
What is the difference between MPLS and network addresses?
Whereas network addresses identify endpoints the labels identify established paths between endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the multiprotocol component of the name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1 / E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL .
What is MPLS and how does it work?
What is MPLS? MPLS is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that guides data starting with one node then onto the next dependent on short way names as opposed to long network addresses, in this way staying away from complex queries in a routing table and speeding traffic flows.
Can MPLS be used in non native networks?
However it evolved in Generalized MPLS (GMPLS) to allow the creation of label-switched paths (LSPs) also in non-native IP networks, such as SONET/SDH networks and wavelength switched optical networks . MPLS can exist in both an IPv4 and an IPv6 environment, using appropriate routing protocols.
What is multiple service support by Mpls?
Multiple service support by MPLS allows the creation of one network for all applications. Until MPLS, organizations maintained separate networks for voice and data, for example, which was very expensive.
What are MPLS connections?
MPLS is a private connection linking data centers and branch offices. MPLS is typically outsourced, managed by service providers who guarantee network performance, quality and availability. Because MPLS is essentially a private network, it is considered reliable and secure, but also expensive.
What is MPLS and how its works?
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is data forwarding technology that increases the speed and controls the flow of network traffic. With MPLS, data is directed through a path via labels instead of requiring complex lookups in a routing table at every stop.
What is MPLS in simple terms?
MPLS Meaning Multiprotocol Label Switching, or MPLS, is a networking technology that routes traffic using the shortest path based on “labels,” rather than network addresses, to handle forwarding over private wide area networks.
Is MPLS the same as Ethernet?
While both Ethernet and MPLS are commonly used to carry IP, there are many fundamental protocol differences between the two. Ethernet is defined from Layer 0 to Layer 2 (but may run over MPLS), while MPLS always requires a foreign server layer to transport it (which may be Ethernet).
What is MPLS example?
MPLS can be used when speed and reliability are highly important. Applications that require near-immediate data delivery are known as real-time applications. Voice calls and video calls are two common examples of real-time applications. MPLS can also be used to set up wide area networks (WANs).
Why do companies use MPLS?
The Benefits of MPLS for Your Business MPLS has a wide range of benefits: better performance, reduced network congestion, higher-quality, better bandwidth management and utilization of resources, scalability, security, and ultimately better end-user perceptibility.
What is the difference between VPN and MPLS?
A VPN connects a private network to another public network, which allows users to transmit and receive data as if their computers were connected to the private network physically. MPLS is a routing technique that is used to improve the speed and control of the network traffic.
Is MPLS a VPN?
MPLS VPN is a type of VPN infrastructure that utilizes multiprotocol label switching techniques to deliver its services. It is a suite of different MPLS-based VPN technologies that provide the ability to utilize multiple different protocols and technologies for creating and managing communications in a VPN environment.
Why is MPLS faster than IP routing?
MPLS is much faster than traditional IP Routing, as it is based on the concept of the label to allow forwarding (rather switching) of packets. This type of forwarding is more efficient as it avoids overloading the CPU.
What is the difference between MPLS and Metro Ethernet?
1) Metro Ethernet is the layer 2 transport for things such as MPLS. Think of it as a really long Ethernet segment between yourself and your service provider. MPLS is what is referred to as a layer 2 1/2 protocol and is used primarily in service provider networks.
What is MPLS over Ethernet?
MPLS stands for Multiprotocol Label Switching. It is a way of connecting sites by bridging them together through the service routers cloud on a private tunnel while using short path labels rather than long network addresses for directing one data to another.
What is a Metro E connection?
A Metro Ethernet Network is the generally defined as the network that bridges or connects geographically separated enterprise LANs while also connecting across the WAN or backbone networks that are generally owned by service providers.
What is the difference between VPN and MPLS?
A VPN connects a private network to another public network, which allows users to transmit and receive data as if their computers were connected to the private network physically. MPLS is a routing technique that is used to improve the speed and control of the network traffic.
How does MPLS LDP work?
LDP is a protocol that automatically generates and exchanges labels between routers. Each router will locally generate labels for its prefixes and will then advertise the label values to its neighbors. It's a standard, based on Cisco's proprietary TDP (Tag Distribution Protocol).
