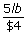
A few examples of rate are given below:
- Time rate: Distance per unit time, average speed (miles/ hour), and interest ( simple or compound) rates.
- Cost Price: cost/pound, quantity per cost (20 oz of juice/ 4 dollars), or for comparing prices.
- Other examples can be the literacy rate, the population, and other rates which provide specific data.
Full Answer
What are the characteristics of a rate in math?
In mathematics, a rate is the ratio between two related quantities in different units. If the denominator of the ratio is expressed as a single unit of one of these quantities, and if it is assumed that this quantity can be changed systematically (i.e., is an independent variable), then the numerator of the ratio expresses the corresponding rate of change in the other variable.
What does rate mean in math?
What Does Rate Mean In Math? – djst’s nest. Dec 28, 2021 · What Does Rate Mean In Math? A rate is a special ratio in which the two terms are in different units . For example, if a 12-ounce can of corn costs 69¢, the rate is 69¢ for 12 ounces.
How to find unit rates in math?
- In essence, you are calculating the distance per unit of time.
- The units will vary depending on the circumstance, but one unit must express distance (mile, kilometre, feet, meters, etc.) and the other unit must express time (hours, minutes, seconds, etc.).
- Example: The Smith family travelled 150 miles in 3 hours. ...
What is an example of an unit rate?
Unit Rate
- 100 cars pass by in 2 hours. The unit rate is 50 cars per hour.
- You can paint 3 boards in half an hour. The unit rate is 6 boards per hour.
- 200 sausages were eaten by 50 people. ...
- They need 5 m of thread to make 2 cm of cloth. ...
- The car can go 1000 km on 50 liters of fuel. ...
- There are 100 students and 4 teachers. ...
- In the last 4 weeks Sam earned $2000. ...
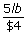
What are the examples of rate?
A rate is a special ratio in which the two terms are in different units. For example, if a 12-ounce can of corn costs 69¢, the rate is 69¢ for 12 ounces. This is not a ratio of two like units, such as shirts. This is a ratio of two unlike units: cents and ounces.
What are three examples of rates?
What are Three Examples of Rate? Distance per unit time, quantity per cost, number of heartbeats per minute are three examples of rate.
What is an example of a unit rate in math?
Some examples of unit rates are: miles per hour, blinks per second, calories per serving, steps per day and heart beats per minute.
How do you write a rate?
A ratio can be written using a colon, 3:5 , or as a fraction 35 . A rate , by contrast, is a comparison of two quantities which can have different units. For example 5 miles per 3 hours is a rate, as is 34 dollars per square foot.
Does rate mean multiply?
The mathematical definition of a rate is a ratio of two numbers with different units. When your rate has a 1 in the denominator, it becomes a special rate called the unit rate. To convert a rate into its unit rate, simply divide both the numerator and denominator by the denominator.
Is a percent a rate?
"Rate" simply means the number of things per some other number, usually 100 or 1,000 or some other multiple of 10. A percentage is a rate per 100.
How do you find the rate?
Use the formula r = d/t. Your rate is 24 miles divided by 2 hours, so: r = 24 miles ÷ 2 hours = 12 miles per hour. Now let's say you rode your bike at a rate of 10 miles per hour for 4 hours.
What is a rate simple definition?
1 : a fixed ratio between two things. 2 : a quantity, amount, or degree of something measured per unit of something else — see death rate, heart rate, metabolic rate, pulse rate, sedimentation rate. rate. noun.
What is rate and unit?
The difference between a rate and a unit rate is that a rate is the ratio between two different units of measure, while a unit rate is the ratio of between two different units of measure for a single thing.
How do you write a rate in simplest form?
Example: Simplify the ratio 6 : 10The factors of 6 are: 1, 2, 3, 6.The factors of 10 are: 1, 2, 5, 10.Then the greatest common factor of 6 and 10 is 2.Divide both terms by 2.6 ÷ 2 = 3.10 ÷ 2 = 5.Rewrite the ratio using the results. The simplified ratio is 3 : 5.6 : 10 = 3 : 5 in simplest form.
How do you solve rate problems?
All rate problems can be solved by using the formula D = R(T), which translates to distance (D) equals rate (R) multiplied by time (T).
Is a ratio always a rate?
A ratio does not have to be a rate. For example. The ratio of boys to girls in a class of 12 students is 2:1. This tells us that for every 1 girl in this class, there are 2 boys.
More About Rate
Unit Rate: Unit rate is a rate in which the second term is 1. For example, Jake types 10 words in 5 seconds. Jake's unit rate is the number of words he can type in a second. His unit rate is 2 words per second.
Examples of Rate
20 oz of juice for $4, miles per hour, cost per pound etc. are examples of rate.
What is the unit of a rate?
In describing the units of a rate, the word "per" is used to separate the units of the two measurements used to calculate the rate (for example a heart rateis expressed "beats per minute"). A rate defined using two numbers of the same units(such as tax rates) or counts (such as literacy rate) will result in a dimensionless quantity, which can be expressed as a percentage(for example, the global literacy ratein 1998 was 80%), fraction, or multiple.
