What is a bladder infection?
A bladder infection is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). This refers to an infection anywhere in the urinary tract, such as the bladder, kidneys, ureters, or urethra. Most cases of bladder infections are acute, meaning they occur suddenly.
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra. Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than are men. Infection limited to your bladder can be painful and annoying.
What is a urethral infection?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra.
What is the best medicine for urinary tract infection?
The most common medication for relieving the pain and burning associated with bladder infections is called phenazopyridine (Pyridium). When you have a UTI, drinking plenty of fluids can help flush the bacteria out of your bladder.

Why does my bladder get infected?
Causes. Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. Although the urinary system is designed to keep out such microscopic invaders, these defenses sometimes fail.
What causes UTIs?
A suppressed immune system. Diabetes and other diseases that impair the immune system — the body's defense against germs — can increase the risk of UTIs.
How to reduce the risk of urinary tract infection?
You can take these steps to reduce your risk of urinary tract infections: Drink plenty of liquids, especially water. Drinking water helps dilute your urine and ensures that you'll urinate more frequently — allowing bacteria to be flushed from your urinary tract before an infection can begin. Drink cranberry juice.
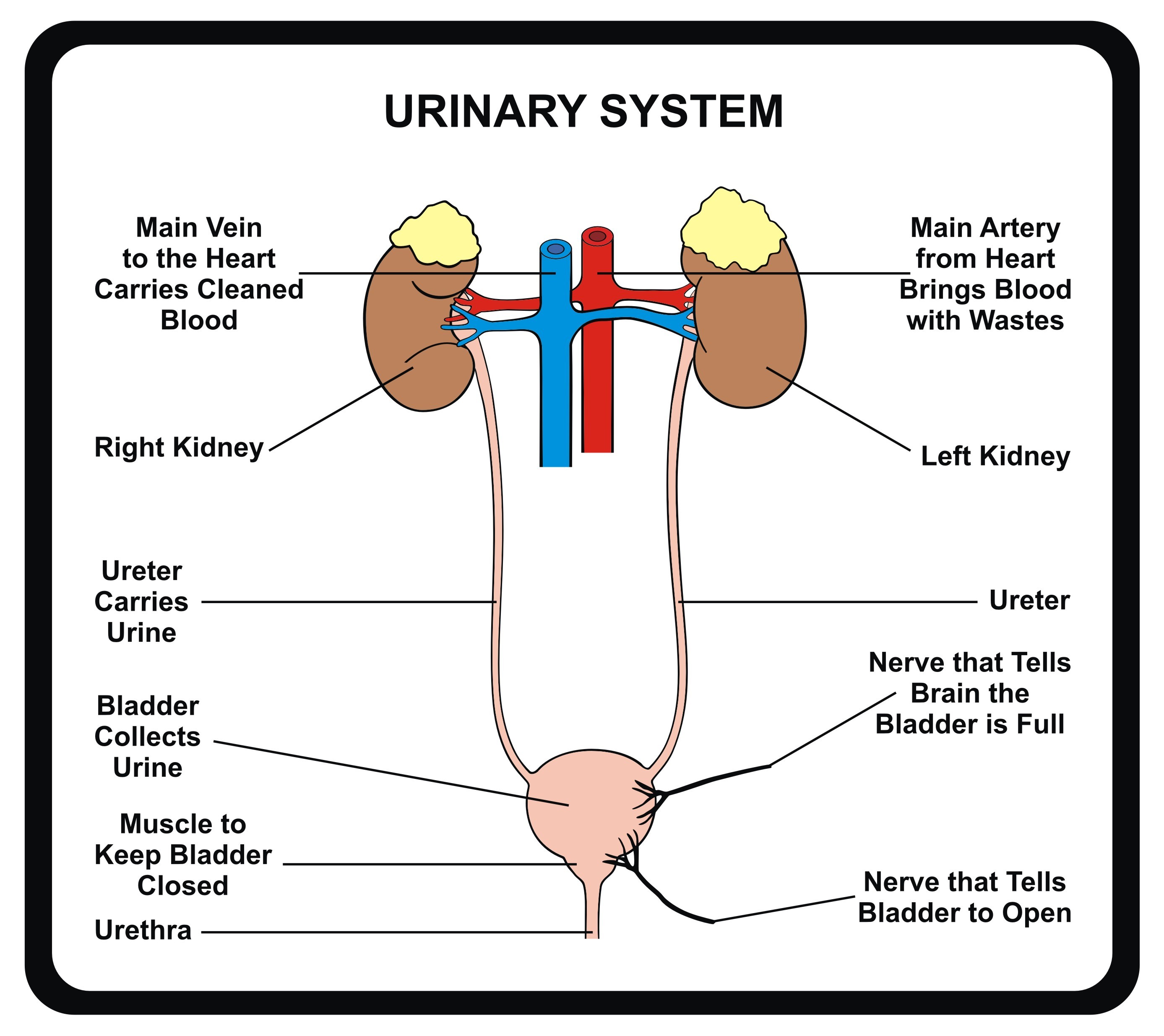
What is the urinary system?
