
What is the difference between an ipsilateral and a contralateral reflex?
Mar 01, 2020 · What is an example of ipsilateral reflex? Both are examples of ipsilateral reflexes, meaning the reflex occurs on the same side of the body as the stimulus. For example, when one foot steps on a nail, the crossed extensor reflex shifts the body's weight onto the other foot, protecting and withdrawing the foot on the nail.
What are the different types of reflexes?
ipsilateral reflex: a reflex in which the response occurs on the side of the body that is stimulated.
What is an example of a single synapse reflex?
This is a rapid, monosynaptic (single synapse), ipsilateral reflex that helps to maintain the length of muscles and contributes to joint stabilization. A common example of this reflex is the knee jerk reflex that is elicited by a rubber hammer striking against the …
Why are reflexes called polynaptic reflexes?
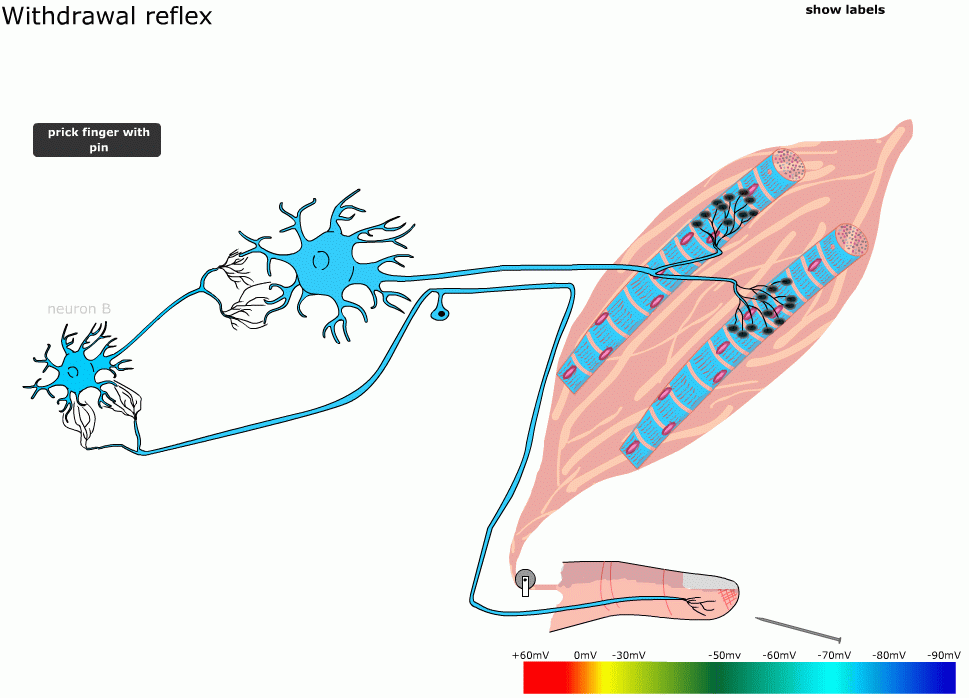
A withdrawal reflex is a single sensory input that brings about many motor responses on the same side of the body. This is an ipsilateral reflex. Example: step on tack with left foot, remove left foot and leg from tack. Name the 3 ipsilateral reflexes. The three ipsilateral reflexes are: 1. stretch reflex. 2. tendon reflex. 3. withdrawal reflex.
What are examples of reflexes?
For example, if you put your hand on a hot stove, a reflex causes you to immediately remove your hand before a "Hey, this is hot!" message even gets to your brain. Other protective reflexes are blinking when something flies toward your eyes or raising your arm if a ball is thrown your way.
Is the stretch reflex ipsilateral or contralateral?
ipsilateral reflexStretch Reflex This is a rapid, monosynaptic (single synapse), ipsilateral reflex that helps to maintain the length of muscles and contributes to joint stabilization.
What is the difference between ipsilateral and contralateral reflexes?
As adjectives the difference between contralateral and ipsilateral is that contralateral is on the opposite side of the body while ipsilateral is (anatomy|medicine) on the same side of the body.
What is the example of reflex action?
