What foods are monosaccharide?
Monosaccharides Glucose -- the body's main source of energy and is found in fruit such as pasta, whole grain bread, legumes and a range of vegetables. Fructose -- this 'fruit sugar' found in foods such as fruit, honey, some vegetables and soft drinks.
What is the most common monosaccharides?
There are 3 monosaccharides:
- Glucose.
- Fructose.
- Galactose.
What is the structure of a typical monosaccharide?
Structure of Monosaccharides. The chemical formula that most monosaccharides have is C x (H2O) y, where generally x≥ 3.The molecule is always formed by three elements and three elements only: Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O). The molecule of monosaccharides is very small and compact in size.
What is the most common monosaccharide?
• The most common monosaccharide found in nature is glucose. It is produced by photosynthesis in plants. Glucose is stored in linked chains in some plants. Starch is the name for these chains. Corn, potatoes, rice, and wheat are all examples of starchy foods.
What are the 10 examples of monosaccharides?
List of monosaccharidesTrioses: Aldotriose: glyceraldehyde. ... Tetroses: Aldotetrose: erythrose and threose. ... Pentoses: Aldopentoses: arabinose, lyxose, ribose and xylose. ... Hexoses: ... Heptoses: ... Octoses: octolose, 2-keto-3-deoxy-manno-octonate.Nonoses: sialose.
What are 3 examples of monosaccharides?
Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch).
What are the 4 types of monosaccharides?
Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide. Galactose, mannose, fructose and ribose are also of major biological importance.
What is monosaccharide and its examples?
In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building blocks of a more complex form of sugars such as oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Examples are fructose, glucose, and ribose. The term monosaccharide etymologically means “single saccharide”.
What are the 3 most common monosaccharides?
The three most common monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. In addition to these three sugars, the monosaccharide category also includes sugar alcohols and pentoses.
Which is the best example of monosaccharide?
Common examples of simple sugars or monosaccharides are glucose and fructose. Both of these monosaccharides are referred to as hexoses, since they have six carbons. Glucose is abundant in many plant sources, and makes up sweeteners such as corn sugar and grape sugar.
What are the 3 disaccharides?
Disaccharides. Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide units, linked together with glycosidic bonds in the α or β orientation. The most important of them are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
How many monosaccharides are there?
There are nine common monosaccharides found in vertebrate glycoconjugates (Figure 2.4). Once incorporated into a glycan, these nine monosaccharide building blocks can be further modified to generate additional sugar structures.
Is glucose a monosaccharide?
Glucose is classified as a monosaccharide because it cannot be broken down further by hydrolysis. It is further classified as a hexose because of its six-carbon skeleton and as an aldose, because of the presence of an aldehyde group on carbon 1.
What is a monosaccharide quizlet?
Monosaccharide is one sugar unit (hexose sugar) and examples are : glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, and deoxyribose. They are called simple sugars, including glucose, fructose, and galactose. They are mostly compared upon glucose.
Is starch a monosaccharide?
Glucose, galactose, and fructose are common monosaccharides, whereas common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose. Starch and glycogen, examples of polysaccharides, are the storage forms of glucose in plants and animals, respectively.
What are monosaccharides simple?
Definition of monosaccharide : a sugar that is not decomposable into simpler sugars by hydrolysis, is classed as either an aldose or ketose, and contains one or more hydroxyl groups per molecule. — called also simple sugar.
What are 3 examples of disaccharides?
Disaccharides. Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide units, linked together with glycosidic bonds in the α or β orientation. The most important of them are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
What are the 3 polysaccharides?
Sometimes known as glycans, there are three common and principal types of polysaccharide, cellulose, starch and glycogen, all made by joining together molecules of glucose in different ways. It has been estimated that 50% of the world's organic carbon is found in one molecule; cellulose.
What are four examples of polysaccharides?
Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, chitin, glycogen, starch, and hyaluronic acid.
What is an example of a disaccharide?
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar ) is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides (simple sugars) are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
What are some examples of monosaccharides?
Examples of Monosaccharides: 1. Glucose. It is the most important carbohydrate fuel in human cells and is concentrated in the blood. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. Glucose provides a source of energy for the human body and is the most important simple sugar used for human metabolism.
What is monosaccharide in science?
Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates and the single form of sugar. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are often called single sugars. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates such as disaccharides and polysaccharides. Physically, they are usually colorless, can dissolve in water, ...
What is the most important simple sugar used for human metabolism?
Glucose provides a source of energy for the human body and is the most important simple sugar used for human metabolism. The small size and solubility in water of glucose molecules allows them to pass through the cell membrane into the cell. Energy is released when the molecules are metabolized.
What are some examples of fructose?
2. Fructose. It is a non-reducing sugar. Fructose reacts with glucose to make sucrose. Cherries are an example of fructose. Commercially, fructose is frequently derived from sugar cane, sugar beets, and corn. About 240,000 tons of crystalline fructose is produced annually.
