
What is the approximate length of a geologic time scale?
What is the approximate length of the geologic time scale? A. 50 billion years B. 5 billion years C. 50 million years D. 5 million years. B. Earth formed about _____ years ago. A. 50 billion B. 5 billion C. 50 million D. 5 million. B. Approximately how many years ago did the Precambrian era begin? A. 50 billion
What are two ways to measure geologic time?
- Apply basic geological principles to the determination of the relative ages of rocks
- Explain the difference between relative and absolute age-dating techniques
- Summarize the history of the geological time scale and the relationships between eons, eras, periods, and epochs
- Understand the importance and significance of unconformities
What is the Order of the geologic time scale?
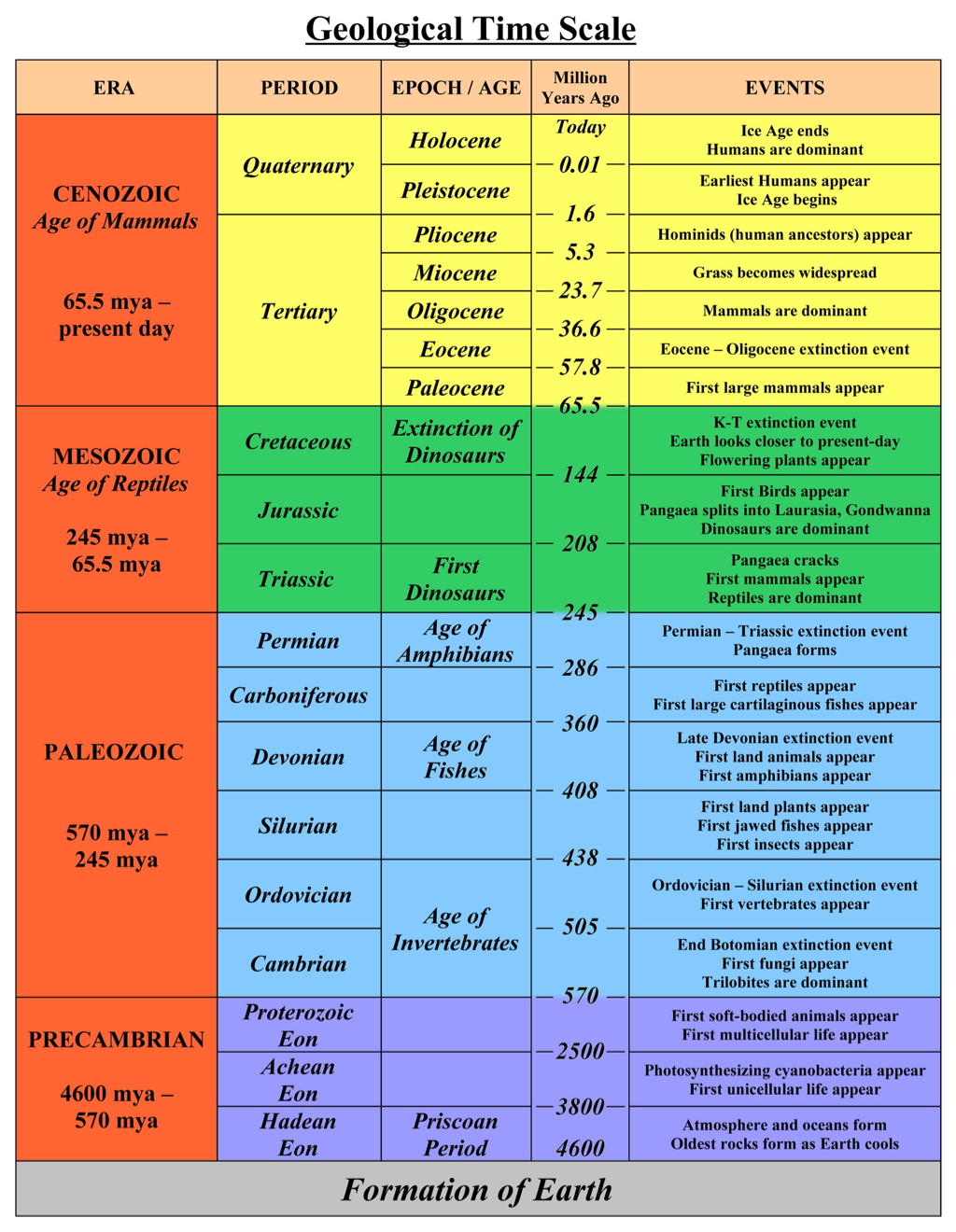
This is most easily done by first breaking the time scale into its component parts: eons, eras, periods, and epochs. The eon is the broadest category of geological time. Earth's history is characterized by four eons; in order from oldest to youngest, these are the Hadeon, Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic.
