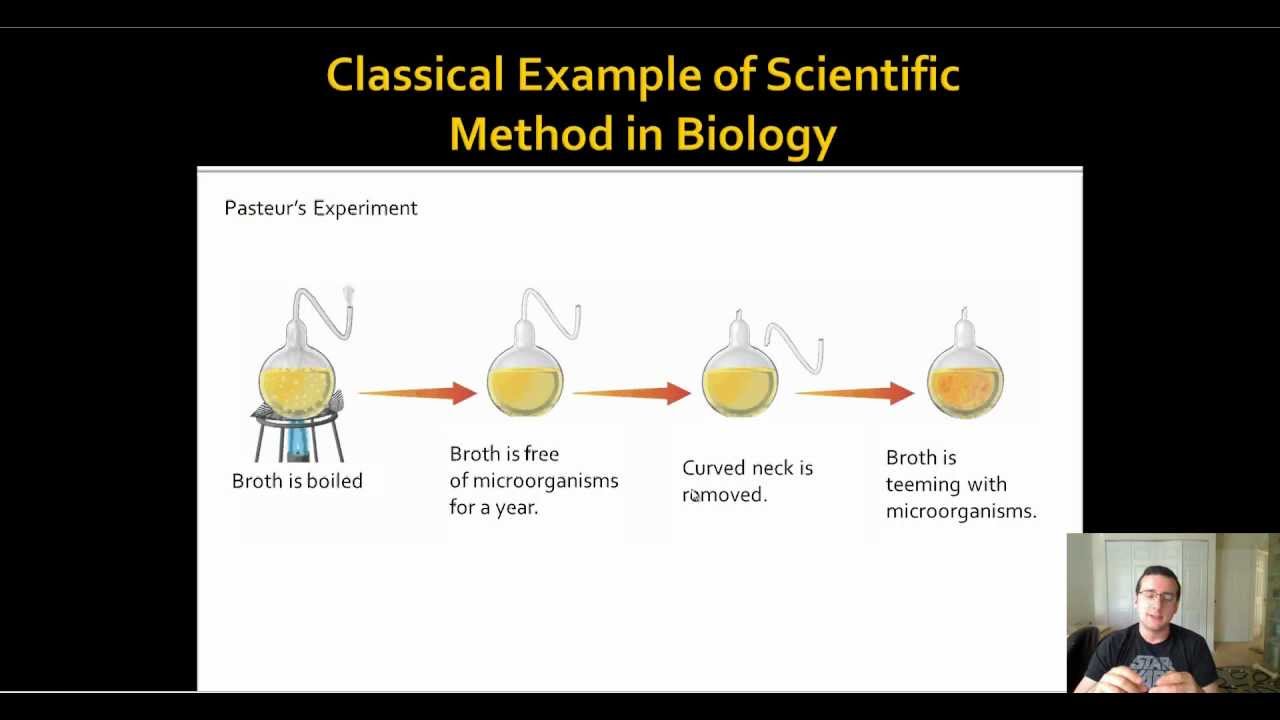
Examples of scientific theories in different areas of science include:
- Astronomy: Big Bang Theory.
- Biology: Cell Theory; Theory of Evolution; Germ Theory of Disease.
- Chemistry: Atomic Theory; Kinetic Theory of Gases.
- Physics: General Relativity; Special Relativity; Theory of Relativity; Quantum Field Theory.
What are some examples of scientific theories?
Feb 11, 2020 · What is an example of scientific theory? Examples of scientific theories are: Issac Newton's “System of the World” which was the first theory in the domain of physics. Einstein's Special Relativity and General Relativity. Darwin's Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection. Thermodynamics, the theory that includes the four Laws of Thermodynamics.
What are 5 scientific theories?
Examples of scientific theories are: Issac Newton's “System of the World” which was the first theory in the domain of physics. Einstein's Special Relativity and General Relativity. Darwin's Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection. Thermodynamics, the theory that includes the four Laws of Thermodynamics.
How is a scientific theory different from an everyday theory?
May 14, 2015 · A scientific theory is an interpretation of observations made of the natural world, based on facts. Learn how to define scientific theory, explore the difference between fact and theories, then ...