Is galactose a monosaccharide?
It can be present in its free form or with other sugars. Most commonly it is known as a component of the milk sugar, lactose. Yogurt is an example of galactose. Galactose is a monosaccharide sugar that is less sweet that glucose and fructose.
Can sugar be a cause of diabetes?
This type of fluctuation in blood sugar, if it occurs frequently, can lead to blood sugar dysregulation conditions such as hypoglycemia and symptoms of diabetes. Processed foods often add high amounts of monosaccharides such as fructose and glucose to promote a sweet taste.
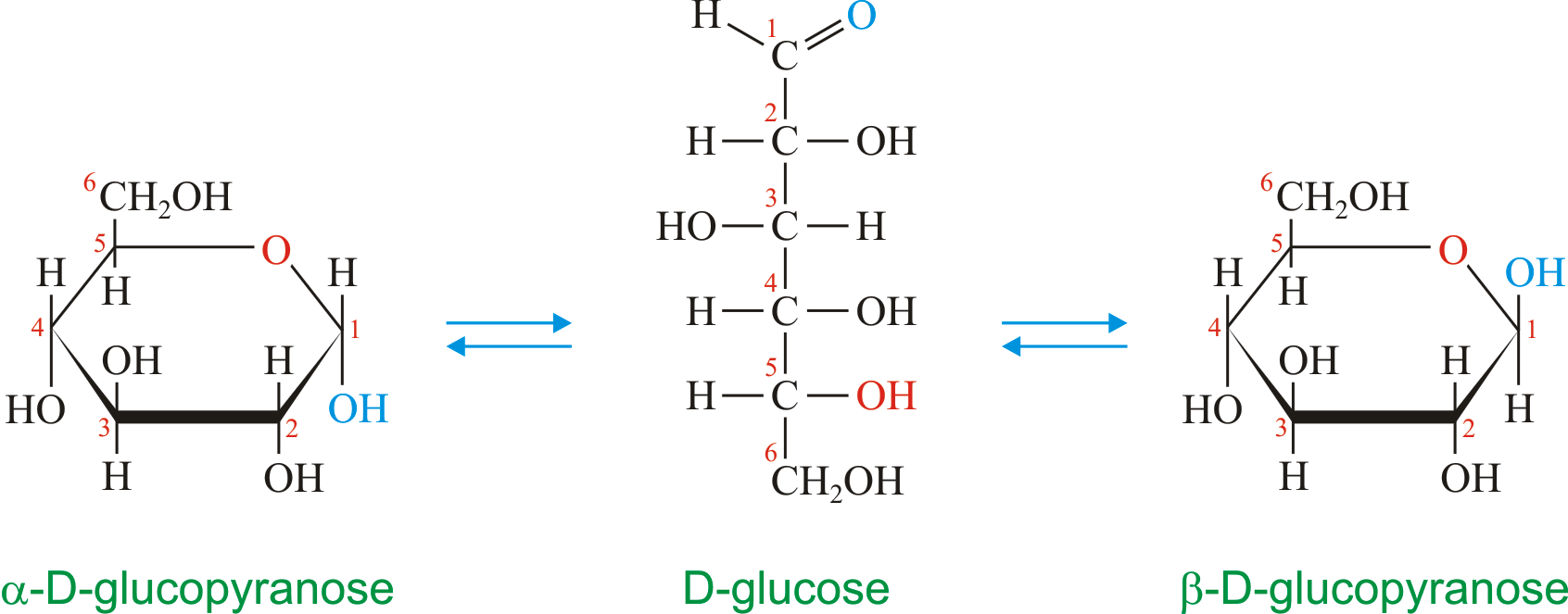
Structure of monosaccharides
As explained in the article on carbohydrates, monosaccharides are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. They can be shown in their linear or ring structure. Have a look at figures 1 and 2, which show the two structures of the same molecule.
Types of monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are categorised according to how many atoms of carbon they contain. These are the three most common types:
Examples of monosaccharides
You will come across three monosaccharides classed as the most important in nutrition: glucose, galactose, and fructose. However, these are not the only ones. Deoxyribose and ribose are of great importance too, being the bases of DNA and RNA.
Monosaccharides form disaccharides and polysaccharides
Monosaccharides are joined together in a process called condensation. The condensation reaction of certain monosaccharides results in the formation of disaccharides and polysaccharides. In disaccharides, two monosaccharides are bonded, while in polysaccharides, there are many (poly- stands for ‘many’).
Monosaccharides
A monosaccharide is a simple carbohydrate. It is an organic biological molecule composed of one molecule of sugar. Monosaccharides are building blocks (monomers) of larger molecules of carbohydrates (polymers).
What is saccharide made of?
They are composed of atoms of Carbon, Hydrogen and to a lesser extent Oxygen, so they were also sometimes called carbohydrates ...
