
What are four products of recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA drug products have been developed that represent the communicator, structural, and modifier classes of proteins. Recombinant communicator proteins include interferons alfa-2a and alfa-2b and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (immune system modulators); epidermal growth factor and erythropoietin (tissue repair ...
What are the strategies of recombinant DNA technology?
What are the Strategies of Recombinant DNA Technology? There is no single method of recombinant DNA technology, but it involves several steps as given below: 1. Isolation of DNA (also called insert DNA, target DNA, foreign DNA) of known function from an organism (A). 2. Enzymatic cleavage (B) and joining (C) of insert DNA to another DNA ...
What can be used to make recombinant DNA?
Recombinant indicates it's not a natural molecules, it is artifical. Ligase. To create recombinant DNA we rely on the hydrogen bonds and complementarity of the bases, but this is unstable, because hydrogen bonds aren't covalent bonds. You increase the temperature, 95 degrees, and strands can separate.
What are some examples of recombinant DNA?
What are some examples of recombinant DNA? Examples of recombinant DNA molecules that are important to humans are pharmaceuticals like human insulin and antibiotics. The human insulin gene was recombined with bacterial DNA so that we can easily and safely generate large amounts of insulin.
What is an example of DNA technology?
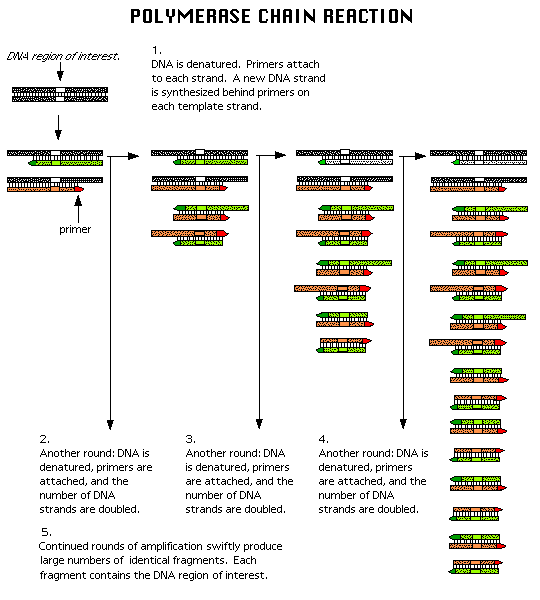
DNA technology is important to both basic and applied (practical) biology. For instance, a technique used to make many copies of a DNA sequence, called polymerase chain reaction (PCR), is used in many medical diagnostic tests and forensics applications as well as in basic laboratory research.
What is a recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA technology comprises altering genetic material outside an organism to obtain enhanced and desired characteristics in living organisms or as their products. This technology involves the insertion of DNA fragments from a variety of sources, having a desirable gene sequence via appropriate vector [12].
What are 3 uses of recombinant DNA?
The below mentioned article will highlight the three important applications of recombinant DNA technology. The three important applications are: (1) Applications in Crop Improvement (2) Applications in Medicines and (3) Industrial Applications.
What is the most common application of recombinant DNA?
basic researchThe most common application of recombinant DNA is in basic research, in which the technology is important to most current work in the biological and biomedical sciences. Recombinant DNA is used to identify, map and sequence genes, and to determine their function.
What are the 7 steps in recombinant DNA technology?
Table of ContentsStage # 1. Isolation of the Genetic Material (DNA):Stage # 2. Cutting of DNA at Specific Locations:Stage # 3. Isolation of Desired DNA Fragment:Stage # 4. Amplification of Gene of Interest using PCR:Stage # 5. Ligation of DNA Fragment into a Vector:Stage # 6. ... Stage # 7.
What is recombinant DNA technology quizlet?
recombinant DNA technology. A set of techniques for synthesizing recombinant DNA in vitro and transferring it into cells, where it can be replicated and may be expressed; also known as genetic engineering. biotechnology. The use of living organisms to perform useful tasks; today usually involving DNA technology.
What is the benefit of recombinant DNA technology?
The benefits of recombinant DNA include improvements in cancer research, increased fertility, vaccine production, diabetes treatment and the production of resilient, enriched and plentiful foods.
What is the importance of recombinant DNA technology in environment?
Applications of recombinant DNA technology are discussed as a backdrop for evaluation of the environmental impacts of this technology. Some of applications include using traditional biological techniques for specific purposes, including nitrogen fixation, microbial pesticides, and waste treatment.
How is DNA technology used in medicine?
There are many ways that DNA technology is used to make vaccines, such as altering the pathogen's genes and mimicking surface proteins of harmful pathogens. Therapeutic hormones, such as insulin and human growth hormone, are also the result of DNA technology in medicine.