Reflex action is a sudden and involuntary response to stimuli. It helps organisms to quickly adapt to an adverse circumstance that could have the potential to cause bodily harm or even death. Pulling our hands away immediately after touching a hot or cold object is a classic example of a reflex action.
What is ipsilateral reflex?
a reflex in which the response occurs on the side of the body that is stimulated.
Which reflex stimulates ipsilateral extensors?
The crossed extensor reflex is contralateral, meaning the reflex occurs on the opposite side of the body from the stimulus.
What is an innate reflex?
Definitions of innate reflex. an automatic instinctive unlearned reaction to a stimulus. synonyms: inborn reflex, instinctive reflex, physiological reaction, reflex, reflex action, reflex response, unconditioned reflex.
Which area of the nervous system integrates reflexes to stimuli?
The central nervous system CNS is responsible for integrating sensory information and responding accordingly. It consists of two main components: The spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It also controls simple musculoskeletal reflexes without input from the brain.
What is tendon reflex?
Tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflexes or tendon jerks) are monosynaptic stretch reflexes, elicited during clinical examination, by percussion of the tendon of a muscle. This causes rapid, brief stimulation of dynamic stretch receptors. Each tendon reflex is subserved by specific spinal cord segments: Reflex.
What are the 4 types of reflexes?
We have different types of reflexes in the body. Four key examples are the stretch reflex, the flexor reflex, the crossed-extensor reflex, and the Golgi tendon reflex.
What are 3 reflexes in humans?
Types of human reflexesBiceps reflex (C5, C6)Brachioradialis reflex (C5, C6, C7)Extensor digitorum reflex (C6, C7)Triceps reflex (C6, C7, C8)Patellar reflex or knee-jerk reflex (L2, L3, L4)Ankle jerk reflex (Achilles reflex) (S1, S2)
What is reflex action give Example Class 10?
Reflex action is the extremely quick, automatic, sudden action in response to something in the environment. Example- i) Immediately pulling back of fingers after touching a hot plate. ii) Closing of eyes when flashed with high intensity light. iii) Salivation when hungry.
What happens when you step on a sharp object?
Imagine what would happen if, when you stepped on a sharp object, it elicited a strong withdrawal reflex of your leg. You would likely topple over. In order to prevent this from happening, as the flexor (withdrawal) reflex involving the injured leg happens, an extension reflex of the opposite (contralateral) leg occurs at the same time, creating a crossed-extensor reflex. In this case, the ipsilateral limb reacts with a withdrawal reflex (stimulating flexor muscles and inhibiting extensor muscles on same side), but the contralateral extensor muscles contract so that the person can appropriately shift balance to the opposite foot during the reflex.
What is the knee jerk reflex?
Along with the monosynaptic activation of the alpha motor neuron, this reflex also includes the activation of an interneuron that inhibits the alpha motor neuron of the antagonistic muscle. This aspect of the reflex ensures that contraction of the agonist muscle occurs unopposed.
What is a monosynaptic reflex?
This is a rapid, monosynaptic (single synapse), ipsilateral reflex that helps to maintain the length of muscles and contributes to joint stabilization. A common example of this reflex is the knee jerk reflex that is elicited by a rubber hammer striking against the patellar tendon, such as during a physical exam.
Why are somatic reflexes important?
Because reflexes are quick, it makes sense that somatic reflexes are often meant to protect us from injury. As examples, reflexes contribute to the maintenance of balance and rapid withdrawal of the hand or foot from damaging stimuli. Somatic reflexes can either be intrinsic (present at birth) or learned.
How many components are there in the reflex arc?
The reflex arc consists of 5 components: In a reflex, sensory information activates a receptor that sends information to the CNS via a sensory neuron, some level of processing occurs in the integration center, and then the response is communicated to the effector target via the motor neurons.
What is the reflex arc?
A reflex is an unlearned, rapid, involuntary and predictable response. A reflex arc is a neural pathway involved in a reflex. The reflex arc consists of 5 components: 1. sensory receptor.
Which limb reacts with a withdrawal reflex?
In this case, the ipsilateral limb reacts with a withdrawal reflex (stimulating flexor muscles and inhibiting extensor muscles on same side), but the contralateral extensor muscles contract so that the person can appropriately shift balance to the opposite foot during the reflex. Crossed-Extensor Reflex.