What are the parts of the geological time scale?
geological time-scale divides the history of Earth is divided into eons, e , periods and epochs. Eons are the largest intervals of geologic time. A single eon covers a period of several hundred million years. The history of Earth has been divided into three eons: Archaean, Proterozoic and Phanerozoic.
What are the 4 geologic time scales?
The Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The Geologic Time Scale is the history of the Earth broken down into four spans of time marked by various events, such as the emergence of certain species, their evolution, and their extinction, that help distinguish one era from another.
What are examples of geological?
Geological Features, Events & PhenomenaCaves.Deserts.Earthquakes.Glaciers.Tsunamis.Volcanoes.
What are three geologic time scales?
The Phanerozoic Eon is divided into three eras, the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras.
What are the five geological time scales?
It subdivides all time into named units of abstract time called—in descending order of duration—eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages. The enumeration of those geologic time units is based on stratigraphy, which is the correlation and classification of rock strata.
Which is an example geological disaster?
For example, natural disasters caused by a geological process are called geological disasters; these are earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. Disasters caused by weather-related factors are floods, landslides, droughts, forest fires, and tornadoes.
Which of the following is an example of geologic hazard?
A geologic hazard is an extreme natural events in the crust of the earth that pose a threat to life and property, for example, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis (tidal waves) and landslides.
What geologic time period are we?
The Anthropocene Epoch is an unofficial unit of geologic time, used to describe the most recent period in Earth's history when human activity started to have a significant impact on the planet's climate and ecosystems.
What is geological time scale describe in detail?
The geologic time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological dating that classifies geological strata (stratigraphy) in time. It is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other Earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history.
What is the geologic time scale based on?
the geological rock recordThe geological time scale is based on the the geological rock record, which includes erosion, mountain building and other geological events. Over hundreds to thousands of millions of years, continents, oceans and mountain ranges have moved vast distances both vertically and horizontally.
How do you remember the geologic time scale?
Ø Paleocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene, Pliocene, Pleistocene, Holocene (or Recent): * Pretty Eager Old Men Play Poker Hard. * Pigeon Egg Omelets Make People Puke Heartily. * Put Eggs On My Plate Please Homer.
What are the geological eras in order?
There are three Geologic Eras currently identified. The Paleozoic Era, the Mesozoic Era, and the Cenozoic Era. See illustration at right.
How many geological periods are there?
The further subdivision of the eras into 12 "periods" is based on identifiable but less profound changes in life-forms. In the most recent era, the Cenozoic, there is a further subdivision of time into epochs.
What is the calendar of geology?
For the purposes of geology, the “calendar” is the geologic time scale. One way to distinguish and define each segment of time is by the occurrence of major geologic events and the appearance (and disappearance) of significant life-forms, starting with the formation of Earth’s crust followed by the appearance of ever-changing forms of life on Earth.
Will geologists change the geologic time scale?
As technology of dating methods improves, geologists probably will make small but significant changes to the geologic time scale for years to come. Moreover, as geologists discover more complete sections of rock, which preserve evidence of significant portions of geologic time, and as the International Commission on Stratigraphy evaluates ...
What is the geologic time scale?
A geologic time scale is composed of standard stratigraphic divisions based on rock sequences and is calibrated in years (Harland and others, 1982). Over the years, the development of new dating methods and ...
What are the two color schemes used in geologic maps?
Two principal color schemes are used, one by the Commission for the Geologic Map of the World (CGMW) and another by the USGS.
What is the term for the division of time older than the Phanerozoic?
Precambrian. For many years, the term "Precambrian" was used for the division of time older than the Phanerozoic. For consistency with the time scale in Hansen (1991), the term "Precambrian" is considered to be informal and without specific stratigraphic rank (although it is here capitalized).
Is the tertiary period a time scale?
Although the Tertiary is not recognized by many international time scales, the GNC agrees that it is important that it be recognized as a system/period; the map symbols "T" (Tertiary) and "Q" (Quaternary) have been used on geologic maps for more than a century and are widely used today.
Who first proposed the geologic time scale?
