They serve as a major structural component of most biological membranes. They form the lipid bilayer in cell membranes of organisms. Examples of phospholipids
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. The structure of the phospholipid molecule generally consists of two hydrophobic fatty acid "tails" and a hydrophilic "head" consisti…
Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid and is a component of the cell membrane. It plays a key role in cell cycle signaling, specifically in relation to apoptosis. It is a key pathway for viruses to enter cells via apoptotic mimicry.
Lecithin
Lecithin is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances, and are used for smoothing food textures, emulsifying, homogenizing liquid mixtures, and repelling stick…
Full Answer
What property of phospholipids allows them to form a bilayer?
Which property of phospholipids is responsible for the formation of phospholipid bilayers? Because their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions, with the hydrophobic tails buried in the interior of the membrane and the polar head groups exposed on both sides, in contact with ...
What are phospholipids and why should you care?
Properties Of Phospholipids
- They are signal mediators.
- They are amphipathic molecules.
- They anchor proteins within the cell membranes.
- They are the major constituents of cell membranes.
- They are the components of bile and lipoproteins.
What is the phodpholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell?
The phospholipid bilayer is the two-layer membrane that surrounds many types of plant and animal cells. It's made up of molecules called phospholipids, which arrange themselves in two parallel layers, forming a membrane that can only be penetrated by certain types of substances. This gives the cell a clear boundary, and keeps unwanted ...
What role does the phospholipid bilayer play in a cell?
- What is a Phospholipid?
- The Structure Of The Phospholipid Bilayer
- Functions Of The Phospholipid Bilayer 1. Maintain The Shape Of The Cell 2. Act As A Semipermeable Membrane 3. Important In Cell Recognition And Communication 4. Maintain Its Internal Environment
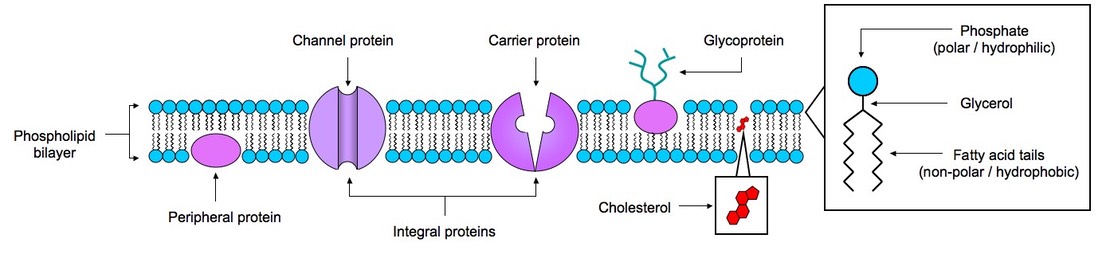
- What else are found in the Plasma Membrane? 1. Cholesterol 2. Glycoproteins 3. Antigens
- References
What is an example of phospholipid bilayer?
The structure of Biological membranes typically includes several types of molecules in addition to the phospholipids comprising the bilayer. A particularly important example in animal cells is cholesterol, which helps strengthen the bilayer and decrease its permeability.
What is a bilayer of phospholipids?
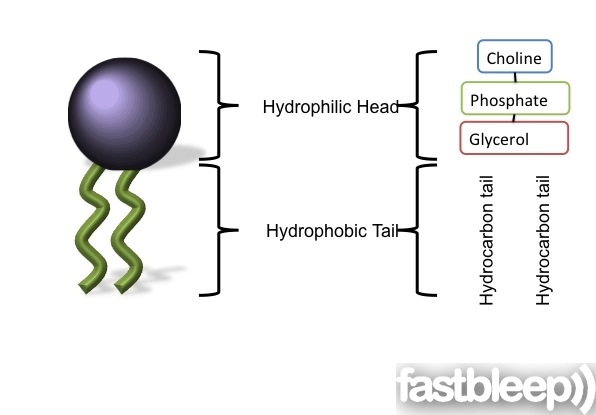
Phospholipid Bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer consists of two layers of phospholipids, with a hydrophobic, or water-hating, interior and a hydrophilic, or water-loving, exterior. The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in the single phospholipid molecule.
Which structures have a phospholipid bilayer?
The cell membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fattyacids and alcohol. The phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer.
Where can you find a phospholipid bilayer?
Biological membranesBiological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. Cholesterol, another lipid composed of four fused carbon rings, is found alongside phospholipids in the core of the membrane.
What is the phospholipid bilayer quizlet?
Phospholipid bilayer. A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes. Hydrophilic head.
What is the phospholipid bilayer and its function?
