
What should I do before an ERCP?
PREPARATION
- Stop eating solid foods at midnight.
- Clear liquids are okay to drink (examples: water, Gatorade, clear broth, black coffee and apple juice).
- Do not drink red liquids or alcoholic beverages.
- You may have nothing by mouth (no water, gum, mints, ice cubes, etc.) at least 4 hours before your exam.
How long does an ERCP procedure take?
ERCP, also known as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, is a procedure used to diagnose and treat biliary system obstructions. The exact scope of the procedure depends on one’s goals, but it usually takes between 30 minutes and several hours to perform.
Is ERCP necessary before an operation?
Your doctor might do ERCP before or after gallbladder surgery in specific situations. For example, they can find and remove gallstones from the bile duct and sometimes from the pancreas. ERCP can also help find cancer or non-cancerous lesions.
What are the risks of ERCP?
What are the risks? ERCP is generally safe but complications can sometimes occur. Minor complications. Mild discomfort in the abdomen and a sore throat, which may last up to a few days. Loose teeth, crowns and bridgework can be dislodged, but this is rare. Mild inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
What is ERCP?
Why do doctors use ERCP?
How do I prepare for ERCP?
What should I expect after ERCP?
What is the camera on an endoscope?
Why do you need sedatives during ERCP?
How many percent of ERCP procedures are complications?
See 4 more
About this website
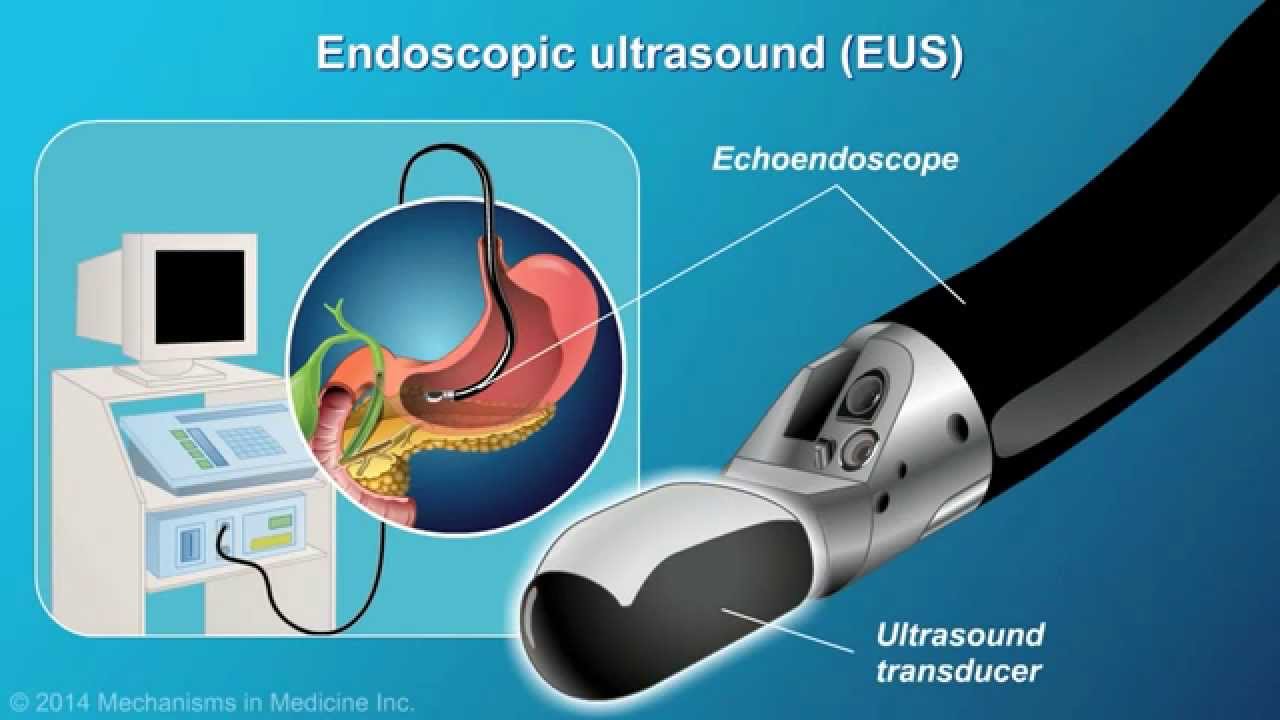
What happens during an ERCP procedure?
