
Trophic Cascade Examples in various Habitats
- 1. Wolves in Yellowstone National Park This is one of the well-documented cases of a trophic cascade. This happened in Yellowstone National Park where gray wolf was reintroduced after an absence of 70 years. ...
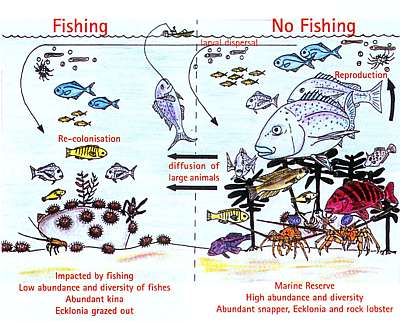
- 2. Kelp Beds ...
- 3. Tropical Rainforests – An example of Top down control ...
- 4. Salt Marshes ...
How to use trophic cascade in a sentence?
trophic cascade. in a sentence. The net effect of direct and indirect relations is called trophic cascades. The trophic cascade in lakes has been researched by Carpenter and Hall. Many of the barriers to top-down trophic cascades also promote stability. Such wide-ranging effects on lower levels of an ecosystem are termed trophic cascades.
What does the highest trophic level contain?
The highest trophic level in the pyramid represents the top of the food chain. The organisms that occupy the base of the pyramid differ in different ecosystems as in terrestrial ecosystems, green plants are present at the bottom, whereas, in aquatic ecosystems, multicellular plants and green algae occupy the level.
What are the examples of a trophic level?
Example 1. Pot marigold ( Calendula officinalis) > European honey bee ( Apis mellifera) > European bee-eater ( Merops apiaster) > Red fox ( Vulpes vulpes) In this example of trophic levels in a terrestrial food chain, the marigold is the producing organism. The bee only feeds on the pollen and nectar of the flower.
What is trophic level 2?
Level 2: primary consumers. The next trophic level in a food chain or an ecological pyramid is trophic level 2. In this level, the organisms occupying this level feed on the primary producers and are called primary consumers. Animals that feed on plant materials are called herbivores.
What is a trophic cascade?
trophic cascade, an ecological phenomenon triggered by the addition or removal of top predators and involving reciprocal changes in the relative populations of predator and prey through a food chain, which often results in dramatic changes in ecosystem structure and nutrient cycling.
How are trophic cascades used in lakes?
In lakes, trophic cascades are used to improve water quality through biomanipulation, a management practice in which humans intentionally remove whole species from ecosystems. The goal of biomanipulation is to reduce the concentration of harmful phytoplankton, such as toxic blue-green algae.
How do trophic cascades affect the ecosystem?
In many instances, trophic cascades have been initiated by human persecution and harvesting of top carnivores, such as wolves and big cats in terrestrial ecosystems and sharks, tunas, and game fish in aquatic ecosystems. The removal of top carnivores triggers significant effects on prey populations, primary producers, and ecosystem processes. Therefore, the conservation of top carnivores helps to preserve the structure and processes of ecosystems in which these predators live. The normal functioning of ecosystems provides many services used by people, including food, fibre, and freshwater supplies as well as processes that maintain the quality of air, water, and soil. The preservation or restoration of top carnivores, however, is sometimes controversial because of the risk such predators pose to people, livestock, or pets.
What is the trophic pyramid?
Trophic pyramid, also called an energy pyramid, showing the progression of food energy. The pyramid base contains producers, organisms that make their own food from inorganic substances. All other organisms in the pyramid are consumers.
What happens to food energy at a trophic level?
Most of the food energy that enters a trophic level is "lost" as heat when it is used by organisms to power the normal activities of life. Thus, the higher the trophic level on the pyramid, the lower the amount of available energy. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
How to control phytoplankton blooms?
The most direct method to control harmful phytoplankton blooms is to reduce inputs of nutrients such as phosphorus that drive their growth. In cases where the arrival of nutrients to the ecosystem is delayed or slow to develop, biomanipulation can be used to hasten the decline of harmful phytoplankton.
What is the trophic cascade?
Trophic cascade meaning in which the highest consumer/predator dominates the primary consumer population is known as a top-down cascade. As a result, the population of primary producers grows. The elimination of the top predator will change the dynamics of the food web. The primary consumers will overcrowd and manipulate the primary producers in this scenario.
Who was the first to describe the trophic cascade?
Depending on his reports of deer overgrazing mountain slopes following human-wolf extinction, Aldo Leopold is commonly acclaimed as being the first one to describe the process of a trophic cascade. While they did not use the trophic meaning, Frederick E. Smith, Nelson Hairston, and Lawrence B. Slobodkin are widely credited for bringing the idea into scientific discourse. Predators, according to Smith, Hairston, and Slobodkin, decrease the density of herbivores, enabling plants to thrive. The green planet hypothesis is a popular term for this. The importance of top-down factors (such as predation) and indirect effects in shaping ecological ecosystems is attributed to the green world hypothesis.
What happens to zooplankton if the number of piscivorous fish in a?
For instance, if the number of large piscivorous fish in a lake increases , the number of smaller fish that consume zooplankton would reduce. As a consequence of rising in zooplankton, the biomass of its prey, phytoplankton, should decrease.
When a trophic level in a food web is disrupted, what are trophic cascade?
When a trophic level in a food web is disrupted, trophic cascades are strong indirect interactions that can influence entire ecosystems. For instance, if predators are good enough to be at predation to decrease the availability or alter the behaviour of their prey, a top-down cascade might occur, freeing the very next lower trophic stage against exploitation/predation. Let us take a closer look at the Cascade definition biology.
