The majority of viruses can be categorized as having helical or icosahedral structure. A few viruses, however, have a complex architecture that does not strictly conform to a simple helical or icosahedral shape. Poxviruses, geminiviruses, and many bacteriophages are examples of viruses with complex structure (Fig. 2.10). Poxviruses, including the viruses that cause smallpox or cowpox, are large oval or brick-shaped particles 200–400 nm long.
What are some examples of helical viruses?
In contrast, all helical animal viruses are enveloped. These include well-known viruses such as influenza virus, measles virus, mumps virus, rabies virus, and Ebola virus (Fig. 2.5). Open in a separate window
What are enveloped and complex viruses?
Enveloped and Complex Viruses. Likewise, some viruses like to give themselves an additional layer as well - although this additional layer is not so much for protection but more for ease of infection. These viruses are called enveloped and are viruses that have a lipid bilayer around their protein capsid.
What is an example of a virus in nature?
A good example is a form of herpes virus, found in mice. This virus, while it is infecting a mouse, provides the mouse with a good defense against the bacteria which carry the plague. While the mechanism is not clear, the virus somehow prevents the bacteria from taking hold in the mouse’s system.
What are the different classes of viruses?
• class V: negative-sense ssRNA viruses • class VI: RNA viruses that reverse transcribe • class VII: DNA viruses that reverse transcribe There are a variety of ways by which viruses could be classified, however, including virion size, capsid structure, type of nucleic acid, physical properties, host species, or disease caused.
Which virus would be a complex virus?
Complex Viruses Many phage viruses are complex-shaped; they have an icosahedral head bound to a helical tail. The tail may have a base plate with protein tail fibers.
What shape is a complex virus?
Complex. These virus structures have a combination of icosahedral and helical shape and may have a complex outer wall or head-tail morphology. The head-tail morphology structure is unique to viruses that only infect bacteria and are known as bacteriophages.
Is a virus cell simple or complex?
Because viruses are so small, they have a simple cell structure. They are much simpler than animal or bacterial cells.
What viruses are complex symmetry?
Examples of complex symmetry viruses are bacteriophages, poxviruses, etc.
Is bacteriophage a complex virus?
Characteristics of bacteriophages Phages are classified in a number of virus families; some examples include Inoviridae, Microviridae, Rudiviridae, and Tectiviridae. Like all viruses, phages are simple organisms that consist of a core of genetic material (nucleic acid) surrounded by a protein capsid.
What type of virus is Ebola?
About Ebola Virus Disease Ebola is caused by infection with a virus of the family Filoviridae , genus Ebolavirus.
What are the 3 types of viruses?
Based on their host, viruses can be classified into three types, namely, animal viruses, plant viruses, and bacteriophages.
What type of virus is COVID-19?
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment.
What is an acellular virus?
Viruses are acellular, parasitic entities that are not classified within any domain because they are not considered alive. They have no plasma membrane, internal organelles, or metabolic processes, and they do not divide.
What is the difference between simple and complex viruses?
In simple viruses, the capsid consists of a number of copies of the same, or a few different proteins organized into a symmetric oligomer. Structurally complex viruses present a larger variety of components in their capsids than simple viruses.
Which of the following as a complex symmetry?
Which of the following has a complex symmetry? Sol: (a) T4 phage.
Is Ebola a spherical virus?
For example, the Ebola virus has diameter of about 80 nm, whereas its length can reach 1–2 μm. In the axisymmetric model, the virus particle is assumed to be spherical, and its region of contact with the membrane is a spherical cap.
What is a complex shape of a virus?
Finally, some viruses have a complex shape. This is when a virus has a combination of shapes arranged in a symmetrical or asymmetrical fashion. Learning Outcomes. After viewing this lesson, you will be able to: Describe the different shapes of viruses. Define capsid, capsomere and protomer.
What is the shape of a virus called?
A special type of icosahedral shape, called a prolate, is a variant of the icosahedral viral shape and is found in bacteriophages. A lot of viruses are either helical or icosahedral in shape. Many animal viruses, which include those that infect humans, are icosahedral in shape.
What is a helical virus?
A helical virus is a virus that has a capsid shaped in a filamentous or rod-shaped structure that has a central cavity that encloses its nucleic acid. An icosahedral virus is a virus consisting of identical subunits that make up equilateral triangles that are in turn arranged in a symmetrical fashion.
What is a virus enveloped?
These viruses are called enveloped and are viruses that have a lipid bilayer around their protein capsid. This lipid bilayer is derived from the host cell's outer membrane or an internal membrane, like the endoplasmic reticulum or the nuclear membrane.
What is the protective protein shell of a virus called?
The protective protein shell of each virus is called a 'capsid.'. This capsid is made up of protein subunits called 'capsomeres,' which are in turn made of subunits called 'protomers.'. With that in mind, one type of car driving around in the viral world is known as a helical virus.
Do viruses have different shapes?
In the end, they are all a type of vehicle regardless of their shape, size and color. Likewise, viruses have many different shapes as well, and some of their shapes are unique to certain viruses and the things they infect. These shapes aren't just for looks. Like certain types of automobiles, they actually confer a function.
What are the diseases that humans can get from animals?
Animal Viruses That Cause Human Diseases. Zoonotic diseases are infectious diseases in animals that can cause human diseases when spread to humans. You may have heard of these diseases that have transmitted to humans in the past: Virus: Influenza type A (transmitted from pigs) Disease: Swine flu.
Can a virus be spread directly or indirectly?
Viruses That Cause Infectious Diseases in Humans. An infectious disease can be spread directly or indirectly from person to person. Most people are more familiar with the disease name rather than the virus name.
What is a good example of a virus?
A good example is a form of herpes virus, found in mice. This virus, while it is infecting a mouse, provides the mouse with a good defense against the bacteria which carry the plague. While the mechanism is not clear, the virus somehow prevents the bacteria from taking hold in the mouse’s system.
How do scientists classify viruses?
Scientists classify viruses based on how they replicate their genome. Some virus genomes are made of RNA, others are made of DNA. Some viruses use a single strand, others use a double strand. The complexities involved in replicating and packaging these different molecules places viruses into seven different categories.
What does a virus look like?
Each virus looks like a little bent worm. However, these are not cells. Inside of the protein coat is a carefully folded RNA molecule, which contains the information necessary to replicate the protein coat, the RNA molecule, and the components necessary to hijack a cell’s natural processes to complete these tasks.
How many viruses can be released from a single cell?
When the cell is completely full, it ruptures and releases the virus particles into the blood or environment. Up to 10,000 virus particles can be release from a single cell. The virus genomes in Class V are also single-stranded RNA. However, they run in the opposite direction from normal mRNA.
How does a virus spread from a plant to a plant?
In some plant virus species, the virus is passed from cell to cell within the plant. When seeds are created within the plant, the virus spreads to the seeds. In this way the virus can live within cells its entire existence, and never need a protein coat to protect it in the environment.
What is the chain of nucleic acids that a virus uses to reproduce?