What are the major theories in science?
Jan 19, 2011 · A scientific theory is a verifiable explanation of natural phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why an apple always falls to the ground when dropped. A law, on the other hand, is an observation. In simpler terms, a law …

What are some examples of scientific theories?
Examples of scientific theories in different areas of science include:Astronomy: Big Bang Theory.Biology: Cell Theory; Theory of Evolution; Germ Theory of Disease.Chemistry: Atomic Theory; Kinetic Theory of Gases.Physics: General Relativity; Special Relativity; Theory of Relativity; Quantum Field Theory.More items...•Jun 30, 2013
What does scientific theory mean example?
But for scientists, a theory has nearly the opposite meaning. A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of an aspect of the natural world that can incorporate laws, hypotheses and facts. The theory of gravitation, for instance, explains why apples fall from trees and astronauts float in space.
What is a real life example of a scientific theory?
A scientific theory is a verifiable explanation of natural phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why an apple always falls to the ground when dropped. A law, on the other hand, is an observation. In simpler terms, a law predicts what happens and a theory explains why.
What is a good example of a theory?
The definition of a theory is an idea to explain something, or a set of guiding principles. Einstein's ideas about relativity are an example of the theory of relativity. The scientific principles of evolution that are used to explain human life are an example of the theory of evolution.
How is the theory of evolution an example of a scientific theory?
This means that if an environment changes, the traits that enhance survival in that environment will also gradually change, or evolve. Natural selection was such a powerful idea in explaining the evolution of life that it became established as a scientific theory.Jun 7, 2019
What is scientific theory?
A theory is a carefully thought-out explanation for observations of the natural world that has been constructed using the scientific method, and which brings together many facts and hypotheses.Mar 10, 2017
What is a good scientific theory?
According to Kitcher, good scientific theories must have three features: Unity: "A science should be unified…. Good theories consist of just one problem-solving strategy, or a small family of problem-solving strategies, that can be applied to a wide range of problems."
Which statement best describes a scientific theory?
Scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the natural phenomena that can be tested again and again and verified with the help of scientific method of observance and measurement resulting in evaluation of results and are evaluated o the basis of principals of science.Dec 10, 2018
How do you write a scientific theory?
To write a good theory, learn the scientific method.Jot down the goals of your theory paper clearly and succinctly. ... Review the literature. ... Write a hypothesis or an assumption from the research notes. ... Write out in detail how you plan to test the theory. ... Compile and organize the findings.More items...
What is scientific theory?
A scientific theory is an explanation of the natural world that can be repeatedly tested and verified using the scientific method and observation....
What is an example of scientific theory?
One of the most popular scientific theories is Einstein's Special Relativity, which explains the relationship between space and time for objects mo...
Is a scientific law more accurate than a scientific theory?
A scientific theory is a verifiable explanation of natural phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why an apple always falls to the...
What are the five scientific laws?
The five most popular scientific laws are Hooke’s Law of Elasticity, Archimedes’ Principle of Buoyancy, Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures, Bernoull...
What is the best definition of a scientific theory?
A scientific theory is a well-tested and widely accepted explanation for natural phenomena. Scientific theories begin as hypotheses. Over time, as...
What's an example of a scientific theory and a scientific law?
The big bang theory is a an explanatory model of the origin and development of the universe. Kepler's laws of planetary motion describe the shape,...
What are some famous theories?
Theory of evolution by natural selection Plate tectonic theory Cell theory Atomic theory Einstein's theories of special and general relativity...
What are the characteristics of a scientific theory?
Although there are many characteristics of scientific theories, there are five basic characteristics that can help you understand how they work. A scientific theory should be: 1 Testable: Theories can be supported through a series of scientific research projects or experiments. Sometimes a theory is proven to be wrong through evidence: this is called rejecting a theory. However, a theory can never be proven to be absolutely true because it is an interpretation. There is always the possibility that a different interpretation will someday be found to be more correct. 2 Replicable: In other words, theories must also be able to be repeated by others. This means that enough information and data must be available in the theory so that others can test the theory and get similar results. 3 Stable: Another characteristic of theories is that they must be stable. This means that when others test the theory, they get the same results - so a theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it. 4 Simple: A theory should be simple. When we say a scientific theory must be simple, we don't mean that the concept must be basic. We mean that only useful, relevant information should be presented in the theory. 5 Consistent: A theory should agree with other theories, meaning that no principles in one theory should contradict another already accepted theory. However, some differences may be evident because the new theory may provide additional evidence.