Is MPLS copper or fiber?
MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including DSL, T1, DS3, Ethernet Over Copper (EoC), Ethernet Over T1 or DS3, Ethernet Over Fiber (Metro Ethernet), and Ethernet Over Fixed Wireless. Other access technologies you may have heard of are 4G Cellular, Business-Class Cable and A-Synchronous Ethernet.
What layer does MPLS operate?
MPLS allows most data packets to be forwarded at Layer 2 -- the switching level -- of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, rather than having to be passed up to Layer 3 -- the routing level. For this reason, it is often informally described as operating at Layer 2.5.
What is an MPLS network?
First introduced in 2000, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a data transport protocol enabling highly-efficient network traffic flow between...
How does MPLS work?
MPLS operates similarly to switches and routers by using packet-forwarding technology and labels to make data-forwarding decisions for IP traffic o...
What are the limitations of MPLS?
While MPLS is celebrated as the data transport type offering some of the highest levels of reliability, availability (uptime), and quality of servi...
MPLS vs. SD-WAN: What’s the difference?
People compare MPLS and SD-WAN as though they are both connectivity types in an apples-to-apples comparison. But this is incorrect. SD-WAN is not a...
Is MPLS still relevant as a network data transport service?
In the age of the always-on digital business, MPLS is valuable in that it still offers one of the most highly reliable data transport services for...
MPLS vs. SDN: What’s the difference?
How MPLS improves efficiency and performance: MPLS improves upon the flow of IP data across a traditional network with its ability to efficiently l...
Does Masergy offer MPLS or SDN services?
Masergy’s solutions use both MPLS and our own software-defined network (SDN) to provide private access for clients. The service can use MPLS tech...
What is MPLS network?
MPLS networks are the magic that binds business activities. Without them, a decent segment of current profitability would go to a grinding stop as far as we might be concerned.
What is MPLS in router?
MPLS or Multiprotocol Label Switching is a strategy for accelerating network connections. Every router needs to settle on an autonomous sending choice for every packet dependent on the packet’s network-layer header.
What is MPLS full form?
The MPLS full form is Multiprotocol Label Switching that can epitomize packets of different network protocols, henceforth the “multiprotocol” reference on its name . Multiprotocol Label Switching upholds a scope of access technologies, including DSL, Frame Relay, ATM, and T1/E1.
What is MPLS label type?
What is MPLS? MPLS is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that guides data starting with one node then onto the next dependent on short way names as opposed to long network addresses, in this way staying away from complex queries in a routing table and speeding traffic flows.
What is a multiprotocol label switch?
A Multiprotocol Label Switching connection is a leased line that is devoted to an association.
What is MPLS in business?
Multi-protocol label switching (MPLS), is tried and true networking technology has powered enterprise networks for over two decades. Unlike other network protocols that route traffic based on source an destination address, MPLS routes traffic based on predetermined “lables”. Businesses have used MPLS to connect remote branch offices that require access to data or applications that reside in the organizations data center or company headquarters.
What are the benefits of MPLS?
The benefits of MPLS are scalability, performance, better bandwidth utilization, reduced network congestion and a better end-user experience.
What is the label on an MPLS router?
The Label: The label holds all of the information for MPLS routers to determine where the packet should be forwarded.
What are the pros and cons of MPLS?
MPLS Pros and Cons. The benefits of MPLS are scalability, performance, better bandwidth utilization, reduced network congestion and a better end-user experience. MPLS itself does not provide encryption, but it is a virtual private network and, as such, is partitioned off from the public Internet.
Why is the hub and spoke model inefficient?
Once businesses transition to the cloud the MPLS-based hub-and spoke model becomes inefficient because it routes traffic through companies’ headquarters (hubs), which act as central choke points . It is more efficient to send traffic directly to the cloud. Also, the use of cloud services, video and mobile apps has driven up bandwidth requirements, and MPLS services are difficult to scale on demand.
Is MPLS a layer 2 or 3?
There’s been a lot of confusion about whether MPLS is a Layer 2 or Layer 3 service. But MPLS doesn’t fit neatly into the OSI seven-layer hierarchy, and is sometimes classified as Layer 2.5. In fact, one of the key benefits of MPLS is that it separates forwarding mechanisms from the underlying data-link service.
