
What is an express trust in equity? An express trust is a trust created "in express terms, and usually in writing, as distinguished from one inferred by the law from the conduct or dealings of the parties."
What is an express trust in real estate?
An express trust is a trust created "in express terms, and usually in writing, as distinguished from one inferred by the law from the conduct or dealings of the parties.". Property is transferred by a person (called a trustor, settlor, or grantor) to a transferee (called the trustee), who holds the property for the benefit...
What is the opposite of an express trust?
The opposite of an express trust, in legal terms, is an implied trust. This is a trust that is implied by the circumstances and can be created only with the intervention of a court that is trying to right a wrong or clear up a misunderstanding.
Can a trustee distribute the income from an express trust?
The trustee may distribute the property, or the income from that property, to the beneficiaries. Express trusts are frequently used in common law jurisdictions as methods of wealth preservation or enhancement. Law generally requires only a simple formality to create an express trust.
Do I need a written document to create an express trust?
However a written document is not in fact necessary as is confirmed in another part of HMRC’s Manual (TSEM9510) which provides that an express trust is usually created by a declaration of trust which is made by the legal owner, but this declaration can be written or oral except in the case of land.
What is the opposite of express trust?
What is the role of executor in an estate?
Can you revoke a trust at death?
Is estate planning legal or financial?
Is a grantor a trustee?

What is the difference between an express and an implied trust?
An express trust exists when there is “an explicit declaration of trust followed by an actual conveyance or transfer of property to the trustee.” Bainbridge v. Stoner, 16 Cal. 2d 423, 428 (1940) (citations omitted). Implied trusts can be either constructive trusts or resulting trusts.
What are the types of express trusts?
Types of Express Trusts The most common categories of express trusts are living trusts, testamentary trusts, revocable and irrevocable trusts, fixed trusts, and discretionary trusts. Living Trusts. A living trust, or inter vivos trust, is created for the benefit of another during the settlor's life.
How do you express trust?
There are two ways to create an express trust; these are declaration of self as a trustee and the transfer of property to trustees. For an express trust the three certainties must always be present; certainty of intention, objects and subject-matter. If any of these are doubtful, the trust will be rendered invalid.
What are the 4 types of trust?
The four main types are living, testamentary, revocable and irrevocable trusts.
What is the purpose of an express trust?
An express trust is a trust created deliberately by a settlor, usually (but not always) in the form of a document such as a written deed or declaration of trust.
How do I know if a trust is an express trust?
An 'express' trust is a trust that has been created 'expressly'. This means that it was done so willingly by the person who set it up (known as the 'settlor') and did not get created as a result of a judge's ruling in court or because of new legislation.
Is an express trust a fixed trust?
Normal express trusts are described as "fixed" trusts; the trustees are obliged to distribute property, with no discretion, to the fixed number of beneficiaries.
What are the three types of trust?
To help you get started on understanding the options available, here's an overview the three primary classes of trusts.Revocable Trusts.Irrevocable Trusts.Testamentary Trusts.More items...•
What is the opposite of an express trust?
Trusts which are not express trusts – “implied” trusts The word “implied” is the commonly used antonym for “express”, although the word is used in several ways in legal terminology and indeed in legislation, which may sometimes be confusing and indeed some authors suggest avoiding it altogether.
What are the three certainties of an express trust?
For an express trust to be valid there has to be three certainties. These are certainty of intention, certainty of subject matter, and certainty of objects. Without these certainties, an express trust will not be valid. The purpose of these certainties is to ensure the trust is properly controlled and enforced.
What are the two most common types of trusts?
There are two main types of trusts: revocable and irrevocable.
Which type of trust is best?
What Trust is Best for You? (Top 4 Choices in 2022)Revocable Trusts. One of the two main types of trust is a revocable trust. ... Irrevocable Trusts. The other main type of trust is a irrevocable trust. ... Credit Shelter Trusts. ... Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust.
What are the three certainties of an express trust?
For an express trust to be valid there has to be three certainties. These are certainty of intention, certainty of subject matter, and certainty of objects. Without these certainties, an express trust will not be valid. The purpose of these certainties is to ensure the trust is properly controlled and enforced.