Which of the following is the best definition for recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA Technology is defined by the Encyclopedia Britannica as “the joining together of DNA molecules from different organisms and inserting it into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science, medicine, agriculture and industry.”
How recombinant DNA is produced?
Recombinant DNA is the method of joining two or more DNA molecules to create a hybrid. The technology is made possible by two types of enzymes, restriction endonucleases and ligase. A restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific sequence of DNA and cuts within, or close to, that sequence.
What is the impact of recombinant DNA technology on genetics and society?
Recombinant DNA technology is likely to also have profound effects on society, including better health through improved disease diagnosis, much better understanding of human gene variation, improved drug and pharmaceutical production, vastly more sensitive and specific crime scene forensics , and production of ...
Why recombinant DNA technology is important?
The technology is important because it enables the creation of multiple copies of genes and the insertion of foreign genes into other organisms to give them new traits, such as antibiotic resistance or a new colour.
What is DNA technology used for?
Recombinant DNA technology has been effectively used to produce various human proteins in microorganisms, such as insulin and growth hormone, used in the treatment of diseases (see Chapter 4: Recombinant DNA Technology and Genetically Modified Organisms).
What is the difference between recombinant DNA and recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA and Protein are important molecules in recombinant DNA technology....Recombinant Protein.Recombinant DNARecombinant ProteinConstituentIt is made up of nucleotides.It is made up of amino acids.LocationIt is synthesised outside the cell, i.e, in vitro.It is synthesised inside the cell, i.e, in vivo.6 more rows
How is recombinant DNA produced?
Recombinant DNA is the method of joining two or more DNA molecules to create a hybrid. The technology is made possible by two types of enzymes, restriction endonucleases and ligase. A restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific sequence of DNA and cuts within, or close to, that sequence.
What is recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA technology is the joining together of DNA molecules from two different species. The recombined DNA molecule is inserted into a host...
When was recombinant DNA technology invented?
The possibility for recombinant DNA technology emerged with the discovery of restriction enzymes in 1968 by Swiss microbiologist Werner Arber. The...
How is recombinant DNA technology useful?
Through recombinant DNA techniques, bacteria have been created that are capable of synthesizing human insulin, human growth hormone, alpha interfer...
What is recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA technology is the joining together of DNA molecules from two different species. The recombined DNA molecule is inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science, medicine, agriculture, and industry. Since the focus of all genetics is the gene, the fundamental goal of laboratory geneticists is to isolate, characterize, and manipulate genes. Recombinant DNA technology is based primarily on two other technologies, cloning and DNA sequencing. Cloning is undertaken in order to obtain the clone of one particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. The next step after cloning is to find and isolate that clone among other members of the library (a large collection of clones). Once a segment of DNA has been cloned, its nucleotide sequence can be determined. Knowledge of the sequence of a DNA segment has many uses.
Why is recombinant DNA used?
Recombinant DNA technology also can be used for gene therapy, in which a normal gene is introduced into an individual’s genome in order to repair a mutation that causes a genetic disease. The ability to obtain specific DNA clones using recombinant DNA technology has also made it possible to add the DNA of one organism to the genome of another.
What is a clone in biology?
In biology a clone is a group of individual cells or organisms descended from one progenitor. This means that the members of a clone are genetically identical, because cell replication produces identical daughter cells each time. The use of the word clone has been extended to recombinant DNA technology, which has provided scientists with the ability to produce many copies of a single fragment of DNA, such as a gene, creating identical copies that constitute a DNA clone. In practice the procedure is carried out by inserting a DNA fragment into a small DNA molecule and then allowing this molecule to replicate inside a simple living cell such as a bacterium. The small replicating molecule is called a DNA vector (carrier). The most commonly used vectors are plasmids (circular DNA molecules that originated from bacteria ), viruses, and yeast cells. Plasmids are not a part of the main cellular genome, but they can carry genes that provide the host cell with useful properties, such as drug resistance, mating ability, and toxin production. They are small enough to be conveniently manipulated experimentally, and, furthermore, they will carry extra DNA that is spliced into them.
What is the next step after cloning?
The next step after cloning is to find and isolate that clone among other members of the library (a large collection of clo nes). Once a segment of DNA has been cloned, its nucleotide sequence can be determined.
What is the goal of genetics?
Since the focus of all genetics is the gene, the fundamental goal of laboratory geneticists is to isolate, characterize, and manipulate genes. Although it is relatively easy to isolate a sample of DNA from a collection of cells, finding a specific gene within this DNA sample can be compared to finding a needle in a haystack.
What is the name of the gene that is added to the genome?
The added gene is called a transgene, which can be passed to progeny as a new component of the genome. The resulting organism carrying the transgene is called a transgenic organism or a genetically modified organism (GMO).
Who was the first person to insert recombinant genes into bacterial cells?