Is MPLS dead?
This is question makes sense given the strong momentum behind SD-WANs. While MPLS isn’t dead, its role has certainly changed. Small and mid-size businesses can likely sunset MPLS and shift solely to an all-broadband WAN becuase many of them have moved to an all-cloud IT model.
How does MPLS work?
MPLS operates similarly to switches and routers by using packet-forwarding technology and labels to make data-forwarding decisions for IP traffic on a network. The label is imposed between the Layer 2 (data link) and Layer 3 (network) headers and results in excellent quality of service and reliability.
Why use MPLS?
This explains why businesses typically use MPLS to carry their high-priority IP traffic across the WAN. MPLS is commonly used to support voice, VoIP, and real-time video conferencing applications that are sensitive to jitter and latency.
What are the limitations of MPLS?
While MPLS is celebrated as the data transport type offering some of the highest levels of reliability, availability (uptime), and quality of service , there are drawbacks. Its stability comes at a higher per-megabit cost when compared to the cost-efficiencies of public internet connectivity types like broadband. MPLS is also subject to geographical boundaries, because each MPLS link is deployed by the local telecommunications carriers and dependent upon their physical points of presence (PoP).
What is the difference between MPLS and SDN?
MPLS vs. SDN: What’s the difference? 1 How MPLS improves efficiency and performance: MPLS improves upon the flow of IP data across a traditional network with its ability to efficiently label and forward packets on a network. The flow of IP data across a network is measured in units referred to as “packets,” and network performance is related to how quickly a packet can travel between routers, switches, and other nodes on a network. 2 How a SDN improves efficiency and performance: Traditional networks were decentralized, using integrated hardware and software to direct IP traffic across a series of routers and switches. SDN is considered revolutionary because it has centralized network control, using a hardware controller with purpose-built software (often in the cloud) to intelligently manage all network traffic. With centralized cloud-based control, an IT professional can quickly configure networks, tune segments of the network for specific application use cases, and restrict access to certain network segments for a higher level of cybersecurity. How does SDN create centralized control? Derived from the concepts of virtualization and cloud computing, SDN separates the control plane (which manages the network) from the data plane (where all IP traffic flows). This decoupling unlocks core components, allowing for centralized visibility, management, and control.
What is SD WAN?
Instead, SD-WAN provides the freedom to choose among many connectivity types, empowering IT leaders to mix and match both MPLS and broadband—using both together. This is known as a hybrid WAN or a hybrid connectivity strategy.
How does MPLS improve performance?
How MPLS improves efficiency and performance: MPLS improves upon the flow of IP data across a traditional network with its ability to efficiently label and forward packets on a network . The flow of IP data across a network is measured in units referred to as “packets,” and network performance is related to how quickly a packet can travel between ...
What is Masergy platform?
Masergy’s platform was built uniformly using software-defined principles. It’s a global network with an SD-architecture all across the world.
How does MPLS work?
But while IP routing works hop-by-hop with the route lookup determining the next router, MPLS determines complete path to the destination. The edge device appends this path to the packet so subsequent devices can forward packets without additional routing lookups.
What are the benefits of MPLS?
Improvements in silicon have largely eliminated lookup problem, but MPLS still brings three major benefits: MPLS traffic engineering allows fine-grained control over how the network routes traffic. The network engineer can then prevent traffic congestion, manage line capacity, and prioritize services more effectively.
What are the Technical Benefits of MPLS?
Initially, the primary benefit of MPLS came about because routing lookups was difficult to implement efficiently in software. By minimizing them, MPLS offered a significant reduction in latency. Improvements in silicon have largely eliminated lookup problem, but MPLS still brings three major benefits:
How Does MPLS Compare with Leased Lines?
MPLS provides business with a number of concrete benefits when compared with other private data services, such as leased lines. These include:
How to add new sites to a VPLS network?
With a VPLS-enabled network, a new site can be added by simply changing the network router that connects the site to the VPLS network. With layer-3 MPLS solutions, adding new sites is a much more complex process as all of the service provider’s routers need to be changed.
Why is layer 2 VPLS a fraction of layer 3 MPLS?