What are the three types of trusts?
With that said, revocable trusts, irrevocable trusts, and asset protection trusts are among some of the most common types to consider. Not only that, but these trusts offer long-term benefits that can strengthen your estate plan and successfully protect your assets.
What is an express private trust?
An “express private trust” is a trust which is expressly created either by a trust deed or under a will.
What are the two most common types of trusts?
There are two main types of trusts: revocable and irrevocable.
How to create an Express Trust: The Basics - InBrief.co.uk
The three basic essential requirements need for the creation of a trust are the requirement of the three certainties, the correct and appropriate formalities are to be properly implemented and that the correct constitution is applied. There are four types of trusts that may arise, an express trust, resulting trust, constructive trust or statutory trust. Which definition will be given to the ...
A comprehensive guide to trusts in the UK - Net Lawman
Trust funds 101: what, why, who, how, types and tax. Trusts have a reputation as mysterious legal instruments (or financial frameworks) favoured by the rich and used to avoid tax.
TRSM21030 - Types of trust that need to be registered: contents ...
An express trust is a trust created deliberately by a settlor, usually in the form of a document such as a written deed or declaration of trust.
Trusts and taxes: Types of trust - GOV.UK
A trust is a way of managing assets (money, investments, land or buildings) for people - types of trust, how they are taxed, where to get help.
There Are Two Ways to Create an Express Trust - LawTeacher.net
There are two ways to create an express trust; these are declaration of self as a trustee and the transfer of property to trustees. For an express trust the three certainties must always be present; certainty of intention, objects and subject-matter.
Trust creation – What is an express trust? - the PFS
This document is believed to be accurate but is not intended as a basis of knowledge upon which advice can be given. Neither the author (personal or corporate), the CII group, local institute or Society, or any of the officers or employees of those organisations accept any responsibility for any loss occasioned to any person acting or refraining from action as a result of the data or opinions ...
What is express trust?
An express trust is a trust created "in express terms, and usually in writing, as distinguished from one inferred by the law from the conduct or dealings of the parties.". Property is transferred by a person (called a trustor, settlor, or grantor) to a transferee (called the trustee), who holds the property for the benefit ...
What are the three certainties of express trust?
Three Certainties of Express Trust 1 Certainty of intention: Must be real intention by the settlor to dispose of property and create trust, not just make a gift – a trust also can't be created contrary to the intention of the settlor alleged to have created it: Commissioner of Stamp Duties (Qld) v Jolliffe. 2 Certainty of subject:The property the subject of the trusts must be sufficiently ascertainable at the time the trust was created: Herdegen v Federal Commissioner of Taxation (1988) 3 Certainty of object:Beneficiaries must be ascertainable –
How long can a discretionary trust be indefinite?
Discretionary trusts must not be indefinite and are subject to 'the rule against perpetuities'. In New South Wales, the time prescribed is a statutory period of 80 years from the date the disposition takes effect.
What is an accumulation and maintenance trust?
Accumulation and Maintenance trust. A variation on the discretionary trust, the A&M does not carry the Inheritance tax disadvantages of a discretionary settlement but can only be established for persons under 25 who must be entitled to income at that age. Allows the accumulation of income within the trust until 25.
What is a trust when a life tenant dies?
A trust where, on the death of the life tenant, the property reverts to the person making the gift.
What is the subject of a trust?
Property or rights of a kind which can be the subject of a trust 2. A declaration of trust or disposition on trust by a person legally competent to create a trust 3. Certainty of property and objects (trust must be administratively workable 4. Compliance with requirements regarding evidence 5.
Why do you need more than one trustee?
Often, a trust corporation or more than one trustee is appointed to allow for uninterrupted administration of the trust in the event of a trustee's resignation, death, bankruptcy or incapacity . Additionally a Protector may be appointed who, for example, is authorized to appoint new trustees and to review the trustees' annual accounts.
What is express trust?
