Difference Between EPSP and IPSP
- Definition. EPSP: An EPSP is an electrical charge on the postsynaptic membrane, which is caused by the binding of excitatory neurotransmitters and makes the postsynaptic membrane generate an action potential.
- Name. ...
- Cause. ...
- Type of Polarization. ...
- To the Threshold. ...
- Excitation. ...
- Firing of an Action Potential. ...
- Results. ...
- Types of Ligands. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What happens during IPSP and EPSP?
IPSP is an electrical charge that occurs within the post-synaptic membrane as a result of binding of non-excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters and prevents the generation of an action potential. Depolarization occurs during the EPSP. Hyperpolarization occurs during IPSP.
What is an EPSP?
EPSP: An EPSP is an electrical charge on the postsynaptic membrane, which is caused by the binding of excitatory neurotransmitters and makes the postsynaptic membrane generate an action potential.
What is IPSP (IPSP)?
IPSP: An IPSP is an electric charge on the postsynaptic membrane, which is caused by the binding of inhibitory neurotransmitters and makes the postsynaptic membrane less likely to generate an action potential.
What ions are involved in EPSP and IPSP?
Glutamate ions and aspartate ions are involved during the EPSP. Glycine and Gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) are involved during the IPSP. EPSP is referred to as excitatory postsynaptic potential. It is an electrical charge that occurs within the post-synaptic membrane of the neuron as a result of excitatory neurotransmitters.
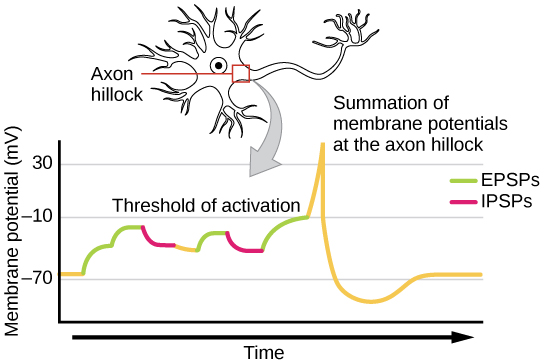
What are EPSPs and IPSPs and what is their function?
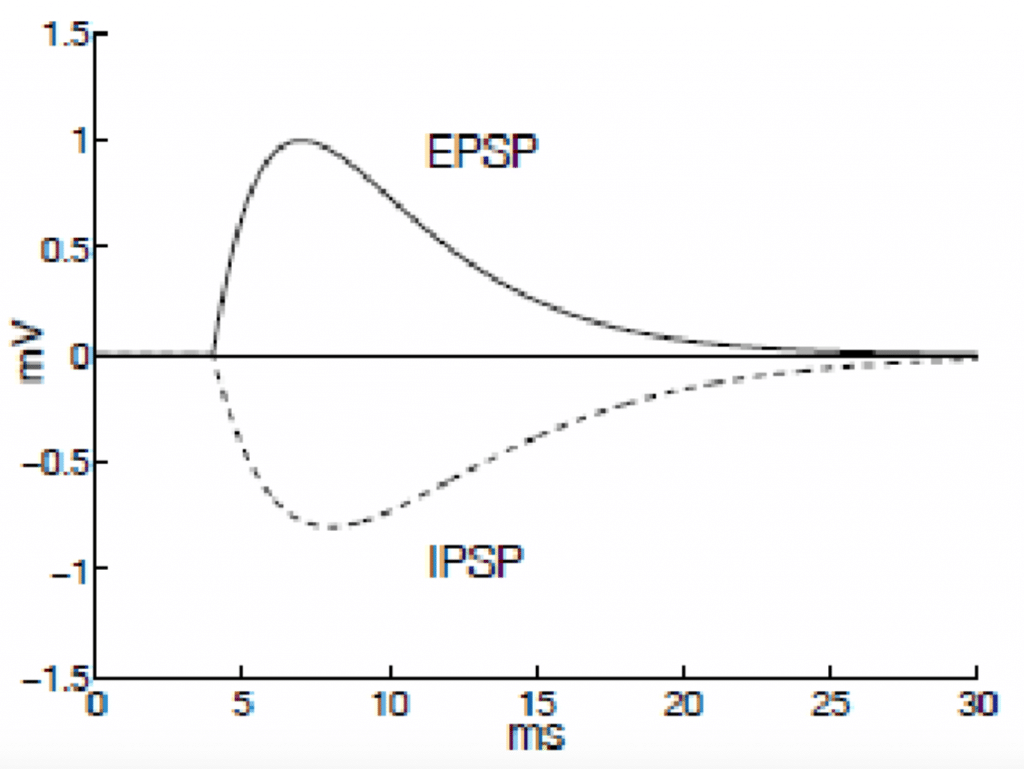
Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials In this case, the shift in membrane potential is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential, or EPSP. In other cases, the change makes the target cell less likely to fire an action potential and is called an inhibitory post-synaptic potential, or IPSP.
What is EPSP IPSP quizlet?
STUDY. EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential) is a temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell as a result of opening of ligand-sensitive channels. IPSP (inhibitory postsynaptic potential)
What is an example of IPSP?