Male urinary system. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part ...
What is the system that removes waste from the body?
Overview. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
Part of urinary tract affected. Signs and symptoms. Kidneys (acute pyelonephritis) Back pain or side (flank) pain. High fever.
Which organs remove waste from the body?
Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood.
How to help a bladder infection?
Applying warm compresses or a cloth-covered heating pad to the pubic area may help to ease some of the discomfort associated with a bladder infection.
Why does my bladder itch when I pee?
Because most UTIs are bladder infections , these are the symptoms most people experience when they have a UTI. People with urethritis — an infection of the urethra, or the tubes that connect the bladder to the opening of the body — may also experience itching or irritation at the end of the urethra where the pee comes out.
Why are women more likely to get UTIs than men?
Women are also more likely than men to get UTIs because their urethra is shorter. The bacteria have less distance to go to reach the bladder and can cause infections.
What is the worst UTI?
Most doctors regard kidney infections as the worst type of UTI, according to the NIDDK. A kidney infection is usually caused by a bladder or urethra infection where the bacteria multiply and travel upward toward the kidneys.
What is the most common type of UTI?
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), bladder infections are the most common type of UTI. Doctors may also call them cystitis. A UTI is an infection in one or more parts of the urinary tract, which includes the ureters, kidneys, urethra, and bladder.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for a UTI?
Kidney infections usually fall into this category. If you have a complicated UTI, you may require IV antibiotics and have to take antibiotics for a week or more .
Why is not drinking enough water bad for bladder?
Not drinking enough water is another risk factor for bladder infections because your body doesn’t move as much urine through the bladder as quickly. Risk factors for urethritis include having a sexually transmitted infection or from trauma to the urethra, such as due to the insertion of a urinary catheter.
What causes a bacterial infection in the bladder?
Bladder infection. A bladder infection is most often caused by a bacterial infection within the bladder. For people with weakened immune systems, yeast can cause bladder infections as well. A bladder infection is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). This refers to an infection anywhere in the urinary tract, such as the bladder, kidneys, ...
How to diagnose a bladder infection?
A doctor can diagnose your bladder infection by performing a urinalysis. This is a test performed on a sample of urine to check for the presence of: 1 white blood cells 2 red blood cells 3 nitrites 4 bacteria
How to treat a recurrent bladder infection?
Preventive antibiotic treatment. If you’re a woman experiencing recurrent bladder infections, your doctor may give you a prescription for daily antibiotics to prevent infections or to take when you feel the symptoms of a bladder infection. They may also have you take a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual activity.
Why are women more prone to bladder infections than men?
Anyone can get bladder infections, but women are more prone to getting them than men. This is because women have shorter urethras, making the path to the bladder easier for bacteria to reach. Females’ urethras are also located closer to the rectum than men’s urethras.
How long does it take for a bladder infection to subside?
Most bladder infections subside within 48 hours of taking the appropriate antibiotic. It’s important to finish all antibiotics prescribed, even if you’re feeling better.
What is it called when you pee more than usual?
urinating more often than usual, which is called “frequency”. foul-smelling urine. a frequent sensation of having to urinate, which is called “ urgency ”. cramping or pressure in the lower abdomen or lower back. When bladder infections spread, they can also cause mid-back pain. This pain is associated with infection in the kidneys.
Where do bacteria come from?
This type of bacteria is naturally present in the large intestines. An infection can occur when bacteria from the stool get onto the skin and enter the urethra. In women, the urethra is short and the outside opening is not far from the anus, so bacteria can easily move from one body system to another.
What is the most common cause of urinary tract infections?
These infections are caused by bacterial infections in the bladder, usually caused by bacteria traveling up the urethra and into the bladder. When left untreated, UTIs can be very dangerous, as the infection can progress from the bladder into the kidneys. Common symptoms include a burning sensation during urination, cloudy and/or foul-smelling urine, and the frequent urge to urinate, despite little urine being released.
What is the term for the protrusion of the bladder through the wall of the abdomen?
Bladder Exstrophy. Bladder exstrophy is a congenital abnormality which involves the protrusion of the bladder through the wall of the abdomen. This condition is extremely rare and is often accompanied by the abnormal development of the pelvic floor and other muscles, as well as the genitals, especially in women.