Why is scientific theory important?
Scientific theories are very important because they are the key to advancing science through the development of new interventions and treatments. Learning Outcomes. Study this lesson on scientific theory, then test your preparedness to: Define scientific theory.
What is scientific fact?
Scientific facts are measured and/or observed. They never change and are unmistakable evidence. Scientific theories are the scientist's interpretation of the facts. Scientists may have differing opinions regarding the best interpretation of the facts. Theories can change and be rejected.
What is the purpose of a theory?
Theories are used to advance scientific knowledge. Without theories, information that is gathered in research studies could not be put to use. New medications and treatments could not be tested, and no cures for diseases would be found. Example of a Theory.
Do green beans taste the same?
After many hundreds of tests, you move to the theory that no matter the brand name, canned green beans taste the same. Your theory is that there is no difference in the taste of canned green beans based on the brand name. You can disprove this theory if you open a can and the green beans do not taste the same.
What is the theory of relativity?
Let's review: in the non-scientific world, a theory is a supposition. However, in the scientific community, a scientific theory is an explanation of a phenomenon that has been tested over time. A theory begins as an educated guess, known formally as a hypothesis.
Can a hypothesis be disproven?
Over time, the hypothesis can be supported and be called a scientific theory, or it can be disproven and rejected. Scientific theories differ from scientific facts because facts never change and cannot be disputed. However, scientific theories can be tested through research and found to be supported or rejected.
What is the difference between a scientific theory and a law?
A scientific theory is a verifiable explanation of natural phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why an apple always falls to the ground when dropped. A law, on the other hand, is an observation. In simpler terms, a law predicts what happens and a theory explains why.
What are the elements of the scientific method?
Both laws and theories depend on basic elements of the scientific method, such as generating a hypothesis, testing that premise, finding (or not finding) empirical evidence and coming up with conclusions.
What are the laws of thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is the study of how energy works in a system, whether it's an engine or Earth's core. It can be reduced to several basic laws, which Snow cleverly summed up as follows [source: Physics Planet ]: 1 You can't win. 2 You can't break even. 3 You can't quit the game.
What is the scientific law?
A scientific law can often be reduced to a mathematical statement, such as E = mc²; it's a specific statement based on empirical data, and its truth is generally confined to a certain set of conditions. For example, in the case of E = mc², c refers to the speed of light in a vacuum.
Who said a nonscientist who didn't know the second law of thermodynamics was like a scientist
The British physicist and novelist C.P. Snow once said that a nonscientist who didn't know the second law of thermodynamics was like a scientist who had never read Shakespeare [source: Lambert ]. Snow's now-famous statement was meant to emphasize both the importance of thermodynamics and the necessity for nonscientists to learn about it.
What is Hubble's law?
What matters most is that Hubble's law provides a concise method for measuring a galaxy's velocity in relation to our own. And perhaps most significantly, the law established that the universe is made up of many galaxies, whose movements trace back to the big bang.
What is Newton's law?
We may take it for granted now, but more than 300 years ago Sir Isaac Newton proposed a revolutionary idea: that any two objects, no matter their mass, exert gravitational force toward one another. This law is represented by an equation that many high schoolers encounter in physics class. It goes as follows:
What are some examples of scientific theories?
Scientific Theory Examples. Scientific theory examples include: Plate tectonics: The theory of plate tectonics describes how the Earth's crust changes over time. It states that the Earth's outer crust consists of multiple plates that move around over the asthenosphere, the molten layer of the Earth.
What is the difference between scientific facts and scientific theories?
There is a difference between scientific theories and scientific facts. Theories explain universal mechanisms or concepts across the natural world and are well tested. By contrast, a scientific fact is a confirmed observation of a particular phenomenon or object.
Why do scientists develop theories?