Even if you do require a service provider change, the typical time to make network changes to Layer 2 VPLS networks is a fraction of layer-3 MPLS because network planning is much simpler, which could be crucial for some businesses. Another feature which aids agility is the ease of adding new sites.
What is the difference between MPLS and SD-WAN?
MPLS vs. SD-WAN: What’s the Difference? MPLS is one type of data service that can be used by software-defined wide area networks (SD-WANs). Other types of data services that might be part of an SD-WAN include Internet access delivered across xDSL, cable or 4G.
What is MPLS in telecommunications?
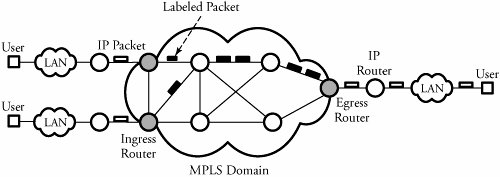
Multiprotocol Label Switching ( MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, thus avoiding complex lookups in a routing table and speeding traffic flows. The labels identify virtual links ( paths) between distant nodes rather than endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the "multiprotocol" reference on its name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1 / E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL .
How does MPLS work?
MPLS works by prefixing packets with an MPLS header, containing one or more labels. This is called a label stack . Each entry in the label stack contains four fields: A 20-bit label value. A label with the value of 1 represents the router alert label.
What is a LER in IP?
When forwarding an IP datagram into the MPLS domain, a LER uses routing information to determine the appropriate label to be affixed, labels the packet accordingly, and then forwards the labeled packet into the MPLS domain. Likewise, upon receiving a labeled packet which is destined to exit the MPLS domain, the LER strips off the label and forwards the resulting IP packet using normal IP forwarding rules.
What is a label switch router?
Label switch router. An MPLS router that performs routing based only on the label is called a label switch router ( LSR) or transit router . This is a type of router located in the middle of an MPLS network. It is responsible for switching the labels used to route packets.
How does MPLS differ from ATM?
The most significant difference is in the transport and encapsulation methods. MPLS is able to work with variable length packets while ATM transports fixed-length (53 bytes) cells. Packets must be segmented, transported and re-assembled over an ATM network using an adaptation layer, which adds significant complexity and overhead to the data stream. MPLS, on the other hand, simply adds a label to the head of each packet and transmits it on the network.
What is MPLS in ATM?
MPLS is designed to have lower overhead than ATM while providing connection-oriented services for variable-length frames, and has replaced much use of ATM in the market. In particular, MPLS dispenses with the cell-switching and signaling-protocol baggage of ATM.
What is the role of LSR in packet routing?
It is responsible for switching the labels used to route packets . When an LSR receives a packet, it uses the label included in the packet header as an index to determine the next hop on the label-switched path (LSP) and a corresponding label for the packet from a lookup table.
What is MPLS used for?
MPLS is replacing the older technologies at a rapid pace. It dispenses the signaling-protocol and cell-switching baggage of ATM.
What is a leased line and MPLS?
MPLS and leased line both provide WAN connectivity. While MPLS is implemented as a full mesh, a leased line establishes a connection between two points.
What is the difference between MPLS and leased line?
1.An MPLS and a leased line provide WAN connectivity.#N#2.The main difference is that an MPLS, if desired, can be implemented as full mesh, while a leased line connects two sites.#N #3.A leased line is an end user solution, while an MPLS is a complex framework of functions.
What is packet forwarding in MPLS?
It is a data-carrying mechanism. Data packets are assigned labels in an MPLS network. Instead of examining the packet itself, packet-forwarding decisions are made based purely on the contents of this label.
Why is MPLS layer 2.5?
MPLS is often referred to as layer 2.5 protocol because of its operation on an OSI model. It is designed to provide a unified data-carrying service for both packet-switching and circuit-based clients. It is used in many kinds of traffic such as Ethernet frames, SONET, native ATM, or IP packets.
Does a leased line have a telephone number?
It does not have a telephone number, unlike traditional PSTN lines. Each side of the line is connected to the other. Leased lines can be used for data, Internet, or telephone. Some connect two PBXs, while others are ring down services. Leased lines are mostly used by businesses to connect their distant offices.