Avicenna also first proposed one of the principles underlying geologic time scales, the law of superposition of strata, while discussing the origins of mountains in The Book of Healing (1027). The Chinese naturalist Shen Kuo (1031–1095) also recognized the concept of " deep time ".
Who created the first global geologic time scale?
In 1841 John Phillips published the first global geologic time scale based on the types of fossils found in each era. Phillips' scale helped standardize the use of terms like Paleozoic ("old life"), which he extended to cover a larger period than it had in previous usage, and Mesozoic ("middle life"), which he invented.
What is the largest division of time?
The primary and largest catalogued divisions of time are periods called eons . The first eon was the Hadean, starting with the formation of the Earth and lasting over 600 million years until the Archean eon, which is when the Earth had cooled enough for continents and the earliest known life to emerge.
What is GSSP in geology?
In 1977, the Global Commission on Stratigraphy (now the International Commission on Stratigraphy) began to define global references known as GSSP ( Global Boundary Stratotype Sections and Points ) for geologic periods and faunal stages. The commission's work is described in the 2012 geologic time scale of Gradstein et al.
How old is the Earth?
Evidence from radiometric dating indicates that Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The geology or deep time of Earth's past has been organized into various units according to events that are thought to have taken place. Different spans of time on the GTS are usually marked by corresponding changes in the composition of strata which indicate major geological or paleontological events, such as mass extinctions. For example, the boundary between the Cretaceous period and the Paleogene period is defined by the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which marked the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs as well as many other groups of life. Older time spans, which predate the reliable fossil record (before the Proterozoic eon ), are defined by their absolute age.
What is the geologic table based on?
Geologists and paleontologists constructed the geologic table based on the relative positions of different strata and fossils, and estimated the time scales based on studying rates of various kinds of weathering, erosion, sedimentation, and lithification.
What are the four types of rocks that form the Earth's crust?
The most influential of those early attempts (championed by Werner, among others) divided the rocks of Earth's crust into four types: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary. Each type of rock, according to the theory, formed during a specific period in Earth history. It was thus possible to speak of a "Tertiary Period" as well as of "Tertiary Rocks." Indeed, "Tertiary" (now Paleogene and Neogene) remained in use as the name of a geological period well into the 20th century and "Quaternary" remains in formal use as the name of the current period.
Geological Time Scale: Description
The Geological Time Scale has been reworked many times to reflect the latest knowledge of Earth’s history. It is organised into 5 subgroups: – Eons, Eras, Periods, Epochs and Ages.
The Geological Time Scale: Chart
Below we have provided the chart of geological time scale for your reference:
Summary
From the above discussion, we can conclude that Steno, Arduino and Smith, modern scientists, have contributed to the formation of the Geological Time Scale or GTS. The First Geological Time Scale was published in 1913 by the British geologist Arthur Holmes. Geological Time Scale is organised into 5 subgroups: – Eons, Eras, Periods, Epochs and Ages.
FAQs on Geological Time Scale
Q.1. What are the 5 major divisions of geologic time? Ans: 5 major divisions of geologic time are- eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
What is the geological time scale?
The geological time scale is currently maintained by the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), which is part of the International Union of Geological Sciences. The time scale is continuously being updated as we learn more about the timing and nature of past geological events. ...
Why are time scales relative?
The early time scales were only relative because 19th century geologists did not know the ages of the rocks. That information was not available until the development of isotopic dating techniques early in the 20th century. The geological time scale is currently maintained by the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), ...
How many eras are there in the Phanerozoic?
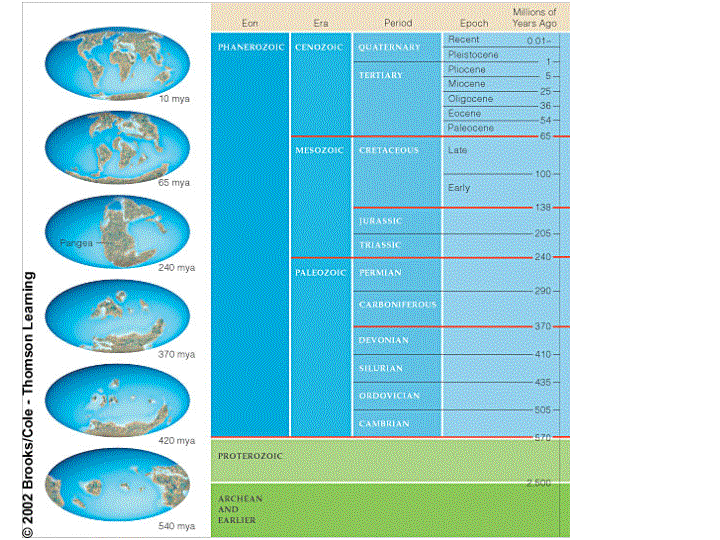
The Phanerozoic — the past 540 Ma of Earth’s history — is divided into three eras: the Paleozoic (“early life”), the Mesozoic (“middle life”), and the Cenozoic (“new life”), and each of these is divided into a number of periods (Figure 8.4).
