What disease is caused by duplication mutation?
Deletions, Duplications, and DiseaseGenetic DiseaseType of RearrangementLocation AffectedCharcot-Marie-Tooth disease type IDuplication17p12Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsiesDeletion17p12Smith-Magenis syndromeDeletion17p11.2Williams-Beuren syndromeDeletion7q11.23
What are the three types of duplication?
Gene duplication can occur by several mechanisms, including whole-genome duplication (WGD) and single gene duplication. Single gene duplication includes four types, tandem (TD), proximal (PD), retrotransposed (RD), DNA-transposed (DD) and dispersed duplication (DSD) (Freeling, 2009; Hahn, 2009; Wang et al., 2012b).
What are 3 ways gene duplication can occur?
Gene duplication is the process by which a region of DNA coding for a gene is copied. Gene duplication can occur as the result of an error in recombination or through a retrotransposition event. Duplicate genes are often immune to the selective pressure under which genes normally exist.
Is Down Syndrome a duplication?
Causes. Most cases of Down syndrome result from trisomy 21 , which means each cell in the body has three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two copies.
What are the causes of duplication in humans?
Duplications arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over that occurs during meiosis between misaligned homologous chromosomes. The chance of it happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes.
What causes gene duplication quizlet?
Name 4 ways that gene duplication can occur? -results from an error in pairing and crossing-over in non-homologous chromosomes in which non-equivalent sites are involved in a recombination event. -Retrotransposition refers to the insertion of DNA sequences mediated by an RNA intermediate.
What is the most common fate of a duplicated gene?
The most common outcome of gene duplication is loss of the duplicated copy from the genome. There are three distinct outcomes if the two copies are retained. Different functions of the genes are indicated with red and blue colors.
What type of mutation is Down syndrome?
Typically, a baby is born with 46 chromosomes. Babies with Down syndrome have an extra copy of one of these chromosomes, chromosome 21. A medical term for having an extra copy of a chromosome is 'trisomy. ' Down syndrome is also referred to as Trisomy 21.
Can 2 Down syndrome parents have a normal child?
Many pregnancies in women with Down syndrome produce children both with normal and with trisomy 21, whereas males are infertile. However, Down syndrome males are not always infertile and this is not global. Here we reported a 36-year-old man with proved nonmosaic trisomy 21 fathered two normal boys.
Can a man with Down syndrome have a baby?
Abstract. Men with Down syndrome are considered as infertile although the causes of infertility are not known in detail yet. Although this constitutes a general rule there are three confirmed cases of parenting by fathers with Down syndrome.
What are the types of duplication?
Gene duplication can occur by several mechanisms, including whole-genome duplication (WGD) and single gene duplication. Single gene duplication includes four types, tandem (TD), proximal (PD), retrotransposed (RD), DNA-transposed (DD) and dispersed duplication (DSD) (Freeling, 2009; Hahn, 2009; Wang et al., 2012b).
What are the two types of duplications?
Broadly, duplications are divided into two types which are further subdivided into different subtypes.Inter-Chromosomal duplication: ADVERTISEMENTS: The duplicated segment of a chromosome is present in another chromosome of the genome. ... Intra-Chromosomal duplication: ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the process of duplication?
Duplication Duplication, as related to genomics, refers to a type of mutation in which one or more copies of a DNA segment (which can be as small as a few bases or as large as a major chromosomal region) is produced. Duplications occur in all organisms.
What's the difference between duplication and replication?
Replication refers to the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules while duplication refers to the process by which the amount of DNA inside the nucleus gets doubled. Hence, this is the main difference between replication and duplication of DNA.
What is an example of duplication mutation?
An example of duplication mutation is the duplication of genetic material, which can result in additional copies of a gene or several genes. It can...
Why does duplication mutation happen?
Duplication mutations can happen due to three main reasons: unequal crossing over (uneven exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosom...
What disease is caused by duplication mutation?
An example of gene duplication is MECP2 duplication syndrome. This occurs when the gene coding for the protein MeCP2 is duplicated, resulting in ad...
What is the purpose of gene duplication?
Gene duplication is one of the various means that cells use to make proteins with multiple functions. It can be DNA-based, resulting from repeated copies of genes or chromosomes. Gene duplication can also be RNA-based, resulting in the formation of a retrogene. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
How Do Genes Get Duplicated?
For this lesson, we will focus on DNA replication during meiosis (formation of egg and sperm cells). When a gene is duplicated in the genome of an egg or sperm cell, the organism's offspring will inherit the duplicated gene. We will then discuss RNA-based gene duplication, which happens when an mRNA is turned back into DNA and then reinserted into the genome.
Why is duplication beneficial?
Sometimes, gene duplication is beneficial to the organism and may eventually lead to the development of a new species. The various types of keratin in the body are the result of duplications of a single gene. Over time, as species diversified, new genes for keratin with different functions arose in different species.