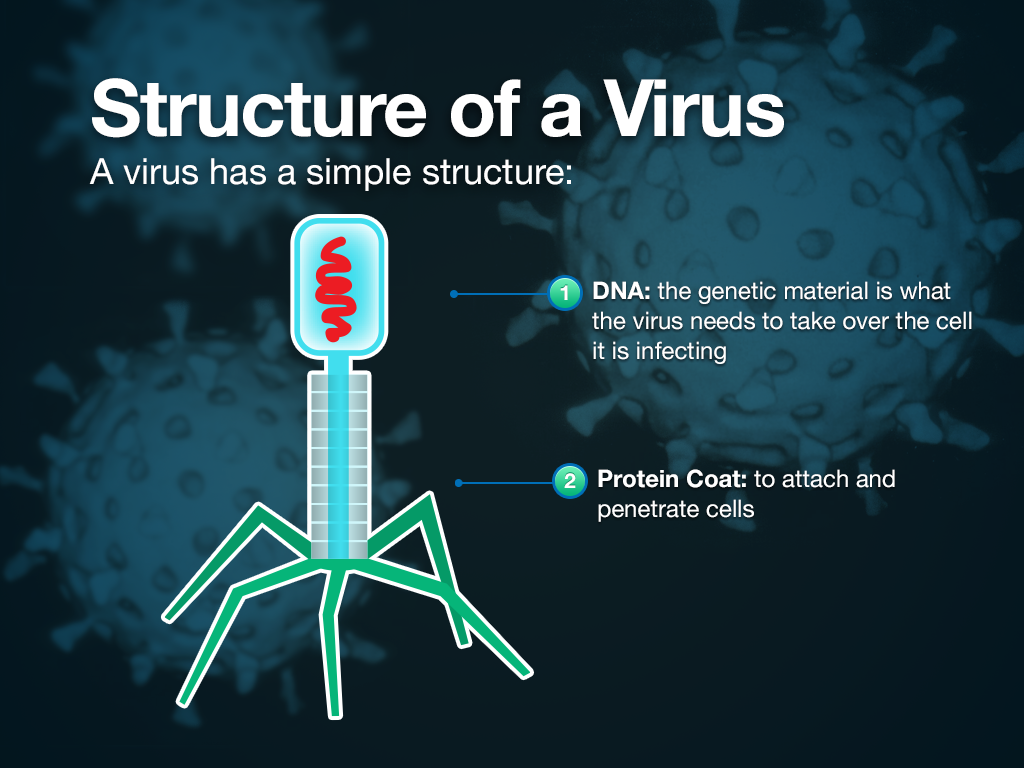
A virus is a chain of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) which lives in a host cell, uses parts of the cellular machinery to reproduce, and releases the replicated nucleic acid chains to infect more cells. A virus is often housed in a protein coat or protein envelope, a protective covering which allows the virus to survive between hosts.
What is the tail fiber of a virus?
The tail fibers grasp the bacterial cell, pulling the base plate up to the cell wall or membrane. The sheath and collar compress, puncture the cell, and deposit the DNA into the bacterial cell. Some virus molecules have no protein coat whatsoever, or have never been identified making on.
What is the structure of a virus?
Viruses vary in their structure. A virus particle consists of DNA or RNA within a protective protein coat called a capsid. The shape of the capsid may vary from one type of virus to another. The capsid is made from the proteins that are encoded by viral genes within their genome.
What is the envelope of a virus?
Some viruses have an envelope of phospholipids and proteins. The envelope is made from portions of the host’s cell membrane. It surrounds the capsid and helps protect the virus from the host’s immune system. The envelope may also have receptor molecules that can bind with host cells.
What type of virus has a helical tail?
Many phage viruses are complex-shaped; they have an icosahedral head bound to a helical tail. The tail may have a base plate with protein tail fibers. Some complex viruses do not have tail fibers. This “moon lander”-shaped complex virus infects Escherichia coli bacteria.
What is the capid of a cytomegalovirus?
Diagram of a Cytomegalovirus. The capsid encloses the genetic material of the virus. The envelope which surrounds the capsid is typically made from portions of the host cell membranes (phospholipids and proteins). Not all viruses have a viral envelope.
What is the icosahedron in a virus?
This saves space in the viral genome. Adenovirus, an icosahedral virus. An icosahedron is a three-dimensional shape made up of 20 equilateral triangles. Viral structures are built of repeated identical protein subunits, making the icosahedron the easiest shape to assemble using these subunits.
What is a helical virus?
Helical Viruses. Helical capsids are made up of a single type of protein subunit stacked around a central axis to form a helical structure. The helix may have a hollow center, which makes it look like a hollow tube. This arrangement results in rod-shaped or filamentous virions.
What are the proteins in the envelope?
The proteins in the envelope can include glycoproteins, which act as receptor molecules. These receptor molecules allow host cells to recognize and bind the virions, which may result in easier uptake of the virion into the cell. Most enveloped viruses depend on their envelopes to infect cells.