According to the Manual, an express trust is a trust created deliberately by a settlor, usually in the form of a document such as a written deed or declaration of trust. However a written document is not in fact necessary as is confirmed in another part of HMRC’s Manual (TSEM9510) which provides that an express trust is usually created by a declaration of trust which is made by the legal owner, but this declaration can be written or oral except in the case of land.
What are the two types of implied trusts?
The two types of “implied trust” include constructive trusts and resulting trusts. These are trusts that are implied by the circumstances and can be created only by a court that is trying to right a wrong or clear up a misunderstanding. Such trusts will not need to be registered with HMRC unless they become “taxable trusts”.
What is the HMRC TRS manual?
The recently published HMRC TRS Manual contains information on a number of areas such as registration requirements, information required to register and data retention, and HMRC has promised to add further material on related subjects , including more details on treatment of life insurance policies, deadlines, penalties and third-party information sharing provisions.
What happens if there is no written document for a trust?
Cleary, if there is no written document there may be problems with providing evidence of the existence of the trust. In another part of the Manual, TSEM9550, HMRC states that there must be evidence of: the intention to create a trust, the beneficial interest in the property, and who holds the beneficial interest (i.e. the “three trust certainties” mentioned earlier); as well as the date from which such a trust is said to exist.
Is a bare trust taxable?
The Manual also confirms that there is no specific exclusion from registration for bare trusts. A bare trust (also called an absolute trust) is a trust where a beneficiary is absolutely and irrevocably entitled to both the income and capital of the trust. In general, if a bare trust is an express trust it should register on the TRS, unless it falls within the definition of excluded trusts. So, unfortunately, there is no concession for bare trusts, despite the fact that such trusts will never become taxable trusts as the trust income and gains are always taxed on the beneficiary (unless caught by the parental settlor provisions).
Do express trusts have to register?
Whilst we are used to the idea that trusts which have tax liabilities have to be registered with HMRC (this has been the law since 2017), which trusts or possibly trust-like arrangements will have to register even if they have no tax to pay? The legal requirement here is that only express trusts (which are not "excluded trusts") need to register. So, what exactly is an express trust? This is where we need to get back to the basic understanding of what is a trust and then to distinguish between express trusts and other trusts.
Can a settlor be a trustee?
The settlor can either transfer the property to the trustees or the settlor may declare themselves to be a trustee of the property. As things stand now, in England it is not even necessary to inform anybody, including the beneficiary, that a trust has been created, although this will change with the expansion of the TRS.
What is express trust?
An express trust, also known as a direct trust, is a type of trust that is created purposefully and intentionally instead of being imposed by a court. A trust is a legal arrangement in which the trustee controls finances or property for another person, who is the beneficiary, generally until the beneficiary comes of age.
Who is the settlor of an express trust?
There are a few definitions to keep in mind when establishing an express trust: Settlor: the person who creates the trust and transfers the property to the trustee. Trustee: the individual or legal entity who maintains the trust property and gives the beneficiary distributions according to the trust terms.
Why do fixed trusts provide tax benefits?
This type of trust can provide tax benefits to the beneficiaries because the beneficiaries have no interest in the trust assets until the trustee decides to distribute them. Fixed trusts allow beneficiaries to receive funds or trust property on a set schedule as decided by the settlor.
What is a living trust?
A living trust, also referred to as an inter-vivos trust, is established for a beneficiary during the settlor's lifetime. Revocable trusts allow the settlor, or creator of the trust, to retain control. The settlor doesn't receive tax benefits, but may withdraw funds from the trust, or cancel or alter it at will.
What are the two types of trusts?
Trusts are divided into two categories: Express trusts. Non-express trusts. Express trusts are defined by the creator of the trust. They are also governed by three certainties or elements: Subject matter. Intention. The object. Express trusts are essentially designed with the expressed intention of the settlor in mind.
What are the benefits of distributing a trust?
One of the biggest benefits of distributing a trust is to pass on assets while minimizing estate, gift, and income taxes. Since there is no uniform trust legislation on the federal level, individual states are responsible for governing trust establishment and maintenance.
Can a settlor create an express trust?