In 1973 American biochemists Stanley N. Cohen and Herbert W. Boyer became the first to insert recombined genes into bacterial cells, which then reproduced. Read more below: Invention of recombinant DNA technology. Restriction enzyme.
What is recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA is a molecule of DNA that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through laboratory techniques. In the lab, bacteria can be transformed with recombinant DNA. Genetic recombination occurs during meiosis in a process known as crossing over.
Why do scientists use recombinant DNA?
Scientists regularly use recombinant DNA to add traits to certain species of bacteria or produce organisms which have additional traits. There is a basic process for getting recombinant DNA into cells, though the exact method varies depending on the specific organism.
Why do bacteria need recombinant DNA?
The final process of creating organisms with recombinant DNA is to allow the cells to cool and grow. Often, the plasmid introduced also has a gene which enables the bacteria to survive antibiotic treatments. When growing the transformed bacteria, an antibiotic is introduced. Any bacteria that survive are ones that have been transformed with recombinant DNA. They now have the plasmid, which includes both the recombinant DNA and a gene for antibiotic resistance.
Why is recombinant DNA important in eukaryotes?
Recombinant DNA in eukaryotes is responsible for increasing genetic diversity. Alleles of genes that were previously linked on a chromosome can be completely redistributed to create new combinations of traits. This process happens regularly during meiosis to mix and match genes from paternal and maternal sources.
How many alleles are there for eye color?
For example, pretend that there are only two alleles for coat color in a population, black and white. There are also two alleles for eye color, brown and blue. If the gene for eye color and the gene for coat color exist on the same chromosome, they are called linked genes. Without recombinant DNA, an organism could only pass on the combination ...
How does genetic engineering help in crop production?
With the advent of genetic engineering, scientists are able to identify and segregate genes of interest and place them in crop species. To increase insect resistance, for instance, scientists have placed genes from bacteria into the DNA of corn, cotton, and other crops. The genes they selected produce the protein Bt.
Which organisms can be added to a plasmid?
In general, the first part of the process includes creating a plasmid which contains the sequence of DNA which will be added to an organism. The simplest organism to add recombinant DNA to is bacteria. Bacterial cells reproduce quickly, which allows many chances for the recombinant DNA to enter a cell and proliferate.
What is recombination DNA?
Recombination DNA technology or rDNA technology is developed to produce essential biologicals on a wide scale.
What crops can be grown with rDNA?
For biotechnology crops like cotton, vegetables, etc. rDNA technology can produce high yielding plants with the desired quality.
What is the role of recombinant hormones in diabetes?
Diabetes is a hormonal deficiency disease caused due to insufficient formation of Insulin in the pancreas. For such patients, pure human insulin is required for treatment.
What hormones are produced by recombinant hormones?
Other recombinant hormones produced are growth hormone (somatotrophin), erythropoietin used in the treatment of anemia.
What bacteria produce B12?
Vitamins like B12 are produced by recombinant bacteria like Paracoccus denitrificans, Propionibacterium shermanii, E.Coli bacteria on a large scale by fermentation. Vitamin-C is produced on a large scale from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zygosaccharomyces bailii yeast and Gluconobacter oxydans bacteria.
Why is recombinant DNA important?from americanhistory.si.edu
Following the success of Humulin, recombinant DNA technology was quickly adopted to replace older methods of producing medical products from human growth hormone to vaccines. Although scientists have since developed new biotechnology techniques, recombinant DNA still plays an important role in the production of several major medical products. Among the objects below are several of the early formulations of Humulin as well as some of the other early recombinant pharmaceuticals produced in the 1980s and 1990s.
How are recombinant pharmaceuticals created?from americanhistory.si.edu
Recombinant pharmaceuticals are created by inserting genes from one species into a host species, often yeast or bacteria, where they do not naturally occur . The genes code for a desired product, and therefore the genetically modified host organisms can be grown and used as a kind of living factory to produce the product. In this case, genes coding for tPA are inserted into cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. The ovary cells produce tPA, which is harvested and used as the active ingredient in Activase.
When was recombinant insulin first made?from si.edu
In 1982 Food and Drug Administration approved Humulin, Eli Lily’s recombinant insulin made from Genentech’s specially modified bacteria. It was the first drug produced through recombinant DNA technology and among the first genetically engineered products to be available to consumers.
Who invented Humulin?from americanhistory.si.edu
Developed by Genentech, the first American biotechnology company, Humulin was licensed to Eli Lilly and became the first marketable product created through recombinant DNA technology. Its licensing by the FDA in October 1982 also made it the first recombinant pharmaceutical approved for use in the United States.
Can a genetically modified host be grown?from americanhistory.si.edu
The genes code for a desire d product, and therefore the genetically modified host organisms can be grown and used as a kind of living factory to produce the product. In this case, genes coding for human white blood cell interferons are inserted into bacteria.