During an ERCP, the doctor uses a special narrow, flexible tube (endoscope) that has a video camera. While the child is asleep, the tube is placed through the child's mouth into the upper digestive system. Contrast dye with X-rays allow the doctor to see stones, abnormal narrowing or blockages in the ducts.
Is ERCP a major surgery?
An ERCP is a minimally invasive interventional procedure that is part of the diagnostic and treatment plan for a number of gastrointestinal conditions. Your ERCP will require that you dedicate about a day to the procedure and recovery. You may experience substantial relief as a result of this intervention.
How long does an ERCP procedure take?
The length of the examination varies between 30 and 90 minutes (but is usually less than an hour). After ERCP, you will be monitored while the sedative medications wear off.
What is the purpose of a ERCP?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a procedure that combines upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and x-rays to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Is ERCP a high risk procedure?
Because ERCP is a high-risk procedure, the indication for ERCP, especially in cases of asymptomatic CBDS, should be determined after careful consideration of the risks and benefits of the treatment. However, no reports are available on the risk of ERCP-related complications focusing on asymptomatic CBDS.
Are you awake for ERCP?
ERCP is usually an outpatient procedure, which means you go home the same day. The procedure can take one to two hours. You'll receive IV anesthesia (medicine to calm you). You'll be awake for the procedure, but you probably won't remember any of it.
Is ERCP better than surgery?
Authors' conclusions. Open bile duct surgery seems superior to ERCP in achieving common bile duct stone clearance based on the evidence available from the early endoscopy era. There is no significant difference in the mortality and morbidity between laparoscopic bile duct clearance and the endoscopic options.
What are the side effects of a ERCP?
However, ERCP side effects pose a risk to the patient. ERCP side effects can be life-threatening, such as organ perforation or infection....ERCP Side EffectsSevere, worsening abdominal pain.A distended, firm abdomen.Fever or chills.Vomiting, especially vomiting blood.Difficulty swallowing or breathing.Severe sore throat.
How do you prepare a patient for ERCP?
You may have diet and/or medication restrictions the week before the ERCP test. ... You will not be allowed any heavy meal for at least 8 hours before the procedure, light meals or opaque liquids for 6 hours before, or clear liquids for at least 2 hours before.Plan to take the day off from work.More items...
Does ERCP require stent?
Both plastic and metal stents tend to clog up after several months and you may require another ERCP to place a new stent. Metal stents are permanent while plastic stents are easily removed at a repeat procedure. Your doctor will choose the best type of stent for your problem.
What is the most common complication of ERCP?
The most common post-ERCP complication is acute pancreatitis, followed by gastrointestinal bleeding, viscous perforation, and biliary tract infections.
What can you not do after an ERCP?
Common ERCP Diet Advice Juices, wine, coffee and other concentrated beverages are strictly off limits. Clear Liquid Diets may also be recommended by your physician after surgery for 24 hours in order to relieve digestive system.
How long after ERCP can you eat?
Since the pancreas plays a role in digestion, eating after an ERCP may contribute to complications such as pancreatitis. The recommendation time for a clear liquid diet varies. Some physicians recommend a clear liquid diet for 24 hours after the procedure. However, some physicians recommend it for 12 hours or less.
How do you prepare a patient for ERCP?
You may have diet and/or medication restrictions the week before the ERCP test. ... You will not be allowed any heavy meal for at least 8 hours before the procedure, light meals or opaque liquids for 6 hours before, or clear liquids for at least 2 hours before.Plan to take the day off from work.More items...
Does ERCP require anesthesia?
ERCP is an uncomfortable procedure requiring adequate sedation or general anesthesia. The required level of sedation during these procedures is often deep. The patient cooperation is an imperative factor for the success of the procedure especially, to avoid intra-operative complications such as duodenal perforations.