A settlor can create an express trust if they have a valid reason for transferring property to a trustee. The trustee will then distribute the property to the beneficiary when terms of the trust are met. There are a few definitions to keep in mind when establishing an express trust:
What court case overturned a finding of the trial judge who had found an express trust over a parcel of property?
The BC Court of Appeal in Xu v Hu 2021 BC CA 2 overturned a finding of the trial judge who had found an express trust over a parcel of property.
What is the condition for a trust to be valid?
In order for a valid trust to be constituted, there must be certainties of intention, subject and object of the trust, and when the property has been vested in the trustee, and express trust is created.
Is intention expressed or implied?
The intention may be express or implied, it may arise from words or acts.
What is express trust?
Express trusts are a device of disposition which, in land, creates a purely nominal (‘legal’) title that vests in the person named by the testator as the trustee. The title is purely nominal in that the property vested in them is not for their benefit, but is instead for the benefit of another, namely the beneficiary. These terms of trusteeship are made explicit in the testamentary disposition of the land in question, and so the trustee must act according to those terms. A breach of those terms is regarded as an affront to the conscience of the court of equity, and therefore a trustee can be required by the court to comply with the express terms of the trust.
What is the equitable owner of a trust?
Resulting trusts will recognise in B, the party which provided the purchase-money to the person with the paper title (A), a degree of ownership over the land which coheres in its degree to the size of the contribution made by B to the purchase. If B provided the entirety of the purchase money, then B is absolutely the equitable owner. In this manner, equity serves to give ‘the force of law to moral obligations’ ( Sekhon v Alissa [1989] 2 F.L.R. 94 per Hoffmann J).
Why is formality required in trusts of land?
The first is that it reduces the likelihood of controversy arising from allegations of fraud or mistake; the second is it is consistent with the English legal system’s preference for formal methods of creations of interests in land .
When do resulting trusts come into existence?
It is said that resulting trusts come into being at the date of acquisition of the property by A: the exact distribution of beneficial entitlement between A and B (i.e. the respective beneficial share of each party over the land) is said to ‘crystallise’ at the date of acquisition ( Bernard v Josephs [1982] Ch. 391). In other words, according to the classic idea of resulting trusts, the only intentions which are relevant are those which existed at the time of the taking of title by A ( Gissing v Gissing [1971]).Therefore, per this classic condition of resulting trusts, any contributions that are subsequent to the date of purchase ought not to be declared relevant for the purposes of a trust ( Curley v Parkes [2005] 1 P. & C.R. DG15).
Do implied trusts of land have to be evidenced in writing?
Hence, unlike with express trusts of land, implied trusts of land are not required to be evidenced in writing and do not require the signature of the settlor (Law of Property Act 1925, s.53 (2)).
Do you have to articulate a trust?
Such a trust does not have to be articulated in any particular form, so long as the words plainly express and evidence an intention. Speaking clearly such that the words give rise to an objective intention ‘create a trust…without knowing it’ ( Re Schebsman, deceased [1944] Ch. 83). Examples of trusts of land include A granting B the right to live rent-free for life on A’s land ( Bannister v Bannister [1948] 2 All ER 133, CA). In the case of a matrimonial home, for example, one spouse expressing to the other that the first spouse regards the second spouse as having equal rights may inadvertently give rise to the existence of such rights ( Hammond v Mitchell [1991] 1 W.L.R. 1127 per Waite J).
Can a declaration of trust be written without evidence?
Nevertheless, those situations where an express declaration of trust can be made without evidence of writing are limited to secret trusts. Where the alleged beneficiary claims a secret trust for their benefit, they cannot rely on the technical significance of a declaration of trust being incomprehensible to a layperson ( Pink v Lawrence (1978) 36 P. & C.R. 98). Rarer still is the invocation of rectification, according to which a court may rectify a declaration of trust so that it is in accord with the testator’s intentions which had hitherto been expressed imperfectly or not at all in the declared trust ( Wilson v Wilson [1969] 1 WLR 1740, ChD).By and large, an express declaration of trust, evidenced and signed for in writing, will be conclusive of the testator’s intention as it is stated in the written form. The declaration, so far as it concerns the persons named in it, ‘necessarily concludes the question of title… for all time’ ( Pettitt v Pettitt [1970] A.C. 777 per Lord Upjohn).