Scientists develop theories to explain the natural world and to advance scientific knowledge. A theory is the highest level of explanation in science. Some features of scientific theories are that they: have been thoroughly tested over an extended period.
What is the purpose of the term "theory"?
provide accurate explanations and predictions for a wide range of phenomena. are widely accepted by the scientific community. demonstrate strong experimental and observational support. It is not uncommon for people to use the word "theory" to refer to something that is uncertain or just a guess.
What does "theory" mean in science?
It is just a theory.". However, in science, "theory" has a different meaning: the best scientific explanation for how things work. A theory is not a guess or an unknown. It represents a heightened and tested level of scientific knowledge.
What are the activities of a scientist?
Scientists engage in a variety of activities as part of the scientific investigation process, including: making observations. forming questions based on observations. developing hypotheses to answer the questions. testing the hypotheses with experiments or investigations.
What is the scientific method?
forming conclusions based on experimental analysis. restarting the cycle at various points, if necessary. The scientific method is best thought of as a cycle rather than as a fixed set of steps. The scientific method can be used not only for specialized scientific research.
What is scientific theory and example?
A scientific law describes a scientific observation but doesn't attempt to say why or how it happens, whereas a scientific theory explains exactly why or how it happens. For example, the law of gravity says that two objects will exert their gravitational pull on each other.
Which are scientific theories?
A scientific theory is a structure suggested by these laws and is devised to explain them in a scientifically rational manner. In attempting to explain objects and events, the scientist employs (1) careful observation or experiments, (2) reports of regularities, and (3) systematic explanatory schemes ( theories ).
What are two scientific theories?
Albert Einstein described two types of scientific theories: "Constructive theories " and "principle theories ". Constructive theories are constructive models for phenomena: for example, kinetic theory. Principle theories are empirical generalisations such as Newton's laws of motion.
Is theory of evolution a fact?
Evolution, in this context, is both a fact and a theory. It is an incontrovertible fact that organisms have changed, or evolved, during the history of life on Earth. And biologists have identified and investigated mechanisms that can explain the major patterns of change."
What is theory testing?
Theory - testing with cases is the process of ascertaining whether the empirical evidence in a case or in a sample of cases either supports or does not support a given theory.
Is gravity a proven theory?
The movement of every object — from a person to a supermassive black hole — produces gravitational waves. Most everyone in the scientific community believe gravitational waves exist, but no one has ever proved it.
Why is the theory of gravity still a theory?
Although Newton's theory has been superseded by Albert Einstein's general relativity, most modern non-relativistic gravitational calculations are still made using Newton's theory because it is simpler to work with and it gives sufficiently accurate results for most applications involving sufficiently small masses, ...
What is evolutionary game theory?
And evolutionary game theory is an important branch of the study of evolutionary biology. Game theory even applies to everyday activities like poker, football and negotiating for higher pay for bloggers. There is also even such a thing as quantum game theory, which is bound to revolutionize something someday.
Who developed game theory?
Game theory: John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern, 1944 (with important embellishments from John Nash in the 1950s) Developed for economics, where it has had some successes, game theory didn’t quite completely revolutionize that field. But it has been widely adopted by many other social sciences.
Who proposed continental drift?
Alfred Wegener, shown here on a trip to Greenland in 1912–1913, proposed his ideas about continental drift as early as 1912, a concept later incorporated into the revolutionary theory of plate tectonics.
Who developed information theory?
Information theory: Claude Shannon , 1948. It’s not exactly the most revolutionary theory, since there really wasn’t a predecessor theory to revolutionize. But Shannon certainly provided the mathematical foundation for a lot of other revolutionary developments involving electronic communication and computer science.
Who won the Nobel Prize for Game Theory?
John Nash won a Nobel Prize for his contributions to game theory, and his troubled life inspired the excellent book A Beautiful Mind. But don’t expect to learn anything about game theory by watching the movie version. 8. Oxygen theory of combustion: Antoine Lavoisier, 1770s.
Did Lavoisier discover oxygen?
Lavoisier did not discover oxygen, but he figured out that it was the gas that combined with substances as they burned. Lavoisier thereby did away with the prevailing phlogiston theory and paved the way for the development of modern chemistry.