As an example of inhibitory postsynaptic action, consider a neuronal synapse that uses GABA as its transmitter. At such synapses, the GABA receptors typically open channels that are selectively permeable to Cl-. When these channels open, negatively charged chloride ions can flow across the membrane.
What is meant by EPSP?
Definition. An excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is the change in membrane voltage of a postsynaptic cell following the influx of positively charged ions into a cell (typically Na+) as a result of the activation of ligand-sensitive channels.
What produces an IPSP?
An inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) is a temporary hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane caused by the flow of negatively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell. An IPSP is received when an inhibitory presynaptic cell, connected to the dendrite, fires an action potential.
What happens in EPSP?
An excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) occurs when sodium channels open in response to a stimulus. The electrochemical gradient drives sodium to rush into the cell. When sodium brings its positive charge into the cell, the cell's membrane potential becomes more positive, or depolarizes.
How are EPSPs and IPSPs produced?
EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC).
How do EPSPs and IPSPs work together?
In short, the summation of EPSPs and IPSPs by a postsynaptic neuron permits a neuron to integrate the electrical information provided by all the inhibitory and excitatory synapses acting on it at any moment.
What is IPSP in biology?
An electrical charge (Hyperpolarisation) in the membrane of a postsynaptic neuron caused by the binding of an inhibitory neurotransmitter from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic receptor; makes it more difficult for a postsynaptic neuron to generate an action potential.
What is the difference between EPSP and IPSP quizlet?
An EPSP is a depolarizing potential in a neuron that is normally caused by synaptic excitation. EPSPs increase the probability that the postsynaptic neuron will fire an action potential. An IPSP is a hyperpolarizing potential in a neuron.
What are the differences between an action potential vs EPSPs IPSPs?
Summary: “EPSP” stands for “excitatory postsynaptic potential.” Excitatory postsynaptic potential occurs when there is a flow of positively charged ions towards the postsynaptic cell, a momentary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential is created. Action potentials are also called nerve impulses or spikes.
What is the Difference Between EPSP and IPSP?
IPSP is an electrical charge that occurs within the post-synaptic membrane as a result of binding of non-excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters and prevents the generation of an action potential.
What is IPSP?
IPSP is referred to as the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. It is an electrical charge that builts up in the post-synaptic membrane inhibiting the firing of an action potential. This is the exact opposite of EPSP. The major reason for the development of IPSP is a sequential step process that involves inhibitory neurotransmitters binding to the post-synaptic membrane receptors. These neurotransmitters include Glycine and Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid (GABA), which are secreted by the pre-synaptic membrane. GABA is an amino acid that acts as a most prevalent inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon release, GABA binds to receptors such as GABAA and GABAB present in the post-synaptic membrane. When these inhibitory neurotransmitters bind, it results in the opening of ligand-gated ion channels that cause the movement of chloride ions (Cl-) into the post-synaptic membrane.
What is the IPSP charge?
IPSP is an electrical charge that occurs within the post-synaptic membrane as a result of binding of non-excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters and prevents the generation of an action potential. Polarization Type. Depolarization occurs during the EPSP. Hyperpolarization occurs during IPSP. Effect.
What is the purpose of IPSP?
It is an electrical charge that built up in the post-synaptic membrane that inhibits the firing of an action potential. The major reason for the development of IPSP is a sequential step process that involves inhibitory neurotransmitters, which are bound to the post-synaptic membrane receptors.
What is EPSP in neuron?
It is an electrical charge that occurs within the post-synaptic membrane of the neuron as a result of excitatory neurotransmitters. EPSP creates an exciting environment within the post-synaptic membrane. This excitation results in the firing of an action potential. IPSP is referred to as inhibitory postsynaptic potential. It is an electrical charge that built up in the post-synaptic membrane that inhibits the firing of an action potential. The major reason for the development of IPSP is a sequential step process that involves inhibitory neurotransmitters, which are bound to the post-synaptic membrane receptors. This inhibitory process continues until the inhibitory neurotransmitters detach from the receptors. This is the difference between EPSP and IPSP.
What is an IPSP?
An inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) is a temporary hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane caused by the flow of negatively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell. Click to see full answer. Also to know is, what is the difference between an EPSP and an IPSP?
Why is EPSP important?
IPSPs are important because they can counteract, or cancel out, the excitatory effect of EPSPs.
What is EPSPis in biology?
An EPSPis received when an excitatory presynaptic cell, connected to the dendrite, fires an action potential. An inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) is a temporary hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane caused by the flow of negatively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell.
What causes a temporary depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane?
is a temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell as a result of opening of ligand-sensitive channels.
What is the signal received when an excitatory presynaptic cell, connected to the dendrite?
is received when an excitatory presynaptic cell, connected to the dendrite, fires an action potential. The signal is propagated down the dendrite and is summed with other inputs at the axon hilllock.
When an inhibitory presynaptic cell, connected to the dendrite, fires an action potential?
when an inhibitory presynaptic cell, connected to the dendrite, fires an action potential. The signal is propagated down the dendrite and is summed with other inputs at the axon hilllock.