What is express trust?
Express Trust: a trust created with the Settlor’s express intent (expressing the trust, voluntarily), usually declared in writing; an ordinary trust as opposed to a resulting trust or a constructive trust. Implied trust, which is involuntary; also called constructive trust. (SS account).
What is the meaning of the term "trust" in Black's law?
Trust: the right, enforceable solely in equity, (in court), to the beneficial enjoyment of property to which another person holds legal title; a property interest held by one person (grantee or trustee) at the request of the grantor or settlor, for the benefit of a third party (the beneficiary).
What are the four elements of a trust?
Trusts: If two parties have the four elements of a trust, and employed one of the four methods of formation of the trust, then they have a trust, recognized in law, whether they know it or not, and the trustee can be held liable. Black’s law; two kinds of trusts, Express and Implied.
Why does a trust terminate?
Since they’re the beneficiary, the trust terminates, because they can’t be both. Now the trustee must disperse funds to the beneficiary. As grantor, you instruct the trustee, they’re in breach. Debtor-creditor law is where you’re paying for 30 years. Establish holder in due course status.
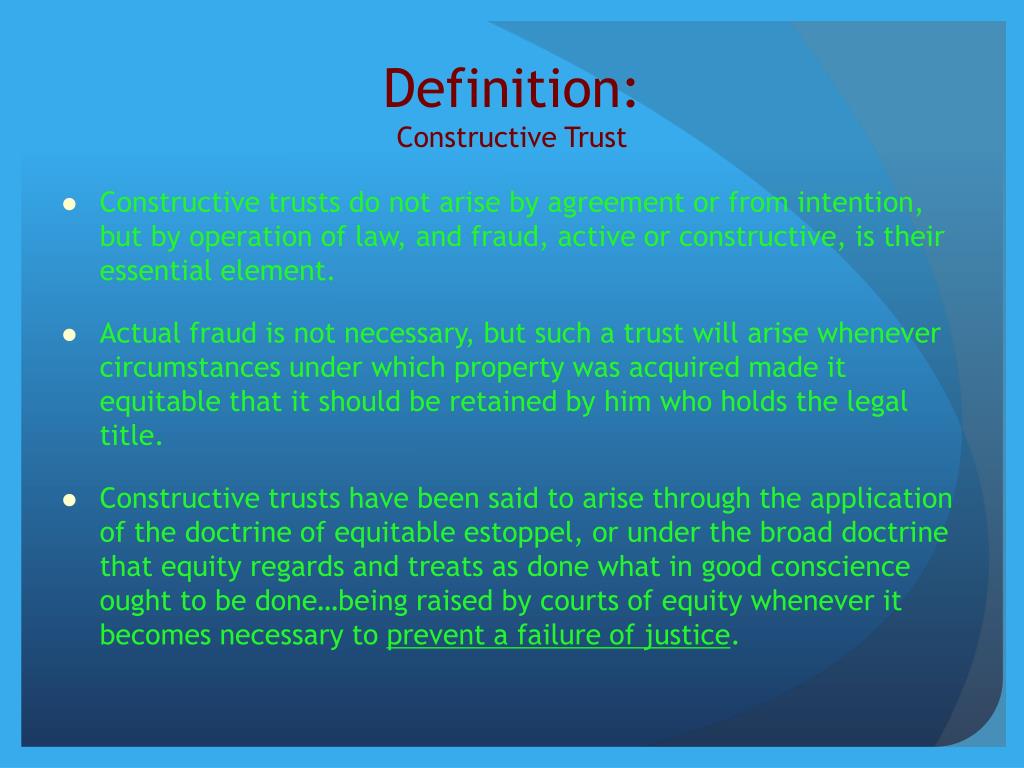
What is a constructive trust?
Specifically, a device by which a legal rule or institution (a trust) is diverted from its original purpose, to accomplish indirectly some other objective.”. The constructive/cestui que/SS/STRAWMAN trust is an example of a legal fiction.