What is the inverse of a ratio?
A ratio r=a/b has both a numerator "a" and a denominator "b". The value of a and/or b may be a real numberor integer. The inverseof a ratio r is 1/r = b/a. A rate may be equivalently expressed as an inverse of its value if the ratio of its units are also inverse. For example, 5 miles(mi) per kilowatt-hour(kWh) corresponds to 1/5 kWh/mi (or 200 Wh/mi).
Why use sequential indices?
A set of sequential indices i may be used to enumerate elements (or subsets) of a set of ratios under study. For example, in finance, one could define i by assigning consecutive integers to companies, to political subdivisions (such as states), to different investments, etc. The reason for using indices i, is so a set of ratios (i=0,N) can be used in an equation so as to calculate a function of the rates such as an average of a set of ratios. For example, the average velocity found from the set of vi's mentioned above. Finding averages may involve using weighted averages and possibly using the harmonic mean.
How to find the average speed of a car?
For example, the average speedof a car can be calculated using the total distance travelled between two points, divided by the travel time, while the instantaneous speed can be determined by viewing a speedometer.
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay, the amount of radioactive material in which one nucleus decays per second, measured in becquerels
What is the definition of birth rate?
Birth rate, and mortality rate, the number of births or deaths scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time
What is the rate of return?
Rate of return, the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested
What is a ratio of zombies to people?
Let's start with ratios. A ratio is a comparison between two terms. Maybe you're in a town with 500 zombies and 1 of you. The ratio of zombies to people is 500 to 1. We can write ratios in a few different ways. For example, we can write it just as we say it: 500 to 1. We can also write it like this: 500:1, with a colon that stands in for 'to.'
What is the difference between a ratio and a rate?
In mathematics, a ratio indicates the number of times that a smaller number is contained within a larger number, while a rate expresses a ratio for two quantities measured in different units. Explore the definitions and examples of ratios and rates, learn how to compare them, and solve practice problems. Updated: 09/30/2021
What is mph in a unit rate?
You're probably familiar with this rate: mph. What's that stand for? Miles per hour - that's a particular kind of rate that's called a unit rate. A unit rate is a rate with a denominator of 1. Remember when you were speeding away from monsters? Oh, I'm sorry. Were you trying to forget that? Well, let's say you were going 60 miles per hour. We write that like this: 60 miles/1 hour. Since that denominator is 1, it's a unit rate. We can rewrite it like this: 60 miles/hour.
What is ratio in math?
To summarize, a ratio is a comparison between two terms. We can write it like this: 5 to 1; with a colon, like 100:3; or as a fraction, like 3/4.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
How to find the number of Trekkies in Star Wars?
To solve this, just set up an equation like this: Star Wars/Trekkies = 5/4 = 130/ x, where x is the number of Trekkies.
How much is an 18 pound bag of chips?
With rates, you may be asked to simplify a fraction like this: At a local warehouse store, an 18-pound bag of potato chips costs 42 dollars. Express this in its simplest form. That's a lot of potato chips. What's the rate? 18 lbs/42 dollars. To make it simpler, we just simplify the fraction. The greatest common factor here is 6. Divide both numbers by 6, and we get 3 lbs/7 dollars. That's not a bad deal on chips.
Unit Rate Definition
A rate is a ratio that is used for comparing two different kinds of quantities which have different units. On the other hand, the unit rate illustrates how many units of quantity correspond to the single unit of another quantity. We say that when the denominator in rate is 1, it is called unit rate.
Unit Rate Examples
Solution: Given a man travels 20 kilometers in 2 hours we need to find the unit rate.
Overview
Introduction
Rates and ratios often vary with time, location, particular element (or subset) of a set of objects, etc. Thus they are often mathematical functions.
A rate (or ratio) may often be thought of as an output-input ratio, benefit-cost ratio, all considered in the broad sense. For example, miles per hour in transportation is the output (or benefit) in terms of miles of travel, which one gets from spending an hour (a cost in time) of traveling (at this velo…
Temporal rates
In chemistry and physics:
• Speed, the rate of change of position, or the change of position per unit of time
• Acceleration, the rate of change in speed, or the change in speed per unit of time
• Power, the rate of doing work, or the amount of energy transferred per unit time
Economics/finance rates/ratios
• Exchange rate, how much one currency is worth in terms of the other
• Inflation rate, ratio of the change in the general price level during a year to the starting price level
• Interest rate, the price a borrower pays for the use of money they do not own (ratio of payment to amount borrowed)
Other rates
• Birth rate, and mortality rate, the number of births or deaths scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time
• Literacy rate, the proportion of the population over age fifteen that can read and write
• Sex ratio or gender ratio, the ratio of males to females in a population
See also
• Derivative
• Gradient
• Hertz
• Slope