How long after ERCP can pancreatitis develop?
Pancreatitis occurs when a patient experiences elevated levels of enzymes in the pancreas. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy defines pancreatitis after ERCP as a threefold increase in pancreatic enzymes. This increase is present for more than 24 hours after the procedure.
ERCP Test (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatogram): Procedure ...
ERCP (short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is a procedure used to diagnose diseases of the gallbladder, biliary system, pancreas, and liver.The test looks "upstream" where ...
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or ERCP, is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas.
ERCP: Gallstones, Pancreatic Cancer, Pancreatitis, Treatment
During ERCP, doctors use an endoscope and X-rays to view injectable dye as it travels through pancreatic and bile ducts. ERCP helps providers diagnose and treat gallstones, inflamed gallbladders, bile duct blockages, pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and other conditions.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) - SGNA
2 Indications 1. Jaundice of undetermined etiology. 2. Biliary obstruction, extrinsic or intrinsic (e.g., stones, tumor, stricture, sclerosing cholangitis, papillary ...
What is ERCP?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a procedure that combines upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and x-rays to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Why do doctors use ERCP?
Doctors use ERCP to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts. Doctors also use ERCP to diagnose problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts if they expect to treat problems during the procedure. For diagnosis alone, doctors may use noninvasive tests—tests that do not physically enter the body—instead of ERCP.
How do I prepare for ERCP?
To prepare for ERCP, talk with your doctor, arrange for a ride home, and follow your doctor’s instructions.
What should I expect after ERCP?
In some cases, you may need to stay overnight in the hospital after ERCP.
What is the camera on an endoscope?
A small camera mounted on the endoscope will send a video image to a monitor. The endoscope pumps air into your stomach and duodenum, making them easier to see. During ERCP, the doctor. locates the opening where the bile and pancreatic ducts empty into the duodenum.
Why do you need sedatives during ERCP?
You typically receive sedatives during ERCP to help you relax and stay comfortable. Tell your doctor if you are, or may be, pregnant. If you are pregnant and need ERCP to treat a problem, the doctor performing the procedure may make changes to protect the fetus from x-rays.
How many percent of ERCP procedures are complications?
Research has found that these complications occur in about 5 to 10 percent of ERCP procedures. 2 People with complications often need treatment at a hospital.
What is ERCP?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or ERCP, is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. It combines X-ray and the use of an endoscope—a long, flexible, lighted tube. Your healthcare provider guides the scope through your mouth and throat, then down the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). Your healthcare provider can view the inside of these organs and check for problems. Next, he or she will pass a tube through the scope and inject a dye. This highlights the organs on X-ray.
What happens during ERCP?
An ERCP may be done on an outpatient basis or as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary based on your condition and your healthcare provider's practices.
What are the risks of ERCP?
You may want to ask your healthcare provider about the amount of radiation used during the test. Also ask about the risks as they apply to you.
Why do you give a rectal suppository after ERCP?
Many times, a rectal suppository of a certain medicine is given after the ERCP to decrease the risk of pancreatitis.
Is it normal to take a rectal suppository after ERCP?
This is normal. Many times, a rectal suppository of a certain medicine is given after the ERCP to decrease the risk of pancreatitis. You may go back to your usual diet and activities after the procedure, unless your healthcare provider tells you otherwise. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following:
Is ERCP necessary for pancreatitis?
Keep in mind, though, that ERCP is often performed to help relieve the disease in certain types of pancreatitis. Infection. Bleeding.
What is ERCP in medical terms?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography ( ERCP) is a diagnostic procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas.
Why is an ERCP done?
An individual may need endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to determine the cause of unexplained and recurrent abdominal pain or yellowing of the skin and eyes ( jaundice ). It also helps in the diagnosis of the following conditions:
Why is endoscopy called conscious sedation?
This is called “conscious sedation” because the patient is awake, but the body is relaxed and pain is numbed. In some more complicated cases, the patient may be sedated more heavily or given anesthesia (put to sleep) for the ERCP procedure.