Is constructive trust a construct?
The expression ‘constructive trust’ is absurd, because “constructive” is derived from “construe”, not ‘construct’; the court ‘construes’ the circumstances, it explains them; it does not ‘construct’ them.” (Black’s). We don’t express the trust, so they construe it to their benefit. Cestui que trust is an implied or constructive trust.
Is a cestai que trust a beneficiary?
We don’t express the trust, so they construe it to their benefit. Cestui que trust is an implied or constructive trust. (Social Security # Trust Account) It is a beneficiary of the foreign situs trust because you didn’t express the trust after age 18.
What is the opposite of express trust?
The opposite of an express trust, in legal terms, is an implied trust. This is a trust that is implied by the circumstances and can be created only with the intervention of a court that is trying to right a wrong or clear up a misunderstanding. There are several kinds of implied trusts, which may be called constructive trusts or resulting trusts, ...
What is the role of executor in an estate?
Many people who serve as the executor of an estate also play the role of trustee —that is, they are in charge of property that has been left to beneficiaries in a trust, not a will. Many kinds of trusts are used in estate planning, and virtually all of them can be classified as express trusts.
Can you revoke a trust at death?
This gives them complete control over the trust property, so that if they someday change their mind and want revoke the trust or name different beneficiaries, they can. It's also common for people to create express trusts that take effect only at their death.
Is estate planning legal or financial?
Obviously, in estate planning as with other legal and financial matters, it's always best to create documents that clearly express the planner's wishes and avoid disputes or a court fight. Litigation, with its expense and acrimony, imposes a big cost on everyone.
Is a grantor a trustee?
In many kinds of common trusts used in estate planning, the grantor is also the trustee. For example, the most common kind of trust is probably the revocable living trust, which essentially performs the same function as a will: to leave property at one's death.
Overview
Terms
Law generally requires only a simple formality to create an express trust. In certain jurisdictions, an express trust may even be established orally. Typically, a settlor would record the disposition, where real property is to be held in trust or the value of property in trust is large. Where legal title to property is being passed to a trustee, a "deed of settlement" or "Trust Instrument" (for jurisdictions that do not recognise Deeds) may be used. Where property is to continue to be hel…
Common forms of express trust
Bare trust property transferred to another to hold e.g. for a third person absolutely. May be of use where property is to be held and invested on behalf of a minor child or mentally incapacitated person.
Life Interest trust the income from property transferred is paid to one person, "the life tenant" (e.g. a widow/er), during their lifetime and thereafter is transferred to another person (who may take a…
Three Certainties of Express Trust
• Certainty of intention: Must be real intention by the settlor to dispose of property and create trust, not just make a gift – a trust also can't be created contrary to the intention of the settlor alleged to have created it: Commissioner of Stamp Duties (Qld) v Jolliffe.
• Certainty of subject:The property the subject of the trusts must be sufficiently ascertainable at the time the trust was created: Herdegen v Federal Commissioner of Taxation (1988)
Variation of Trusts in English Law
The Variation of Trusts Act 1958 gave the courts the power to vary trusts in the following circumstances
• s1(1)(a) Any person having, directly or indirectly, an interest, whether vested or contingent, under the trusts who by reason of infancy or other incapacity is incapable of assenting; or
• s1(1)(b) Any person (whether ascertained or not) who may become entitled, directly or indirectly, to an interes…
Forms of trust used by UK taxpayers
Accumulation and Maintenance trust A variation on the discretionary trust, the A&M does not carry the Inheritance tax disadvantages of a discretionary settlement but can only be established for persons under 25 who must be entitled to income at that age. Allows the accumulation of income within the trust until 25.
Disabled Trust Similar to an A&M trust but established for a disabled person.
Forms of trust used by US persons
Certain US jurisdictions and other jurisdictions have developed a radically different interpretation of the trust. Valid trusts can be established by persons who then continue to deal with property as if it were their own during their lifetime, the trust crystallising on death. Trust funds can be taxed as legal entities by election ("checking the box").