What happens when a gene is duplicated in the genome of an egg or sperm cell?
When a gene is duplicated in the genome of an egg or sperm cell, the organism's offspring will inherit the duplicated gene. We will then discuss RNA-based gene duplication, which happens when an mRNA is turned back into DNA and then reinserted into the genome.
Is chromosome duplication the same as gene duplication?
Chromosome duplication is very similar to gene duplication, except that much more than one gene is repeated. With the exception of some plants, duplicated chromosomes are detrimental. For instance, Down syndrome is cause by partial or complete duplication of chromosome 21 in an egg (or less commonly, sperm) cell.
How do duplicates occur?
Duplications occur when there is more than one copy of a specific stretch of DNA. This can occur in several different contexts. During a disease process, extra copies of the gene can contribute to a cancer. Genes can also duplicate through evolution, where one copy can continue the original function and the other copy of the gene produces a new function. On occasion, whole chromosomes are duplicated. In humans this causes disease. Throughout evolution, there have been several occasions, both in fish and plants, where whole genomes have been duplicated.
What is the process of producing one or more copies of a gene?
Duplication . Duplication is a type of mutation that involves the production of one or more copies of a gene or region of a chromosome. Gene and chromosome duplications occur in all organisms, though they are especially prominent among plants. Gene duplication is an important mechanism by which evolution occurs.
Can a whole genome be duplicated?
Genes can also duplicate through evolution, where one copy can continue the original function and the other copy of the gene produces a new function. On occasion, whole chromosomes are duplicated. In humans this causes disease. Throughout evolution, there have been several occasions, both in fish and plants, where whole genomes have been duplicated.
What is duplication in biology?
Duplication is the inclusion of extra segments of genetic material, such that a part of a gene, all of a gene, or several genes are redundant. It's really as easy as it sounds. One type of duplication is a situation where there are more than two sets of homologous chromosomes.
What are the things that can contribute to genome evolution?
Another thing that can contribute to genome evolution is rearrangement . Rearrangement is an abnormality that involves a structural alteration in a chromosome, through things like deletions, inversions, translocations, or duplications.
What is a translocation?
Translocations would be akin to taking something on your desk and sticking it to the end of another item on your desk. An example of this would be like tearing off a post-it note from a post-it note pad and sticking it to the computer on your desk.
How do spontaneous mutations affect DNA replication?
Most of the time, errors in DNA replication or segregation are quickly repaired by enzymes or the cell is destroyed before they can cause lasting damage. When DNA repair attempts fail, spontaneous mutations stay within the DNA. Benign spontaneous mutations increase the genetic variance and biodiversity of a population.
What are some examples of mutations in germline cells?
Defective genes on chromosomes are passed on, as well as too many or too few chromosomes per cell when these mutations happen in germline cells. Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders, cell overgrowth, tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer.
When Do Gene Mutations Occur?
Mutations frequently occur just before the process of mitosis when DNA is being replicated in the cell nucleus. During mitosis or meiosis, mishaps can occur when chromosomes are not lined up correctly or fail to separate properly. Chromosomal mutations in the germ cells can be inherited and passed along to the next generation.
What is frameshift mutation?
Frameshift mutations: These are point mutations that result when a nucleotide pair is added or omitted in a gene sequence that shifts how codons are read. Such mutations often result in different amino acids being added to the protein being synthesized. An example is beta thalassemia, a blood disorder caused by mutations to the HBB gene.
What is a mutation that changes the number of nucleotides?
Changes in the number or type of nucleotides are called point mutations . The effects of point mutation can range from harmless to life threatening. Mispairing or reordering of nucleotide bases are considered silent mutations when the change doesn’t affect cell functioning.
What is genetic mutation?
Genetic mutations are slight alterations of DNA or RNA nucleotides, genes or chromosomes that may occur during replication or cell division. Random, uncorrected errors may be beneficial or harmful in relationship to evolution. Some effects of gene mutation go unnoticed.
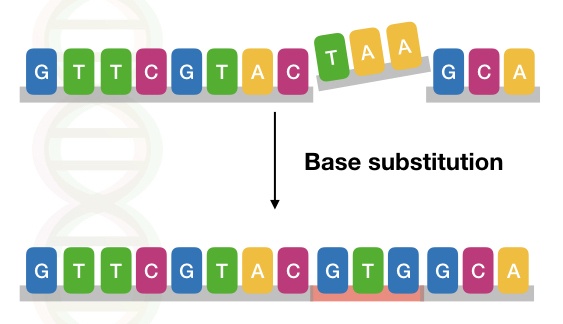
What type of mutation occurs when one nucleotide is replaced with another?
The new amino acid may even perform the same functions as the one it replaced. The following are types of point mutations that can occur: Missense mutation: This happens when one nucleotide is replaced with another. Substitutions of bases can interfere with normal protein syntheses and functioning.