How long does it take to get an endoscope removed?
After the X-rays and any other procedures are done, the endoscope will be withdrawn. The length of the examination varies between 30 and 90 minutes ( usually about an hour).
Where is the oxygen tube in the nose during ERCP?
They will be positioned on their left side or, more often, on their belly on the X-ray table.
Can ERCP be done outpatient?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be done on an outpatient basis or as part of hospital stay. Procedures may vary based on patient’s condition. Generally, during an ERCP procedure: An intravenous (IV) line will be put in on the patient’s arm or hand for anesthesia.
How does an ERCP work?
A small camera mounted on the endoscope will send a video image to a monitor. The endoscope pumps air into your stomach and duodenum , making them easier to see. The ERCP instrument does not interfere with breathing, but you might feel a bloating sensation because of the air introduced through the instrument.
Why do doctors perform ERCP?
Doctors perform ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) when your bile or pancreatic ducts have become narrowed or blocked because of: gallstones that form in your gallbladder and become stuck in your common bile duct. trauma or surgical complications in your bile or pancreatic ducts.
How do I prepare for ERCP?
To prepare for ERCP, talk with your doctor, arrange for a ride home, and follow your doctor’s instructions.
What is ERCP in GI?
ERCP is an abbreviation for a medical procedure called Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography that combines upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and x-rays to to study the bile ducts, pancreatic duct and gallbladder and to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts. ERCP is an advanced endoscopic procedure where a long, thin flexible tube with a camera at the end called the endoscope is passed through your mouth, esophagus and stomach into the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) down to where the bile and pancreatic duct opens into the small intestine. After your doctor sees the common opening to the ducts from the liver and pancreas, called the major duodenal papilla, your doctor will pass a narrow plastic tube called a catheter through the endoscope and into the ducts. Your doctor will inject a contrast material (dye) into the pancreatic or biliary ducts and will take X-rays.
What is the tube that slides through the endoscope called?
slides a thin, flexible tube called a catheter through the endoscope and into the ducts
Where to take tissue samples for ERCP?
One procedure that is commonly performed through the ERCP scope is to take samples of tissue from the papilla or from the bile or pancreatic ducts. There are several different sampling techniques although the most common is to brush the area with subsequent examination of the cells obtained.
Where is the ERCP tube?
ERCP is an advanced endoscopic procedure where a long, thin flexible tube with a camera at the end called the endoscope is passed through your mouth, esophagus and stomach into the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) down to where the bile and pancreati c duct opens into the small intestine. After your doctor sees the common opening ...
What is ERCP procedure?
ERCP is a relatively low-risk procedure. It helps your healthcare provider determine the cause of certain bile duct and gastrointestinal problems. ERCP can also help treat these problems. Your provider may share findings and treatment options with you on the day of the procedure or after receiving biopsy results.
What is an ERCP?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a test that uses a combination of X-rays and an endoscope. An endoscope is a lighted flexible tube with an attached camera.
What is ERCP used for?
Doctors use ERCP to diagnose and treat problems that affect the: Bile ducts , including cancer, stones and strictures. Gallbladder, including gallstones and cholecystitis (inflamed gallbladder). Pancreas, including pancreatitis (inflamed, swollen pancreas), pancreatic cancer and pancreatic cysts and pseudocysts.
What is ERCP in medical terms?
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) During ERCP, doctors use an endoscope and X-rays to view injectable dye as it travels through pancreatic and bile ducts. ERCP helps providers diagnose and treat gallstones, inflamed gallbladders, bile duct blockages, pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and other conditions.
Why do you need ERCP?
It helps your healthcare provider determine the cause of certain bile duct and gastrointestinal problems. ERCP can also help treat these problems. Your provider may share findings and treatment options with you on the day of the procedure or after receiving biopsy results.
How long does it take to get an ERCP?
ERCP is usually an outpatient procedure, which means you go home the same day. The procedure can take one to two hours. You’ll receive IV anesthesia (medicine to calm you). You’ll be awake for the procedure, but you probably won’t remember any of it. Someone will need to drive you home afterward.