When predators restrict the density and/or action of their prey, the trophic cascade concept occurs?
Ans. When predators restrict the density and/or action of their prey, the trophic cascade concept occurs, enhancing the survival of the next lower trophic stage.
Where did trophic cascades originate?
While Hairston, Smith, and Slobodkin presented their case in terms of terrestrial food chains, the first empirical evidence of trophic cascades originated from marine and, in particular, aquatic
How do invasive species disrupt the food chain?
Invasive species can disrupt the food chain by eliminating or replacing top predators. Such relationships do not have to be negative all of the time. Some invasive species also started to change cascade meaning, according to research, and so as a result, habitat destruction has indeed been restored.
What is a trophic cascade?
Endangered Species. A trophic cascade is an ecological event that involves changes to the structure of an ecosystem resulting from changes to animals or plants at one or more levels of the food chain.
Why are trophic cascades more common?
Trophic cascades have become more common, however, as a result of human actions. Pollution, habitat destruction, and development of farms and plantations in formerly wild areas are all causes of trophic cascade. Climate change is also a primary cause of trophic cascades. Relatively small events, such as a prolonged drought, shrinking habitat, ...
Where Do Trophic Cascades Occur?
Trophic cascades occur all over the world, in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. They have occurred throughout the planet’s history, sometimes on a catastrophic level. Prehistoric mass extinctions completely changed the evolution of life on Earth.
What did John Terborgh discover about the trophic cascade?
What Terborgh discovered was that the islands without predators had an over-abundance of seed and plant eaters, along with a scarcity of seedlings and young canopy-forming trees. Meanwhile, the islands with predators had normal vegetative growth. This discovery helped to define the importance of apex predators in ecosystems; it also provided researchers with the tools to recognize trophic cascade even where it might not be obvious.
How do trophic cascades affect the food chain?
When organisms are removed from their ecosystems, the impact can cascade up and down the food chain , causing significant stress. Researchers have also found that changes to aquatic ecosystems can have an impact on the chemical makeup of the water. 7
What is a bottom up cascade?
A bottom-up cascade is the result of changes to the bottom level of the food chain. This type of trophic cascade occurs when, for example, swathes of rainforest vegetation are burned — leaving little for herbivores to eat. Herbivores may die off or migrate; either way, top predators have less to eat.
How does subsidy cascade occur?
Subsidy cascades occur when animals rely on food sources that are external to their ecosystem. For example, when appropriate plants are less available, herbivores may come to rely on farmers’ crops. More herbivores lead to more predators — creating an ecological imbalance.
What are some examples of trophic cascades?
A classic example of a terrestrial trophic cascade is the reintroduction of gray wolves ( Canis lupus) to Yellowstone National Park, which reduced the number, and changed the behavior, of elk ( Cervus canadensis ). This in turn released several plant species from grazing pressure and subsequently led to the transformation of riparian ecosystems. This example of a trophic cascade is vividly shown and explained in the viral video "How Wolves Change Rivers".
Why is the trophic cascade important?
For example, it can be important for understanding the knock-on effects of removing top predators from food webs, as humans have done in many places through hunting and fishing .
What is the effect of clerid beetle on piper plants?
The Clerid beetle, by reducing the abundance of ants , increases the leaf area removed from Piper plants by insect herbivores. Critics pointed out that published terrestrial trophic cascades generally involved smaller subsets of the food web (often only a single plant species).
What is subsidy cascade?
In a subsidy cascade, species populations at one trophic level can be supplemented by external food. For example, native animals can forage on resources that don't originate in their same habitat, such as native predators eating livestock.
How does a top down cascade affect the food web?
The removal of the top predator can alter the food web dynamics. In this case, the primary consumers would overpopulate and exploit the primary producers. Eventually there would not be enough primary producers to sustain the consumer population. Top-down food web stability depends on competition and predation in the higher trophic levels. Invasive species can also alter this cascade by removing or becoming a top predator. This interaction may not always be negative. Studies have shown that certain invasive species have begun to shift cascades; and as a consequence, ecosystem degradation has been repaired.
Where did trophic cascades originate?
Although Hairston, Smith and Slobodkin formulated their argument in terms of terrestrial food chains, the earliest empirical demonstrations of trophic cascades came from marine and, especially, aquatic ecosystems. Some of the most famous examples are:
What is the primary producer in a bottom up cascade?
Primary producers are plants, phytoplankton and zooplankton that require photosynthesis . Although light is important, primary producer populations are altered by the amount of nutrients in the system. This food web relies on the availability and limitation of resources. All populations will experience growth if there is initially a large amount of nutrients.

Key Terminology
Where Do Trophic Cascades occur?
- While Hairston, Smith, and Slobodkin presented their case in terms of terrestrial food chains, the first empirical evidence of trophic cascades originated from marine and, in particular, aquatic ecosystems. The following are amongst the most well-known examples: 1. Piscivorous fish might drastically decrease zooplanktivorous fish populations in Nor...
Trophic Cascades in Terrestrial Ecosystems
Trophic Cascades in Aquatic Ecosystems
Climate Change and Trophic Cascades
- Trophic cascades occur all over the world, in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. They have occurred throughout the planet’s history, sometimes on a catastrophic level. Prehistoric mass extinctions completely changed the evolution of life on Earth. Some trophic cascades occur as a result of natural disasters or weather events; others are directly caused by human actions. Exper…