
What are the four types of sampling?
What are the 4 types of non probability sampling?
- Accidental, Haphazard or Convenience Sampling. One of the most common methods of sampling goes under the various titles listed here.
- Purposive Sampling. In purposive sampling, we sample with a purpose in mind.
- Modal Instance Sampling.
- Expert Sampling.
- Quota Sampling.
- Heterogeneity Sampling.
- Snowball Sampling.
What are some examples of sampling techniques?
Real world examples of simple random sampling include:
- At a birthday party, teams for a game are chosen by putting everyone's name into a jar, and then choosing the names at random for each team.
- On an assembly line, each employee is assigned a random number using computer software. ...
- A restaurant leaves a fishbowl on the counter for diners to drop their business cards. ...
What is multi stage sampling method?
Multistage sampling is a method of obtaining a sample from a population by splitting a population into smaller and smaller groups and taking samples of individuals from the smallest resulting groups.. For example, suppose we’re interested in estimating the average household income in the U.S. For simplicity, let’s assume there are 100 million households.
What are the types of random sampling methods?
Types of Random Sampling Methods
- Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population.
- Systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is the selection of specific individuals or members from an entire population. ...
- Stratified sampling. ...
- Cluster sampling. ...
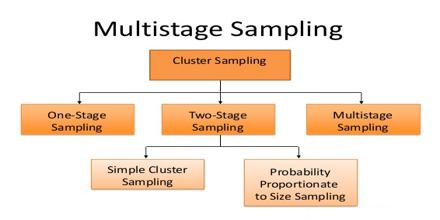
What is an example of two stage sampling?
Two-stage sampling is used when the sizes of the clusters are large, making it difficult or expensive to observe all the units inside them. This is, for example, the situation when one wishes to estimate total landing per trip of a fishery with many landing sites and also with a large number of vessels.
What is a good example of cluster sampling?
An example of single-stage cluster sampling – An NGO wants to create a sample of girls across five neighboring towns to provide education. Using single-stage sampling, the NGO randomly selects towns (clusters) to form a sample and extend help to the girls deprived of education in those towns.
What is multiple sampling method?
Multiple sampling is an extension of double sampling. It involves inspection of 1 to k successive samples as required to reach an ultimate decision. Mil-Std 105D suggests k=7 is a good number. Multiple sampling plans are usually presented in tabular form. Procedure for multiple sampling.
What is multistage and stratified random sampling?
With Stratified Sampling, the sample includes the elements from each stratum. With cluster sampling, in contrast, the sample includes the elements from the sampled cluster. With Multistage Sampling, we select a sample by using the combinations of different samples.
What is the difference between cluster and multistage sampling?
Cluster sampling: The process of sampling complete groups or units is called cluster sampling, situations where there is any sub-sampling within the clusters chosen at the first stage are covered by the term multistage sampling.
What is an example of a stratified sample?
A stratified sample is one that ensures that subgroups (strata) of a given population are each adequately represented within the whole sample population of a research study. For example, one might divide a sample of adults into subgroups by age, like 18–29, 30–39, 40–49, 50–59, and 60 and above.
Is multistage sampling the same as stratified?
What is the Difference between Stratified Sampling and Multistage Sampling? In stratified sampling, all groups are samples but it is different in the case of multistage sampling as only a subset of the groups or clusters is sampled.
Which of the following are the advantages of multi stage sampling?
Advantages of Multistage Sampling Practical for primary data collection for large populations that are geographically dispersed. Reduces the costs and time associated with data collection. Provides flexibility, as researchers can break down the population as often as necessary to create the sample population they need.
What is design effect in multistage sampling?
A design effect(DEFF) is an adjustment made to find a survey sample size, due to a sampling method (e.g. cluster sampling, respondent driven sampling, or stratified sampling) resulting in larger sample sizes (or wider confidence intervals) than you would expect with simple random sampling(SRS).
What are the 5 main types of sampling?
Probability sampling methodsSimple random sampling.Systematic sampling.Stratified sampling.Cluster sampling.Convenience sampling.Purposive sampling.Snowball sampling.
What is multistage stratified?
Multistage sampling divides large populations into stages to make the sampling process more practical. A combination of stratified sampling or cluster sampling and simple random sampling is usually used.
What is a multi stage?
Definition of multistage 1 : having successive operating stages especially : having propulsion units that operate in turn multistage rockets. 2 : conducted by or occurring in stages a multistage investigation.
Where is cluster sampling used?
Cluster sampling is commonly used by marketing groups and professionals. When attempting to study the demographics of a city, town, or district, it is best to use cluster sampling, due to the large population sizes. Cluster sampling is a two-step procedure.
What is cluster sampling in simple words?
Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method in which you divide a population into clusters, such as districts or schools, and then randomly select some of these clusters as your sample. The clusters should ideally each be mini-representations of the population as a whole.
What are the three types of cluster sampling?
There are three types of cluster sampling: single-stage, double-stage and multi-stage clustering. In all three types, you first divide the population into clusters, then randomly select clusters for use in your sample.
How do you use cluster sampling?
How to cluster sample?First, choose the target population that you wish to study and determine your desired sample size.Then, divide your sample into clusters. ... Next, select clusters by a random selection process. ... In single-stage sampling, collect data from each individual unit of the clusters you selected in Step 3.More items...•
What is meant by probability sampling, and how does it work?
Ans. Probability sampling is selecting individuals for a sample from a target population which ensures that it is representative of the general p...
What is multistage sampling, and how does it work?
Ans. Multistage sampling is a method for selecting the sample by dividing up the entire population into progressively smaller clusters.
What are the sampling methods that can be used in multistage sampling?
Ans. In multistage sampling, probability or non-probability sampling methods can be used.
What is multistage sampling?
In multistage sampling, or multistage cluster sampling, you draw a sample from a population using smaller and smaller groups (units) at each stage. It’s often used to collect data from a large, geographically spread group of people in national surveys.
Why do you need a larger sample size for a multistage sample?
Compared to simple random samples, you’ll need a larger sample size for a multistage sample to achieve the same statistical inference properties.
How to select clusters in a cluster?
You begin by stratifying your clusters at the first stage. After stratification, you select clusters using a probability sampling method.
Why do large scale surveys use cluster sampling?
Large-scale surveys often use a combination of cluster and stratified sampling at the first stage to help ensure that the units are representative of the larger population. This is called a stratified multistage sample.
What is single stage probability sampling?
In single-stage probability sampling, you start with a sampling frame, which is a list of every member in the entire population. It should be as complete as possible, so that your sample accurately reflects your population.
What is the first stage of cluster sampling?
At the first stage, like in cluster sampling, you’ll divide your population into clusters that are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
How to do single stage sampling?
In single-stage sampling, you divide a population into units (e.g., households or individuals) and select a sample directly by collecting data from everyone in the selected units.
What is Multistage Sampling?
Multistage sampling, also called multistage cluster sampling, is exactly what it sounds like – sampling in stages.
Why is multistage sampling important?
Multistage sampling makes data collection more practical for large populations, especially when a complete list of all elements of a population does not exist or isn’t suitable. It is also often used when costs and implementation time need to be minimised.
What information is required to form a multistage random sampling frame?
To form the sampling frames for multistage random sampling, group-level information is required, sometimes at a national level depending on the target population.
What is phase sampling?
It is a more complex form of cluster sampling, in which smaller groups are successively selected from large populations to form the sample population used in your study. Due to this multi-step nature, the sampling method is sometimes referred to as phase sampling.
What is the best way to select the final sample group from the sub-groups?
Select the final sample group from the sub-groups using a form of probability sampling, such as simple random sampling or systematic sampling.
Is a sample 100% representative of the entire population?
The sample will not be 100% representative of the entire population, and there is the potential for biases if there is little variance between members in a sub-group. If, for example, we want to study the vaccination rate in a city, we may divide the city into its towns, and then randomly select households from each town and count the number of vaccinated children within them. Logically, however, it’s likely that when one child in a household is vaccinated, their siblings will also be vaccinated; this can distort the results.
Multistage Sampling: Types, Applications, Pros & Cons
In multistage sampling or multistage cluster sampling, a sample is drawn from a population through the use of smaller and smaller groups (units) at each stage of the sampling. In this article, we are going to discuss multistage sampling, its uses, the advantages, and the disadvantages.
What is Multistage Sampling
Multistage sampling is defined as a method of sampling that distributes the population into clusters or groups so as to conduct research. This is a complex form of group sampling, during which the significant groups from the selected population are divided into subgroups at different stages.
Types of Multistage Sampling
There are two types of multistage sampling and they are multistage cluster sampling and multistage random sampling.
How to Conduct Multistage Sampling
There are four multistage steps that must be followed to conduct multistage sampling:
What are the Applications of Multistage Sampling?
Multistage sampling can be applied to a multistage design where the population is too large and it is practically impossible to research every individual.
What is the Difference between Stratified Sampling and Multistage Sampling?
In stratified sampling, all groups are samples but it is different in the case of multistage sampling as only a subset of the groups or clusters is sampled. Also, only sub-samples are drawn in the second stage from the clusters selected in the first stage so that the total groups can be well estimated.
What is the Difference between Multistage and Multistage Sampling
Multiphase sampling and multistage sampling are sometimes used interchangeably. However, there are still a few things that distinguish the two.
What is multistage cluster sampling?
Multistage cluster sampling is a complex type of cluster sampling. The researcher divides the population into groups at various stages for better data collection, management, and interpretation. These groups are called clusters.
What are the benefits of multistage sampling?
Here are the top 8 benefits obtained from multistage sampling: It allows researchers to apply cluster or random sampling after determining the groups. Researchers can apply multistage sampling to make clusters and sub-clusters until the researcher reaches the desired size or type of group. Researchers can divide the population into groups without ...
Why do we use multiphase sampling?
Multiphase sampling reduces the time taken to research an area. It also keeps a tab on the cost of the research. The information collected from the samples is used to draw inferences from the population as a whole.
Why is finding the right survey sample important?
The researcher mindfully chooses the audience. It decreases the issues faced during random sampling. It does not need a complete list of all the members of the target population, dramatically reducing sample preparation cost.
Can researchers divide a population into groups?
Researchers can divide the population into groups without restrictions. It allows flexibility to the researchers to choose the sample carefully.
Is multiphase sampling a conventional method?
Keep in mind that as there’s no exact definition of multiphase sampling, there’s no conventional method on a route to mix the sampling methods (such as cluster, stratified, and simple random).
What is multistage sampling?
In multistage sampling, or multistage cluster sampling, you draw a sample from a population using smaller and smaller groups at each stage.
What is sampling in statistics?
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
What is categorical variable?
Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups. This includes rankings (e.g. finishing places in a race), classifications (e.g. brands of cereal), and binary outcomes (e.g. coin flips).
What is a sample in research?
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
What is the best method to measure something?
If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods.
What is methodology in research?
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project. It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.

Single-Stage vs Multistage Sampling
- In single-stage sampling, you divide a population into units (e.g., households or individuals) and select a sample directly by collecting data from everyone in the selected units. In multistage sampling, you divide the population into smaller and smaller groupings to create a sample using several steps. You can take advantage of hierarchical groupings (e.g., from state to city to neigh…
Single-Stage Sampling
- In single-stage probability sampling, you start with a sampling frame, which is a list of every member in the entire population. It should be as complete as possible, so that your sample accurately reflects your population. You can use simple random, systematic, stratified, or cluster sampling methods to select a probability samplefrom your sampling frame.
Multistage Sampling
- Multistage sampling is often considered an extended version of cluster sampling. In multistage sampling, you divide the population into clusters and select some clusters at the first stage. At each subsequent stage, you further divide up those selected clusters into smaller clusters, and repeat the process until you get to the last step. At the las...
First Stage: Primary Sampling Units
- At the first stage, like in cluster sampling, you’ll divide your population into clusters that are mutually exclusive and exhaustive. Then, you’ll choose some of your clusters to be your primary sampling units, ideally using a probability sampling method. You can use any of the single-stage sampling methods to select your PSUs. Large-scale surveys often use a combination of cluster …
Second Stage: Secondary Sampling Units
- At the second stage, you divide up your PSUs to get to smaller sampling units. You’ll select only some of these smaller units from within each selected PSU: these are your secondary sampling units (SSUs). If you end your sampling at this point, it’s called two-stage or double-stage sampling. This would mean collecting data from everyone in your secondary sampling units: all students i…
Final Stage: Ultimate Sampling Units
- You can keep repeating the process of dividing up each sampling unit further and selecting a few of them for the next stage. At the final stage, you end with your ultimate sampling units.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Multistage sampling is effective and flexible with large samples, but it may be difficult to ensure your sample is representative of the population.