What are bladder stones?
Bladder stones are hard deposits composed of minerals found in the bladder caused by dehydration and highly concentrated urine residing in the bladder. Stones can vary in size and are typically asymptomatic. Common symptoms are typically pain, blood in the urine, and irritation.
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
Prior to urination, it stores urine produced and delivered by the kidneys through two ureters. The human urinary bladder is hollow, muscular, and can hold up to four cups of urine.
Why does my bladder stop urinating?
This disorder is caused by a sympathetic nervous system response which tightens the sphincters in the bladder in response to adrenaline, thereby preventing urination . Typically, treating this condition requires psychological therapy.
What is the condition where you need to urinate?
Trigonitis is a condition involving inflammation of the trigone region of the bladder. In particular, the trigone is a smooth triangular-shaped region and signals the need for urination in response to stretching. An inflammation of this region can result in an urgent need to urinate, pain in the pelvic region, and pain or difficulty urinating. Although there are several causes of trigonitis, bladder infections are the most common etiology.
What is the name of the condition in which the urethral sphincter cannot be relaxed in coordination?
Bladder Sphincter Dyssynergia. Bladder sphincter dyssynergia refers to a condition in which the urethral sphincter cannot be relaxed in coordination with bladder contraction. This condition is typically caused by a central nervous system injury or disorder.
What makes up the urinary system?
Your bladder, kidneys, ureters and urethra make up your urinary system. When you have interstitial cystitis, the walls of your bladder become irritated and inflamed (shown right), compared with those of a normal bladder (shown top).
What is the pain of a bladder?
The pain ranges from mild discomfort to severe pain. The condition is a part of a spectrum of diseases known as painful bladder syndrome. Your bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine. The bladder expands until it's full and then signals your brain that it's time to urinate, communicating through the pelvic nerves.
Why does my bladder hold less urine?
Reduced bladder capacity. Interstitial cystitis can cause stiffening of the bladder wall, which allows your bladder to hold less urine.
What are the complications of interstitial cystitis?
Interstitial cystitis can result in a number of complications, including: 1 Reduced bladder capacity. Interstitial cystitis can cause stiffening of the bladder wall, which allows your bladder to hold less urine. 2 Lower quality of life. Frequent urination and pain may interfere with social activities, work and other activities of daily life. 3 Sexual intimacy problems. Frequent urination and pain may strain your personal relationships, and sexual intimacy may suffer. 4 Emotional troubles. The chronic pain and interrupted sleep associated with interstitial cystitis may cause emotional stress and can lead to depression.
How do you know if you have interstitial cystitis?
If you have interstitial cystitis, your symptoms may also vary over time, periodically flaring in response to common triggers, such as menstruation, sitting for a long time, stress, exercise and sexual activity.
How many times a day do you pee?
Frequent urination, often of small amounts, throughout the day and night (up to 60 times a day)
Can interstitial cystitis cause a woman to urinate?
With interstitial cystitis, these signals get mixed up — you feel the need to urinate more often and with smaller volumes of urine than most people. Interstitial cystitis most often affects women and can have a long-lasting impact on quality of life.

Overview
Symptoms
- Urinary tract infections don't always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do they may include: 1. A strong, persistent urge to urinate 2. A burning sensation when urinating 3. Passing frequent, small amounts of urine 4. Urine that appears cloudy 5. Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored — a sign of blood in the urine 6. Strong-smelling urine 7. Pelvic pain, in women — …
Causes
- Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. Although the urinary system is designed to keep out such microscopic invaders, these defenses sometimes fail. When that happens, bacteria may take hold and grow into a full-blown infection in the urinary tract. The most common UTIsoccur mainly in …
Risk Factors
- Urinary tract infections are common in women, and many women experience more than one infection during their lifetimes. Risk factors specific to women for UTIsinclude: 1. Female anatomy.A woman has a shorter urethra than a man does, which shortens the distance that bacteria must travel to reach the bladder. 2. Sexual activity. Sexually active women tend to have …
Complications
- When treated promptly and properly, lower urinary tract infections rarely lead to complications. But left untreated, a urinary tract infection can have serious consequences. Complications of a UTImay include: 1. Recurrent infections, especially in women who experience two or more UTIsin a six-month period or four or more within a year. 2. Permanent kidney damage from an acute or …
Prevention
- You can take these steps to reduce your risk of urinary tract infections: 1. Drink plenty of liquids, especially water.Drinking water helps dilute your urine and ensures that you'll urinate more frequently — allowing bacteria to be flushed from your urinary tract before an infection can begin. 2. Drink cranberry juice. Although studies are not conclusive that cranberry juice prevents UTIs, i…