What is the sugar in mushrooms?
Trehalose . Double sugar present in mushrooms and mushrooms, as well as the hemolymph of insects. You can suffer from intolerance to this sugar, lacking the enzyme trehalase.
What is the name of the sugar that contains six carbon atoms?
Galactose . Sugar of six carbon atoms, which together with glucose make up lactose and give it all its nutritional and energetic potential.
What is the main sweetener for humans?
It is the main sweetener for human consumption. Lactose . Resulting from the binding of glucose and galactose, it is secreted in mammary glands of mammals to feed its offspring, and is fermented by lactic acid bacteria during the making of cheese or yogurt. Maltose .
How many atoms are in glucose?
Glucose . Composed of six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms, it is in a free state in fruits and honey. It is the basic energy substance of life.
What is malt sugar?
Known as malt sugar, it contains a high glycemic load and appears naturally in germinating barley grains, as well as beer and other derivatives of this cereal. Cellobiose . Disaccharide composed of two molecules of glucose, appears during the hydrolysis of cellulose and is characterized by being reducing. Trehalose .
Which model obeys the amount of molecules present in each molecule?
Its main classification model, obeys to the amount of molecules present in each, namely: monosaccharides, those composed of a simple molecule of sugar; disaccharides, composed of two molecules joined in one; and polysaccharides, chains of variable complexity that are composed of multiple sugar molecules.
What are the most common monosaccharides in foods?
The most common monosaccharides provided by foods are glucose, fructose and galactose.
What are some foods that contain monosaccharides?
Sweet foods such as honey and cane sugar are rich in monosaccharides, but a wide variety of other foods, such as dairy products, beans and fruit, also contain these simple sugars.
What foods contain galactose?
Dairy products are the richest food sources of galactose. Milk, butter, sour cream, ice cream, yogurt and other dairy products don’t contain actual galactose, but they do have a sugar called lactose, which the body breaks down into glucose and galactose. Ingredients derived from dairy products, such as whey protein, dry milk solids and casein, can also contribute galactose. Fermented and aged dairy products such as cheddar cheese and yogurt generally contain less sugar.
Which fruits contain fructose?
Fruits. Fruits, especially apples, cherries, grapes, guavas, lichees, honeydew melon, watermelon, mangoes, papayas, pears, persimmons and pineapple, are the richest whole-food sources of the monosaccharide fructose. Unless you have a fructose intolerance, health professionals generally recommend getting most of your simple sugars from whole fruits, ...
Which vegetables have less sugar?
Vegetables that tend to contain more fructose include artichokes, asparagus, beans, broccoli, cabbage, chicory, onions and leeks, peanuts, tomatoes and zucchini.
Does cheese have galactose?
Ingredients derived from dairy products, such as whey protein, dry milk solids and casein, can also contribute galactose. Fermented and aged dairy products such as cheddar cheese and yogurt generally contain less sugar. While meats generally contribute little in the way of sugars, organ meats such as liver are the exception.
Is honey a simple sugar?
In addition to table sugar, which is made from either cane or beets, natural sweeteners such as honey and molasses are high in simple sugars. Honey is mostly fructose. Corn syrup -- the regular kind, not high-fructose -- and maple syrup are mostly glucose.

Monosaccharides
Structures of Monosaccharides
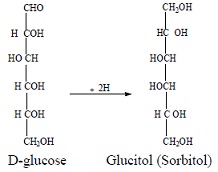
- The simplest monosaccharides are trioses such as glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone, both of which have the molecular formula C3H6O3, glyceraldehyde is aldose while dihydroxyacetone is ketose as shown below: The majority of famed monosaccharides are ribose, C5H10O5, glucose C6H12O6, and fructose C6H12O6. Ribose is aldopentose, glucose is aldohexose while fructose i…
Presence of Asymmetric Carbon Atoms
- On careful examination of monosaccharide molecules, we see that they contain one or more chiral carbon atoms. For example, glucose has four chiral carbon atoms (carbons 2, 3, 4, and 5). We know that if the molecule has n chiral carbon atoms, it will have 2n optical isomers. Therefore, glucose has 24 or sixteen optical isomers. Three of these are sixteen aldohexoses which are D-g…
Examples of Monosaccharide
- Glucose Glucose occurs in nature in an autonomous as well as a related fashion. It is present in sweet fruits and honey. Ripe grapes contain about 20% glucose and that is why it is also known as grape sugar. Glucose in related form is substantial in polysaccharides such as cane sugar and starch and cellulose. Preparation of Glucose 1. From Sucrose ...
Sample Questions
- Question 1: Why are carbohydrates usually optically active? Answer: Question 2: What are monosaccharides? Answer: Question 3: Explain what is meant by the pyranose structure of glucose? Answer: Question 4: What are the structural features of reducing sugars? Answer: Question 5: What are the two functions of carbohydrates in plants? Answer: