
| Probability sampling | Non-probability sampling |
| The samples are randomly selected. | Samples are selected on the basis of the ... |
| Everyone in the population has an equal ... | Not everyone has an equal chance to part ... |
| Researchers use this technique when they ... | Sampling bias is not a concern for the r ... |
| Useful in an environment having a divers ... | Useful in an environment that shares sim ... |
What are the different types of nonprobability sampling?
6 rows · Here are three simple examples of non-probability sampling to understand the subject better. An ...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of non probability sampling?
Jun 26, 2020 · What is an example of non probability sampling? Examples of nonprobability sampling include: Convenience, haphazard or accidental sampling – members of the population are chosen based on their relative ease of access. To sample friends, co-workers, or shoppers at a single mall, are all examples of convenience sampling. Click to see full answer.
What are the major types of nonprobability sampling designs?
Apr 10, 2022 · What Is Probability And Non-probability Sampling Examples? carvadia; What is probability and non-probability sampling examples? For example, if you had a population of 100 people, each person would have odds of 1 out of 100 of being chosen. With non-probability sampling, those odds are not equal. For example, a person might have a better chance of …
What are the types of non random sampling?
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling type that mimics a pyramid system in its selection pattern. You choose early sample participants, who then go on to recruit further sample participants until the sample size has been reached.
What are the types of non-probability sampling?
The commonly used non-probability sampling methods include the following.Convenience or haphazard sampling. ... Volunteer sampling. ... Judgement sampling. ... Quota sampling. ... Snowball or network sampling. ... Crowdsourcing. ... Web panels. ... Advantages and disadvantages of non-probability sampling.Sep 2, 2021
What are the four types of non-probability sampling?
There are five main types of non-probability sample: convenience, purposive, quota, snowball, and self-selection.
Which of the following is not an example of non-probability sampling?
In judgmental sampling researchers select units from the population based on their knowledge and judgement about the unit. This kind of sampling does not provide equal probability of a unit being chosen.
Which of the following is not an example of a non random sampling technique?
Q.Which of the following is not a type of nonrandom samplingB.convenience samplingC.quota samplingD.purposive samplingAnswer» a. cluster sampling1 more row
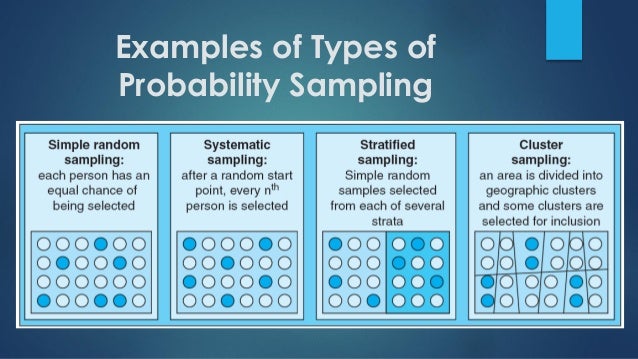
What is probability sampling?
Definition:Probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a larger population using a method based on the theory of probability. For a participant to be considered as a probability sample, he/she must be selected using a random selection. The most critical requirement ...
What is simple random sampling?
Simple random sampling, as the name suggests, is an entirely random method of selecting the sample. This sampling method is as easy as assigning numbers to the individuals (sample) and then randomly choosing from those numbers through an automated process.
How does cluster sampling work?
Cluster sampling usually analyzes a particular population in which the sample consists of more than a few elements, for example, city, family, university, etc. Researchers then select the clusters by dividing the population into various smaller sections.

Convenience Sampling
- This is one of the non-probability sampling techniques where the samples that are readily available in the entire population get selected by the researcher.Convenience sampling is used by researchers because the samples are easy to recruit, and not necessarily because the researcher considers selecting a sample that represents the entire population...
Consecutive Sampling
- Consecutive sampling is similar to convenience sampling in method, although there are a few differences. In this type of non-probability sampling, the researcher selects a person or a group from the population and conducts research with them over a period of time. Thereafter, the result from the research is analyzed and then the researcher goes on to another group from the popula…
Quota Sampling
- To understand quota sampling, let us look at this example. A researcher wants to study the career growth of the employees in an organization with 400 employees. To better understand the population, the researcher will select a sample from the population to represent the total employees or population. If the researcher is interested in a particular department within the pop…
Judgmental Or Purposive Sampling
- In a judgmental sampling technique, the samples are selected based on the credibility and knowledge of the researcher. This means that only those deemed fit by the researcher are selected to participate in the research. It is worthy of note thatpurposive or judgmental samplingis not scientific and it can easily accommodate influence or bias from the researcher. For example…
Snowball Sampling
- Snowball sampling is useful for finding samples that are difficult for the researcher to locate. Researchers make use of snowball sampling techniqueswhen their sample size is not readily available and also small. So this is carried out like a referral program where the researcher finds suitable members and solicits help in finding similar members so as to form a considerably goo…
Example 1
- We have earlier established that quota sampling is a method of grouping your sample into strata or groups. Let us assume that a researcher wants to examine the differences in male and female students of a school with a 20,000 population. To derive a true representative of the larger population from the sample (students), the number of students that the researcher will include i…
Example 2
- A convenience sampling technique is simply one where the people you select for inclusion or as participants in your research sample are those who are most available. Using the example of the 20,000 university students above, let us assume that the researcher is only interested in achieving a sample size of maybe 300 students. To achieve this, the researcher can stand at one of the m…
Example 3
- Purposeful sampling focuses on the judgment of the researcher and the aim of the research in selecting the sample group. If the aim of the research is to launch beauty products that cater to people with vitiligo, the researcher will then select a few people with this condition as the sample group for the research. The few people might not entirely be the best representative for the popu…
Conclusion
- If you want to conduct research that gives everyone a fair opportunity of participation, then you should consider non-probability sampling. Also, if you are working with a stringent budget, and need to work with a lesser time frame, you should also consider using the non-probability sampling technique. Furthermore, it is important that you use the right sampling technique for th…