
What is meant by domestication of plants?
Plant domestication is the process whereby wild plants have been evolved into crop plants through artificial selection. This usually involves an early hybridization event followed by selective breeding.
What is the importance of domestication of plants and animals?
Domestication of Plants and Animals Opens Relational Pathways In the traditional view, the domestication of plants and animals is a watershed moment for humanity. It's when humans begin to control nature, to tame animals, to domesticate the world around them, and turn it to their ends. In the traditional view, hunters and gatherers are part
Are plants domesticating humans?
The culprits were a handful of plant species, including wheat, rice and potatoes. These plants domesticated Homo sapiens, rather than vice versa. "Think for a moment about the Agricultural Revolution from the viewpoint of wheat. Ten thousand years ago wheat was just a wild grass, one of many, confined to a small range in the Middle East.
What is the domestication of plants and animals?
domestication, the process of hereditary reorganization of wild animals and plants into domestic and cultivated forms according to the interests of people. In its strictest sense, it refers to the initial stage of human mastery of wild animals and plants.

What are some examples of domesticated plants?
Examples of domesticated plants and a region that domesticated them include wheat and barley in the Middle East, the potato in South America, and millet and rice in China. Plants that are grown for consumption are known as crops, while plants used for aesthetic purposes indoors are houseplants.
What is the domestication of plants?
Definition. Plant domestication is the process whereby wild plants have been evolved into crop plants through artificial selection. This usually involves an early hybridization event followed by selective breeding.
What are some examples of domesticated plants and animals?
Domestication ExamplesCows: Cows are herbivores that graze. ... Dogs: Dogs were first domesticated for hunting. ... Chickens: Chickens are herbivores that are domesticated for food. ... Cats: Some cats are domesticated and used as pets while others are feral, or wild. ... Wheat: Wheat has been domesticated for food for many years.More items...•
How many plants are domesticated?
Agricultural history and origins of domestication Although only 14 large mammals have been domesticated throughout agricultural history, it is estimated that over 2,000 plant species have been modified through human cultivation.
What was the earliest domesticated plant?
The discovery dates domesticated figs to a period some 5,000 years earlier than previously thought, making the fruit trees the oldest known domesticated crop.
When was the first plant domestication?
The domestication of plants began at least 12,000 years ago with cereals in the Middle East, and the bottle gourd in Asia.
When were plants and animals domesticated?
The first successful domestication of plants, as well as goats, cattle, and other animals—which heralded the onset of the Neolithic Period—occurred sometime before 9500 bce.
What do you mean by domesticated?
Definition of domesticated 1 : adapted over time (as by selective breeding) from a wild or natural state to life in close association with and to the benefit of humans The Incas used one of the first domesticated animals, the llama, to carry goods.—
Why are crops domesticated?
Crop domestication is a special case of plant/animal co-evolution in which plant species have adapted to human control and are propagated in human-manipulated environments to enhance the survival and fitness of Homo sapiens.
Can domesticated plants survive without humans?
Many plants can function properly without humans for their pollination and dispersing of seeds. The plant kingdom does not rely on us for reproduction, no doubt, they can maintain themselves quite well without the human population.
What is the difference between wild and domestic plants?
Domestic plants differ from their wild ancestors because they have been modified by human labor to meet specific human needs. Wild fruits, nuts, and berries were probably the first plant foods of ancient peoples. Later, humans learned to dig up roots and scrape or pound them to a paste for eating.
Why are wild plants as important as domestic plants?
Wild plants are as important as domesticated plants because they also serve important roles in the environment. They are present in great varieties. They are source of food for wild animals in the jungles. So, they constitute important parts of food chain.
What do you mean by domestication?
Domestication is the process of adapting wild plants and animals for human use. Domestic species are raised for food, work, clothing, medicine, and many other uses. Domesticated plants and animals must be raised and cared for by humans. Domesticated species are not wild.
What do you mean by domesticated?
Definition of domesticated 1 : adapted over time (as by selective breeding) from a wild or natural state to life in close association with and to the benefit of humans The Incas used one of the first domesticated animals, the llama, to carry goods.—
What is domestication Class 6 history?
a. Process in which people grow plants and look after animals: The process in which people grow plants and look after animals is known as domestication.
How do plants change during domestication?
Some of these comprise the domestication syndrome phenotypes 5, 9, 86, 87, which in cereals includes reduction in seed dispersal and increased seed retention (non-shattering), increased seed size, changes in shoot branching and stature, loss of seed dormancy, and synchronous germination.
Origins of Domestication
During the Mesolithic Period, the earliest attempts at plant domestication were performed in the Old World.
Domesticated Plants
The sugar beet, for example, was only developed as a sugar-producing agricultural plant in the 19th century, and mint was only developed as an agricultural crop in the 20th century.
Effects of Domestication
Most wild species’ features have been influenced by domestication, which involves three processes: mutation, hybridization, and gem-tic recombination, all of which are influenced by human or natural selection. During domestication, some traits have changed, some have disappeared, and many have evolved.
Significance in Domestication of Plants
The following is a list of possible modifications in plant species as a result of domestication:
Plant Breeding
Plant breeding is the deliberate alteration of plant species to produce desired plant kinds that are more suitable for cultivation, produce higher yields, and are disease resistant.
Summary
Domestication is the process of placing a plant species under human control and gradually modifying it to make it more useful to humans by careful selection, genetic alteration, and handling. Selective breeding is used for domestication.
FAQs on Domestication of Plants
Q.1. What is the domestication of plants? Ans: Domestication is the process of placing a plant species under human control and gradually modifying it to make it more useful to humans by careful selection, genetic alteration, and handling.
What Is a Domesticated Plant?
The traditional definition of a domesticated plant is one that has been changed from its natural state until it is no longer able to grow and reproduce without human intervention. The purpose of plant domestication is to adapt plants to make them optimal for human use/consumption.
What is the process of domestication of plants?
Plant domestication is a slow and tiresome process that is only successful when both parties—humans and plants—benefit from each other through a mutualistic relationship. The result of thousands of years of this symbiosis came to be known as coevolution.
Why did farmers have to learn to tame their tamed plants?
Just as the earliest domesticated crops were groomed to meet human needs, farmers had to learn to meet the needs of their tamed plants so that they would produce high-quality, bountiful, and reliable crops. In a way, they were groomed too.
Why did humans start domesticating plants?
Plant domestication arose as an approach to growing and harvesting more effectively .
How does a farmer select for the properties they desire?
In this way, a farmer can select for the properties they desire by giving special treatment only to the best and most successful plants. Their crop, in turn, starts to take on the desirable properties the farmer selected for and disadvantageous attributes are extinguished over time.
What is coevolution in biology?
Coevolution describes the process of two species evolving to suit each other's needs. Plant domestication through artificial selection is one of the best examples of this. When a human tends a plant with favorable attributes, perhaps because it has the largest and sweetest fruits or most resilient husk, and saves the seeds to replant, they are essentially guaranteeing the continuation of that particular organism.
What are some examples of domesticated plants?
Examples of domesticated plants and a region that domesticated them include wheat and barley in the Middle East, the potato in South America, and millet and rice in China. Plants that are grown for consumption are known as crops, while plants used for aesthetic purposes indoors are houseplants.
What is domestication in biology?
Domestication involves animal adaptations to a human-constructed environment for the benefit of people. Learn more about the definition of domestication, examples of tamed and domesticated animals and why some species aren't fit for domestication. Updated: 10/28/2021
Why isn't my gazelle domesticated?
Certain qualities are needed for domestication to be more likely. In the case of animals, an animal is most likely to be domesticated if it is able to become docile, is non-territorial, willing to breed freely in various circumstances, and grows quickly. Ideally, the animal is not primarily meat-eating, unless this quality can be useful to us, such as dogs hunting other animals or cats taking care of a mice problem.
What is a tamed animal?
Tamed animals are wild animal species that have been captured and conditioned by food and other methods to submit to human control but that are not accustomed as a species to living with humans. Taming involves behavior change in the individual animal, not genetic changes in the species.
What animals are kept on Trevor's farm?
Animals raised for their meat and other products are known as livestock, such as the horses, cows, and goats kept on Trevor's family's farm. By contrast, the domesticated animals that we keep for companionship, such as dogs and cats, are referred to as pets instead.
Why are domesticated animals bred?
Domesticated animals, on the other hand, were also once wild animals, but over time have been bred in order to select traits that make them more useful for human needs and involves genetic, physiological and behavior changes to the species , not just behavior change and training of one particular animal.
Why are dogs a domestic animal?
Dogs, used for hunting and protection in the past, departed from their wolf ancestry by being bred over time by humans to be more docile compared with their genetic origins . Domestication involves genetic, physiological and behavior changes to the species, not just behavior change and training of one particular animal.