How does recombinant DNA help in biotechnology?
In industries, recombinant DNA technique will help in the production of chemical compounds of commercial importance, improvement of existing fermentation processes and production of proteins from wastes. This can be achieved by developing more efficient strains of microorganisms. Specially developed microorganisms may be used even to clean up the pollutants. Thus, biotechnology, especially recombinant DNA technology has many useful applications in crop improvement, medicines and industry.
What is recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA technology has provided a broad range of tools to help physicians in the diagnosis of diseases. Most of these involve the construction of probes: short Segments of single stranded DNA attached to a radioactive or fluorescent marker. Such probes are now used for identification of infectious agents, for instance, food poisoning Salmonella, Pus forming Staphylococcus, hepatitis virus, HIV, etc. By testing the DNA of prospective genetic disorder carrier parents, their genotype can be determined and their chances of producing an afflicted child can be predicted.
What is genetically transformed plant?
Genetically transformed plants which contain foreign genes are called transgenic plants. Resistance to diseases, insects and pests, herbicides, drought; metal toxicity tolerance; induction of male sterility for plant breeding purpose; and improvement of quality can be achieved through this recombinant DNA technology. BT-cotton, resistant to bollworms is a glaring example.
How can a dispute of parentage be solved?
Disputed cases of parentage can now be solved most accurately by recombinant technology than by blood tests.
What are the root nodules in cereal plants?
3. Development of Root Nodules in Cereal Crops: Leguminous plants have root-nodules which contain nitrogen fixing bacteria Rhizobium. This bacteria converts the free atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates in the root nodules.
What are the applications of genetic engineering in medicine?
Applications in Medicines: Biotechnology, especially genetic engineering plays an important role in the production of antibiotics, hormones, vaccines and interferon in the field of medicines. 1. Production of Antibiotics: ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the name of the new system of genetic engineering?
6. Gene Therapy : Genetic engineering may one day enable the medical scientists to replace the defective genes responsible for hereditary diseases (e.g., haemophilia, phenylketonuria, alkaptonuria) with normal genes. This new system of therapy is called gene therapy .
Why is rDNA important?
Recombinant DNA technology is an important development in science that has made the human life much easier. In recent years, it has advanced strategies for biomedical applications such as cancer treatment, genetic diseases, diabetes, and several plants disorders especially viral and fungal resistance.
What are some examples of recombinant DNA technology?
For example, insulin is regularly produced by means of recombinant DNA within bacteria. A human insulin gene is introduced into a plasmid, which is then introduced to a bacterial cell. The bacteria will then use its cellular machinery to produce the protein insulin, which can be collected and distributed to patients.
What is the process of recombinant DNA?
There are six steps involved in rDNA technology. These are – isolating genetic material, restriction enzyme digestion, using PCR for amplification, ligation of DNA molecules, Inserting the recombinant DNA into a host, and isolation of recombinant cells.
Genetics
Reproduction
- Eukaryotic organisms that go through sexual reproduction must also go through the process of meiosis, which reduces the genetic material leading to fertilization. During meiosis, the chromosomes of eukaryotes are condensed, and pair with their homologous chromosome. Each pair of homologous chromosomes represents the same sequence of DNA, from different parent…
Example
- For example, pretend that there are only two alleles for coat color in a population, black and white. There are also two alleles for eye color, brown and blue. If the gene for eye color and the gene for coat color exist on the same chromosome, they are called linked genes. Without recombinant DNA, an organism could only pass on the combination of alleles that was passed from its parents.
Mechanism
- To increase insect resistance, for instance, scientists have placed genes from bacteria into the DNA of corn, cotton, and other crops. The genes they selected produce the protein Bt. This protein is lethal to insect larvae that eat it. Scientists create recombinant DNA from the genomes of these bacteria. The recombinant DNA is then inserted into the genome of the crop being protected. W…
Prevention
- Farmers that do not grow genetically modified crops must spray their crops with pesticides, which are very expensive. Crops that produce Bt protect themselves as they grow. This is important, considering that crop-eating insects do over a billion dollars of damage annually. With genetic engineering, this loss could be averted.
Overview
- Sickle-cell disease is an inherited blood disorder that affects many millions of people worldwide. The condition actually increased in prevalence because in it milder forms it confers resistance to malaria. Like many genetic disorders, there is currently no cure. Patients with sickle-cell disease must undergo a variety of dangerous procedures to extend their life.
Clinical significance
- However, gene therapy is an emerging medical technique that uses recombinant DNA to restore function to cells stricken by genetic disorders. Sickle-cell anemia was one of the first diseases to be reversed by gene therapy. Mice with the sickle-cell traits were treated by Harvard researchers by delivering the recombinant DNA for proper blood cell formation through an altered HIV virus. …