonic stage ends with germination, when the plant begins to grow out of the seed. At this stage, the plant is termed a plantling. The specific processes involved in plant embryogenesis differ depending on the species of plant.
What is the embryonic stage of development?
In humans, the embryonic stage of development is defined as the period from week 5 to week 11 of gestation. After this stage, the embryo transitions into a fetus. In plants, the process of embryogenesis extends from the time ...
How do zygote cells divide?
Following fertilization, the zygote begins to divide by mitosis in a manner in which there is a lack of growth, and the resulting cluster of cells remains the same size as the initial fertilized cell (shown below). After four rounds of cleavage, the 16-celled cluster is termed the morula. The cells comprising the morula eventually form an outer layer called the trophoblast and an inner cluster of cells, termed the inner cell mass, which will form the embryo. Fluid will then fill the space between the trophoblast and the inner cells, with the two cell formations connecting at one pole, termed the embryonic pole.
What is the outer layer of the morula?
After four rounds of cleavage, the 16-celled cluster is termed the morula. The cells comprising the morula eventually form an outer layer called the trophoblast and an inner cluster of cells, termed the inner cell mass, which will form the embryo.
Which layer of the embryo is replaced by a new cell layer?
The first cells which move inward displace the outer layer of cells and are replaced by a new cell layer termed the definitive endoderm. Inside the embryo, the cells that were internalized join and form the definitive ectoderm. The group of cells residing between the definitive ectoderm and endoderm form the definitive mesoderm.
Which part of the embryo is the primitive streak?
D is correct. The primitive streak forms from the cranial end of the embryo and will dictate the division of the caudal, cranial, left, and right sides of the embryo. The primitive streak is also important for the process of gastrulation, providing a site of invagination. 4.

The Fate of The Plant Embryo’S Suspensor: Balancing Life and Death
Embryo
- This definition explains the meaning of Embryo and why it matters. of the seed that grows right into a plant. Following the proper conditions for germination (e. g., light, moisture, temperature, oxygen) are met the small plant embryo germinates and sprouts right into a mature seedling. In botany, an embryo is really a fundamental element that offe...
Plant Embryonic Development
- Plant embryonic development, also plant embryogenesis is a process that occurs after the fertilization of an ovule to produce a fully developed plant embryo. This is a pertinent stage in the plant life cycle that is followed by dormancy and germination. The zygote produced after fertilization must undergo various cellular divisions and differentiations to become a mature em…
Plant Reproduction
- Scientists divide plants into two main groups depending on whether they reproduce by seeds or spores. 1. NOTIFICATIONS 2. Angiosperms – seed plants with flowers 3. Gymnosperms – seed plants with cones