What is Domestication?
The domestication definition is the process that is used to adapt wild plants and animals to be fit for human use. These species are raised to be used in industries such food, clothing, and medicine, as well as for work. Sometimes the domestication of animals and the taming of animals are confused, so what does domesticated mean?
Domestication of Plants and Animals
The domestication of plants and animals has a long history worldwide. They are domesticated for various causes including:
How to Domesticate Animals
Choosing the right species is key to domestication. When domesticating animals, there are certain characteristics that are thought to make an animal a good candidate.
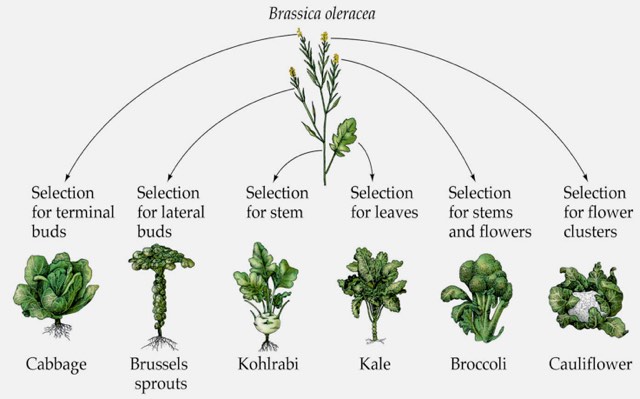
Origins of Domestication
Domesticated Plants
- The sugar beet, for example, was only developed as a sugar-producing agricultural plant in the 19th century, and mint was only developed as an agricultural crop in the 20th century.
- Domestication of vegetatively reproducing plants, such as tubers, is thought to have occurred before that of seed plants, such as cereals, legumes, and other vegetables.
- Some plants were domesticated for the strong fibres found in their stalks, which were used t…
- The sugar beet, for example, was only developed as a sugar-producing agricultural plant in the 19th century, and mint was only developed as an agricultural crop in the 20th century.
- Domestication of vegetatively reproducing plants, such as tubers, is thought to have occurred before that of seed plants, such as cereals, legumes, and other vegetables.
- Some plants were domesticated for the strong fibres found in their stalks, which were used to make fishing nets, among other things.
- One of India’s oldest cultivated plants, Hemp is an example of a multipurpose plant: its seeds yield oil, its stalk yields fibres, and its flowers and leaves yield the narcotic hashish.
Effects of Domestication
- Most wild species’ features have been influenced by domestication, which involves three processes: mutation, hybridization, and gem-tic recombination, all of which are influenced by human or natural selection. During domestication, some traits have changed, some have disappeared, and many have evolved. The following are some of the major characters who hav…
Origin of Crop Plants
- Origin of Rice: 1. Rice (Oryza sativa) was first cultivated in South and Southeast Asia around 300 B.C. 2. The cultivated varieties of rice may have evolved from wild rice species such as O. perennis. 3. Rice spread from India to China, Africa, and America, where it was domesticated into three separate varieties: indica, japonica, and javanica. 4. Many morphological and physiologica…
Significance in Domestication of Plants
- The following is a list of possible modifications in plant species as a result of domestication: 1. Adaptation to a larger range of settings and geographical locations. 2. Flowering and fruiting occur at the same time and are uniform. 3. Seeds are not shattered or scattered. 4. Fruits and seeds have grown in size. 5. Change your habit from a perennial to an annual one. 6. The breeding sy…
Plant Breeding
- Plant breeding is the deliberate alteration of plant species to produce desired plant kinds that are more suitable for cultivation, produce higher yields, and are disease resistant.
- Plant breeding in the old days entailed crossing or hybridising pure lines, then artificial selection to produce plants with desirable features like increased yield, nutrition, and disease resistance.
Summary
- Domestication is the process of placing a plant species under human control and gradually modifying it to make it more useful to humans by careful selection, genetic alteration, and handling. Selective breeding is used for domestication. Individuals with favourable characteristics are chosen to be bred, and these desirable characteristics are passed down to future generation…
FAQs on Domestication of Plants
- Q.1. What is the domestication of plants? Ans:Domestication is the process of placing a plant species under human control and gradually modifying it to make it more useful to humans by careful selection, genetic alteration, and handling. Q.2. How does domestication occur? Ans: Selective breeding is used for domestication. Individuals with favourable characteristics are chos…