Phospholipid bilayers are critical components of cell membranes. The lipid bilayer acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell. However, an important function of the cell membrane is to allow selective passage of certain substances into and out of cells.
Do all membranes have a phospholipid bilayer?
The formation of biological membranes is based on the properties of lipids, and all cell membranes share a common structural organization: bilayers of phospholipids with associated proteins.
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer?
When phospholipids are mixed with water, they spontaneously rearrange themselves to form the lowest free-energy configuration. This means that the hydrophobic regions find ways to remove themselves from water, while the hydrophilic regions interact with water. The resulting structure is called a lipid bilayer.
Why is the cell membrane a bilayer?
Like all lipids, they are insoluble in water, but their unique geometry causes them to aggregate into bilayers without any energy input. This is because they are two-faced molecules, with hydrophilic (water-loving) phosphate heads and hydrophobic (water-fearing) hydrocarbon tails of fatty acids.
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer in water quizlet?
Understanding: Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. Amphipathic means there are both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions in a single molecule. Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head region and hydrophobic tails.
What is meant by a bilayer?
Definition of bilayer : a film or membrane with two molecular layers a bilayer of phospholipid molecules.
Why is the cell membrane a bilayer?
Like all lipids, they are insoluble in water, but their unique geometry causes them to aggregate into bilayers without any energy input. This is because they are two-faced molecules, with hydrophilic (water-loving) phosphate heads and hydrophobic (water-fearing) hydrocarbon tails of fatty acids.
How do phospholipids form a bilayer?
Phospholipids spontaneously form stable bilayers, with their polar head groups exposed to water and their hydrophobic tails buried in the interior of the membrane.
What is another name for the phospholipid bilayer?
Also called lipid bilayer.
What is a phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Definition. Phospholipid Bilayer�is basically a special form of lipid molecule which is mainly the major constituent of the Cell Membrane. Fats, Waxes, and Vitamins are the molecules that are Lipids in nature and composed of Lipids.
What is a phospholipid?
While Phospholipid is comprised of two molecules of Fatty acids, Phosphate Group, and a Glycerol Molecule. Generally, whenever many molecules of Phospholipids are striped up in a straight line, they form a Double Layer which is a vital part of Cell Membranes.
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
Phospholipid Structure. A Phospholipid molecule is comprised of two Fatty Acid tails and Phosphate Group which make its Head. Fatty acids are chemically composed of long chains of Hydrogen and Carbon atoms. While Phosphate groups comprised of a Phosphorus molecule. Four oxygen molecules attached to Phosphate group.
Why do fatty acids have polar heads?
Fatty acids have the ability to form Cell Membranes because the Head of Phosphate group is Hydrophilic. While in contrast, the tails of Fatty Acid tails are Hydrophobic. Hydrophilic is the water-loving while Hydrophobic is water-hating molecules.
Why do fatty acids have cell membranes?
Phospholipids perform various process inside the organisms. Fatty acids have the ability to form Cell Membranes because the Head of Phosphate group is Hydrophilic. While in contrast, the tails of Fatty Acid tails are Hydrophobic. Hydrophilic is the water-loving while Hydrophobic is water-hating molecules. Due to this, inevitably Fatty Acids ...
What is the double layer of phospholipids?
Due to this, Phospholipids double layer is formed in which Heads of Phosphate group are exteriorly, and tails of Fatty acid tails on the inside. This model is known as the Phospholipid Bilayer Model. It is an integral part of the Cell Membrane.
Why are phospholipids important?
They play an essential role in the delivery system of drugs to the targeted area. Phospholipids aid in the transportation of a drug all over the Organism body to the zone that it is inevitable to affect. Phospholipids are also known as High Bioavailable compounds because they are readily absorbed by the body.
What is the purpose of phospholipid bilayers?
Phospholipid bilayers create a selectively permeable barrier to the movement of ions and molecules important for cellular function.
How are phospholipid bilayers formed?
Phospholipid bilayers (SUPER templates) were formed on the surface of 5 μm silica beads by mixing the beads with liposomes. The phospholipids used in the construction of the liposomes were matched to the composition of the inner leaf of the cell membrane.
What are liposomes made of?
