What do mean by Hfr and F+ strains?
HFR vs F+ Strains HFr strains are bacterial strains with Hfr DNA or F plasmid DNA integrated into bacterial chromosomes. Bacterial strains which contain F plasmids are known as F+ strains. F plasmids contain fertility factor coding genes.
What is Hfr strain in E. coli?
Classical Hfr strains of Escherichia coli contain the prototypal conjugative plasmid F integrated into the chromosome. During exponential growth of Hfr cells, F replicates passively as a cluster of bacterial genes (8). Bacterial growth should therefore be unaffected by its presence.
How is an Hfr strain formed?
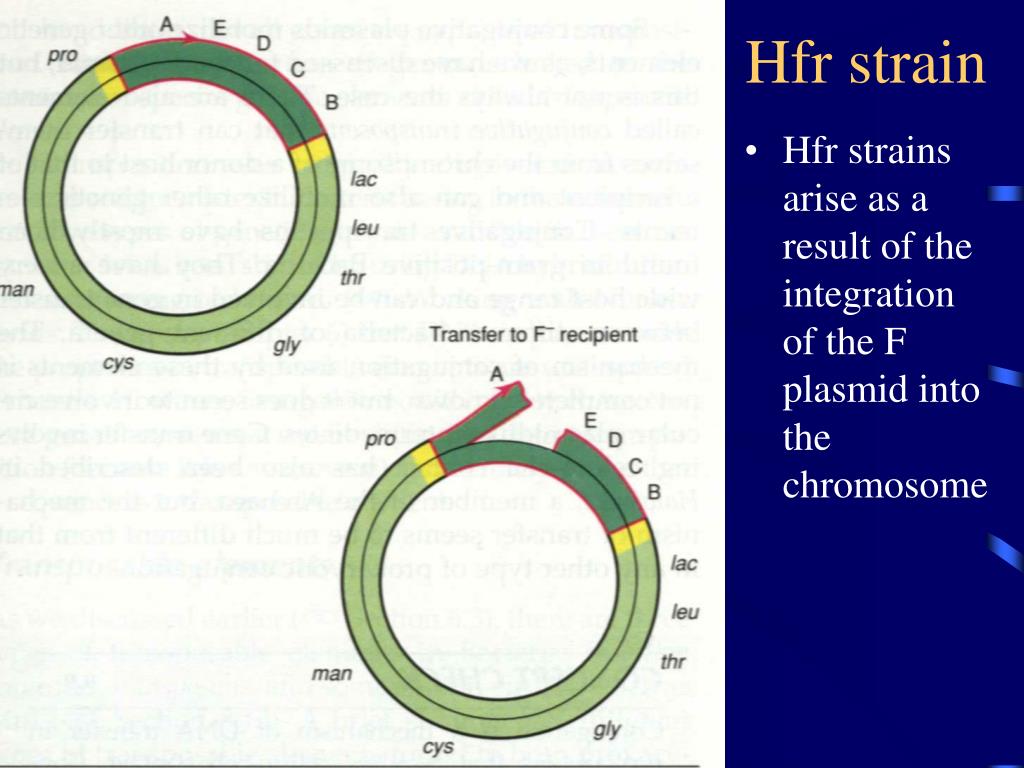
Hfr's can form by homologous recombination between an IS element on the F-plasmid and the same IS element on the host chromosome. Multiple IS insertions are present in many bacterial chromosomes.
Why is it called Hfr cell?
Hfr stands for high frequency of recombination first described by the population geneticist, Luca Cavalli-Sforza. The bacterial cell that acquires F plasmid and incorporates to the bacterial chromosome through crossover, the cell is now designated as Hfr.
Why are Hfr cells high frequency?
After the cross between Hfr cell and F- cell, recipient cell remains recipient. In this conjugation, chromosomal DNA is always almost transfer from donor to recipient cell together with portion of F- factor. So, frequency of recombination is high.
How does Hfr conjugation work?
To initiate conjugation, the Hfr cell makes a physical bridge to the F–cell. A break in the donor DNA initiates a process by which single stranded DNA is synthesized and moved into the recipient (F–) cell. The amount of DNA transported is determined largely by how long the transporter bridge remains intact.
How do Hfr bacterial strains differ from other bacteria?
Hfr cell (high frequency recombination) have F plasmids joined with the chromosomal DNA. Hfr would transfer more because the plasmid is integrated into the bacterial chromosome, with F+, only the F plasmid is transferred; the chromosomal DNA is not.
Why do Hfr cells promote a high level of recombination?
Why do Hfr cells promote a high level of recombination when added to a F minus population of bacteria? -The F plasmid transfers and stimulates mutation in the recipient which needs to be repaired. - The F plasmid often does not transfer to the recipient, but chromosomal DNA does.
Can f+ become Hfr?
This integration is possible because F plasmid also contains the insertion sequence and via homologous recombination it can integrate itself. So when this integration happens, the resultant cells or the derivative of F+ cells is called Hfr cells.
What is Hfr male in bacteria?
Hfr definition. High frequency of recombination. A strain of bacteria that has incorporated an F factor into its chromosome and can then transfer the chromosome during conjugation. In Escherichia coli, a cell having its fertility factor integrated into the bacterial chromosome; a donor (male) cell.
Who discovered an Hfr strain?
Hfr stands for high frequency of recombination first described by the population geneticist, Luca Cavalli-Sforza. The bacterial cell that acquires F plasmid and incorporates to the bacterial chromosome through crossover, the cell is now designated as Hfr.
How does an F+ cell differ from an Hfr cell?
How does an F+ cell differ from an Hfr cell? F+ cells have no plasmids. Hfr cells cannot perform conjugation. Hfr strains can no longer reproduce.
How does an Hfr strain of E. coli transfers chromosomal DNA to an F strain?
It requires close contact between the two bacteria. The transfer of plasmid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) occurs during conjugation. The donor bacteria (F+) strain transfers the plasmid into the recipient bacteria (F-) strain. This is the general mechanism of conjugation.
How do Hfr bacterial strains differ from other bacteria?
Hfr cell (high frequency recombination) have F plasmids joined with the chromosomal DNA. Hfr would transfer more because the plasmid is integrated into the bacterial chromosome, with F+, only the F plasmid is transferred; the chromosomal DNA is not.
What is the time for E. coli Hfr transfer?
This approach is based upon the requirement of 100 minutes to transfer the entire E. coli chromosome from an Hfr donor into a recipient. If the time allowed for mating is limited to 30 minutes, the distal genes cannot be transferred via the Hfr.
Can f+ become Hfr?
This integration is possible because F plasmid also contains the insertion sequence and via homologous recombination it can integrate itself. So when this integration happens, the resultant cells or the derivative of F+ cells is called Hfr cells.