What to expect after ERCP?
You might need to eat soft foods for a day or two until the soreness subsides. After ERCP, you may experience some bloating (a swollen feeling from the pumped-in air) and nausea (an anesthesia side effect).
What Happens During an ERCP Procedure?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, commonly referred to as ERCP, is a highly sensitive endoscopy procedure used to treat symptoms related to a patient’s bile liver, gallbladder and pancreas— such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). The test involves gaining access ducts, which are channels inside organs that allow bodily fluids to travel throughout the body—primarily biliary ducts that channel fluid through the liver and pancreatic ducts that channel fluid through the pancreas.
How does an ERCP work?
During an ERCP procedure, the patient is kept under deep sedation, as the test lasts a longer time than other endoscopic tests and is quite sensitive. A long and flexible tubular device called an endoscope is passed through the patient’s mouth, down the esophagus and through the stomach until it reaches a segment of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract called the duodenum, which is the uppermost part of the patient’s small intestine. When the endoscope reaches this area, another plastic device called a catheter is guided through the endoscope and passed through a tiny duct between the liver and pancreas known as the papilla. The catheter is designed to inject a contrast solution into either the pancreas or the liver, which will make those ducts show up very brightly on x-rays and give doctors a clear view of how those organs are functioning. If the patient has pancreatitis, for instance, your doctor will be able to see it on the final x-ray image produced.
How long do you have to fast before an ERCP?
Fasting is required for at least 6 hours before undergoing ERCP. The goal is to empty the patient’s stomach so that food content does not obstruct the endoscope’s path or cause distortion during the x-ray. We with any medical procedure, also remember to inform your gastroenterologist (GI doctor) of any allergies you have (especially to sedation medication or contrast material used in prior imaging tests), any medications you are currently taking or any conditions or diseases you may have. Knowing this information will help you and your doctor to minimize risks of the procedure and to decide whether ERCP is the best endoscopy procedure for you.
Can pancreatitis develop after ERCP?
Complications after a highly trained professional performs ERCP are pretty uncommon. In some cases, pancreatitis may develop after the ERCP procedure (about a 1% risk), in which case further treatment will need to be implemented.
What is ERCP procedure?
Facts you should know about ERCP. ERCP is a diagnostic procedure designed to examine diseases of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas. ERCP is usually best performed under general anesthesia. It may be done using IV sedation. There is a low incidence of complications.
What are the reasons for ERCP?
The liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, pancreas and the papilla of Vater can be involved in numerous diseases, causing myriad of symptoms. ERCP is used in diagnosing and treating the following conditions:
What can be expected during and after the ERCP procedure?
If done with IV sedation, the patient will be given medications through a vein to cause relaxation and sleepiness. The patient will be given some local anesthetic to decrease the gag reflex. Some physicians do not use local anesthetic and prefer to give the patients more intravenous medications for sedation. This also applies to those patients who have a history of allergy to Xylocaine or cannot tolerate the bitter taste of the local anesthetic and the numbness sensation in the throat. While the patient is lying on the left side on the X-ray table, the intravenous medication is given, and then the instrument is inserted gently through the mouth into the duodenum. The instrument advances through the food pipe and not the air pipe. It does not interfere with the breathing and gagging is usually prevented or decreased by the medication. If using general anesthesia, then the above procedure does not apply.
What are the side effects and risks of the ERCP procedure?
The success rate in performing this procedure varies from 70% to 95% depending on the experience of the physician. Complications can occur in approximately one to five percent depending on the skill of the physician and the underlying disorder. The most common complication is pancreatitis which is due to irritation of the pancreas from the dye used to take pictures and can occur even with very experienced physicians. This "injection" pancreatitis usually is treated in the hospital for one to two days. Another possible complication is infection. Other serious risks including perforation of the intestine, drug reactions, bleeding, depressed breathing. Irregular heart beat or heart attack are extremely rare and is mainly due to the sedation. In case of complications, patients usually need to be hospitalized, but surgery rarely is required.
What are the symptoms of ERCP?
The liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, pancreas and the papilla of Vater can be involved in numerous diseases, causing myriad of symptoms. ERCP is used in diagnosing and treating the following conditions: 1 Blockage of the bile duct by gallstones, cancer, strictures (scarring) or compression from adjacent organs or tumors 2 Jaundice (yellow coloring of the skin) due to obstruction of the bile duct, also causing darkening of the urine and light colored stool. 3 Persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain which cannot be diagnosed by other tests such as MRCP/MRI, CT 4 Confirming the diagnosis of cancer of the pancreas or the bile duct, so that surgery or other treatment can be tailored to the disease 5 When there is suspicion that the Sphincter of Oddi within the Papilla of Vater, that controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice, is not working normally (Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction)
How does a duodenoscope work?
The modern duodenoscope uses a thin fiber -optic bundle to transmit light to the tip of the endoscope, and a thin wire with a chip also at the tip of the endoscope to transmit digital video images to a TV screen.
How long does ERCP surgery last?
The procedure can last anywhere from fifteen minutes to one hour, depending on the skill of the physician, what needs to be accomplished, and the anatomy or abnormalities in that area. ERCP also may be performed under light, general anesthesia.
What Is ERCP?
An ERCP is a specialized procedure that combines endoscopy and imaging technology to visualize the bile ducts and, in some cases, allow for therapeutic intervention.
What is ERCP in medical terms?
An ERCP is a specialized procedure that combines endoscopy and imaging technology to visualize the bile ducts and, in some cases, allow for therapeutic intervention .
What is ERCP in a biliary system?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an invasive procedure used for the diagnosis and treatment of obstruction in the biliary system . With ERCP, a camera-equipped endoscope is placed into the mouth and advanced for visualization of the bile ducts, gallbladder, pancreas, or liver. Often, this procedure is used for obtaining a biopsy, repairing a lesion, or clearing a blockage in these structures.
Why postpone ERCP?
You might need to postpone your ERCP if you have an infection that could be exacerbated by this procedure. 2
How long does it take to recover from an ERCP?
Your ERCP will require that you dedicate about a day to the procedure and recovery. You may experience substantial relief as a result of this intervention.
Where is the ERCP located?
You will have your ERCP in a procedural suite that is used for gastrointestinal procedures. This may be located in a hospital or an outpatient surgical center.
How long do you have to abstain from food before ERCP?
You will need to abstain from food or drink for eight hours before having your ERCP.
Liver Health: 14 Best and Worst Foods for Your Liver
Get some simple diet tips to keep your liver healthy, including the best veggies to keep disease away and some snacks you'll want...
Liver Quiz
Do you know the symptoms of liver disease? What is hepatitis? Take this quiz to learn about your liver and how to keep it healthy.
Picture of Liver
Front View of the Liver. The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. See a picture of the Liver...
What is ERCP?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a procedure that combines upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and x-rays to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Why do doctors use ERCP?
Doctors use ERCP to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts. Doctors also use ERCP to diagnose problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts if they expect to treat problems during the procedure. For diagnosis alone, doctors may use noninvasive tests—tests that do not physically enter the body—instead of ERCP.
How do I prepare for ERCP?
To prepare for ERCP, talk with your doctor, arrange for a ride home, and follow your doctor’s instructions.
What should I expect after ERCP?
In some cases, you may need to stay overnight in the hospital after ERCP.
What is the camera on an endoscope?
A small camera mounted on the endoscope will send a video image to a monitor. The endoscope pumps air into your stomach and duodenum, making them easier to see. During ERCP, the doctor. locates the opening where the bile and pancreatic ducts empty into the duodenum.
Why do you need sedatives during ERCP?
You typically receive sedatives during ERCP to help you relax and stay comfortable. Tell your doctor if you are, or may be, pregnant. If you are pregnant and need ERCP to treat a problem, the doctor performing the procedure may make changes to protect the fetus from x-rays.
How many percent of ERCP procedures are complications?
Research has found that these complications occur in about 5 to 10 percent of ERCP procedures. 2 People with complications often need treatment at a hospital.