Liposomes are phospholipid bilayer membrane constructs consisting of diverse characteristic groups such as phosphoric residues, hydrophobic chains, and a polar head . Liposomes have varied physicochemical properties due to different phospholipid compositions, surficial charges, the size of the liposomal carrier, and the use of preparation methodology (Maheshwari, Tekade, Sharma, & Kumar Tekade, R., 2015b; Sharma, Maheshwari, Tekade, & Kumar Tekade, 2015 ). Liposomes are ideal nanodevices for drug delivery applications. Over the last several decades, liposomal formulations have been studied extensively for the targeted delivery of molecules ( Allen & Cullis, 2013; Daraee, Etemadi, Kouhi, Alimirzalu, & Akbarzadeh, 2016; Lian & Ho, 2001; Torchilin, 2005 ). The liposomal formulation provides regulated retentive entrapment and improved uptake of drugs by targeted cells. The “stealth liposomes,” coated with biocompatible polymers, have been used widely for targeted drug delivery applications ( Allen & Cullis, 2013; Bae & Park, 2011; Gabizon, 2001 ). Macrophages are unable to recognize the stealth liposomes, and thereby these types of nanodevices have a longer biological half-life ( Cattel, Ceruti, & Dosio, 2003; Deshpande, Biswas, & Torchilin, 2013; Moghimi & Szebeni, 2003; Silvander, 2002 ). In the last few years, rapid advancements have been made to utilize liposomal nanoconstructs in targeted drug delivery for brain tumors.
What is liposome bupivacaine?
Liposomes are phospholipid bilayer that formed a self-assembled nanostructure through hydrophobic interactions. Liposomal bupivacaine is a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved local anesthetic with prolonged drug release up to 72 h [24]. Effectiveness of liposomal bupivacaine was studied on 28 patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Treated patients with liposomal bupivacaine demonstrated decreased length of stay and decreased narcotic equivalent usage during the first 24 h following total hip arthroplasty [25]. Bacterial infections cause chronic and nonhealing ulcers of musculoskeletal injuries. Improving antimicrobial delivery to the wounds provides more precise dosing control and complete killing of wound-resident bacteria. Nigatu et al. [26] designed and studied an elastin-like polypeptide- based thermally sensitive liposomes (ELP-TSLs) loaded with ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin is a highly charged molecule and may complex with liposome membrane by electrostatic interaction to affect encapsulation and release of the drug efficiencies. Their results showed the controlled drug permeation of antimicrobials in vitro, which may have clinical utility against musculoskeletal infections. Icariin is a type of flavonoid, which showed potential application in osteoporosis therapy. But its clinical application is limited by its poor water solubility and low bioavailability. Recently a targeting delivery system of biomineral-binding liposomes mediated by pyrophosphate ions has been designed to enhance the therapeutic effects of icariin. The designed nanocarrier showed a rapid and strong binding ability with hydroxyapatite. The in vivo results proofed that treatment with this new delivery system was statistically superior to control group treatment in increasing femoral midshaft peak load, stiffness, ultimate strength, and Young’s modulus [27].
What are the functions of diacyl and plasmalogen phospholipids?
Combined, both diacyl and plasmalogen phospholipids provide a lipid bilayer environment that is critical for maintaining the function of integral membrane proteins. As a result, alterations in phospholipid content or composition can result in alterations in the function of these membrane proteins. This includes key proteins involved in the control of cellular electrophysiology.
What is a phospholipid membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer membranes (BLM’s) represent a useful model system to examine fundamental aspects of the lipid bilayer components of biological cell membranes and , particularly , to investigate their elastic properties. They are self-assembled structures of amphipatic molecules with physical features closely similar to those of smectic liquid crystals [1]. Lipid bilayer matrix is capable of incorporating both hydrophobic and amphipatic molecules like proteins, other lipids, peptides, steroids and cosurfactants. The elastic properties of lipid membranes regarded as continuous media have been used in a variety of studies ranging from local phenomena, such as lipid-lipid [1-11], lipid-protein [12-25] and protein-protein interactions [26-27], to shape fluctuations of the whole cells [28-32]. In addition, the liquid hydrocarbon nature of the bilayer is maintained by inter-molecular interactions between phospholipids at nanoscopic scale: electrostatic and dipole-dipole interactions between the polar headgroups [33, 34], interactions mediated by water molecules [35], and van der Waals dispersion interactions between hydrocarbon chains [36-38].
What are the functions of phospholipids in the cardiomyocyte?
The normal function of membrane-associated pumps, ion channels, and cellular transducers contained within the phospholipid membrane is critically dependent on the composition of phospholipids in the microenvironment around these proteins. In addition to these important functions, cardiac phospholipids also serve as a storage depot for a number of second messengers important in cell signaling , including aracidonic acid, eicosanoids, diacylglycerides, and inositol phosphates.
Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water?
Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules.
What allows materials to be taken into cells by endocytosis or released by exocytosis?
The fluidity of membranes allows materials to be taken into cells by endocytosis or released by exocytosis. Vesicles move materials within cells.
What control the composition of cells by active and passive transport?
Essential idea: Membranes control the composition of cells by active and passive transport.