What is the current epoch?
The current epoch is known as the Holocene. Epochs are further divided into ages (a.k.a. stages), but we won’t be going into that level of detail here. Figure 8.5 The periods (middle row) and epochs (bottom row) of the Cenozoic [SE] Most of the boundaries between the periods and epochs of the geological time scale have been fixed on the basis ...
What is the boundary between the Cretaceous and the Paleogene?
For example, as already noted, the boundary between the Cretaceous and the Paleogene coincid es exactly with the extinction of the dinosaurs. That’s not a coincidence.
What are the three periods of the phanerozoic?
Figure 8.4 The eras (middle row) and periods (bottom row) of the Phanerozoic [SE] The Cenozoic, which represents the past 65.5 Ma, is divided into three periods: Paleogene, Neogene, and Quaternary, and seven epochs (Figure 8.5).
What did Smith discover about fossils?
Smith noticed the textural similarities and differences between rocks in different locations, and more importantly, he discovered that fossils could be used to correlate rocks of the same age. Smith is credited with formulating the principle of faunal succession (the concept that specific types of organisms lived during different time intervals), ...
What Is The Geologic Time Scale?
What Period of The Geologic Time Scale Are We Currently Living in?
- We are currently living in the Meghalayan Age of the Holocene Epoch of the Quaternary Period of the Cenozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon.
Geologic Time Scale Divisions
- The main divisions of the geologic time scale, from largest to smallest, are: 1. Eon 2. Era 3. Period 4. Epoch 5. Age Unlike units of time such as seconds, hours and days, the units of the geologic time scale are not equal. Earth’s entire history is divided into four eons; the Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic and Phanerozoic. The first three eons are referred to as Precambrian; the Phaneroz…
Why Is The Geologic Time Scale Useful?
- The geologic history of the Earth dates all the way back to the time that the Earth was formed, some 4.6 billion years ago. Since it is difficult to work with such vast timespans, geologists and other scientists divided the Earth’s geologic history into smaller, more manageable units of time, together known as the geologic time scale. This scale acts like a ‘calendar’ of the geologic event…
How Was The Geologic Time Scale invented?
- The geologic time scale was not invented by any one person. Instead, it is the result of centuries of research and experimentation. One of the first people to realise that rocks formed in layers was Nicolaus Steno, a Danish scientist and part-time fossil collector. In the 1660s, Steno published a paper in which he stated that layers of sedimentary rock are laid down horizontally in successio…
How Are Fossils Important in The Geologic Time Scale?
- Fossils are very important in the geologic time scale. Long before scientists had the technology to date ancient rocks, they used fossils to understand events that had happened in the Earth’s history and when they happened. The fact that particular rock strata could be recognized by the fossils they contained allows geologists to match layers of rocks between different parts of a co…
The Geologic Time Scale and Evolution
- Investigation of the fossilized remains of organisms in rock layers gives scientists clues about how living creatures have evolved. The oldest, lowest strata contain the fossils of simple, soft-bodied animals, while higher layers contain animals that are more complex and specialized. The fossil record, written in Earth’s rocks through the eons, shows how some species have evolved, …
How Do We Know The Ages of The Ancient Rocks?
- Although following the patterns of fossil distribution in rock layers enabled early geologists to state that one stratum was older than another, there was no way for them to know the exact ages of the rocks. Today, radiometric dating is used to assign actual ages to the rocks of the Earth’s crust. The layers of igneous rock between the sedimentary, fossil-bearing layers can be dated us…
Who Uses The Geologic Time Scale?
- Knowledge of the geologic timescale is vital for miners who are searching for particular types or ages of rocks to mine for important minerals. Farmers may wish to know the age and origin of the sediments on their lands so that they can plant suitable crops and find water sources. Geologists use the geologic time scale to determine the ages of surface rocks all over the world. This help…