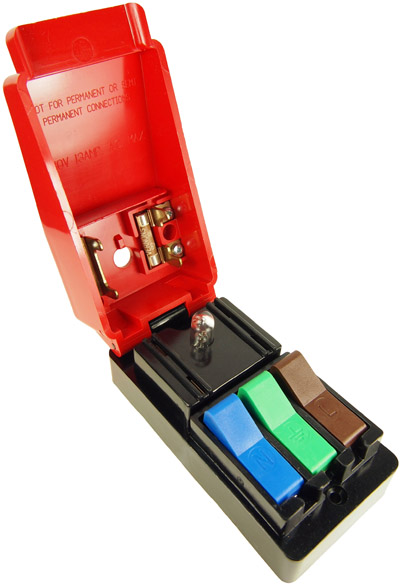

What is the function of a fuse in a circuit?
Fuse (electrical) Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, and it must be replaced or rewired, depending on type.
What are automotive fuses used for?
Automotive fuses are used to protect the wiring and electrical equipment for vehicles. There are several different types of automotive fuses and their usage is dependent upon the specific application, voltage, and current demands of the electrical circuit.
What is fuse in Linux?
What is FUSE? ¶ FUSE is a userspace filesystem framework. It consists of a kernel module (fuse.ko), a userspace library (libfuse.*) and a mount utility (fusermount). One of the most important features of FUSE is allowing secure, non-privileged mounts.
What is a true fuse?
A true fuse typically consists of a piece of metal, most commonly an encased wire, that actually melts when overheated. This is what stops the fault (aka “short” or “power surge” ).
How does voltage drop affect a fuse?
What are the different types of fuses?
What is a fuse in electrical?
How long does it take for a fuse to blow?
What is a fuse?
Why are fused devices used?
What is a fuse element made of?
See 4 more
About this website
What is fuse short answer?
A fuse is a safety device in an electric circuit. It contains a piece of wire which melts when there is a fault, so that the flow of electricity stops.
What does fuse out mean?
2 verb When an electric device fuses or when you fuse it, it stops working because of a fault.
Which word is closest in meaning to the word fuse?
Some common synonyms of fuse are amalgamate, blend, coalesce, commingle, merge, mingle, and mix.
What is fuse Science?
A fuse is a small, thin conductor designed to melt and separate into two pieces for the purpose of breaking a circuit in the event of excessive current.
What happens when a fuse goes out?
Inside the fuse, there is a metal ribbon through which all the current on the circuit passes. The ribbon is sized to match the circuit wire gauge, and if too much current passes through the ribbon, it melts through, or "blows," and the circuit goes dead.
How do you tell if a fuse is blown?
Remove the fuse from its holder. In some cases you may need a small screwdriver to unscrew the fuse holder cap. Look at the fuse wire. If there is a visible gap in the wire or a dark or metallic smear inside the glass then the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
What is a five letter word for fuse?
There are Crossword Clues with 3 to 11 Letters for FUSE. 5 Letters: MERGE.
What things fuse together?
fuse (together) As they heal, the bones will fuse together. fuse (into something) Our different ideas fused into a plan. Their lips fused in a passionate kiss....fuse.present simple I / you / we / they fuse/fjuːz/ /fjuːz/he / she / it fuses/ˈfjuːzɪz/ /ˈfjuːzɪz/past simple fused/fjuːzd/ /fjuːzd/2 more rows
What is the sentence of fuse?
The fuse blew as he pressed the button to start the motor. Remove the circuit fuse before beginning electrical work. The wire snapped at the wall plug and the light fused. Rainwater had fused the bulbs.
What are the 3 types of fuses?
Classification of Fuses Fuses can be classified as “One Time Only Fuse”, “Resettable Fuse”, “Current limiting and non – current limiting fuses” based on the usage for different applications.
What are the 5 types of fuses?
The low voltage fuses are divided into five types and those are of the rewirable, cartridge, drop out, striker, and switch fuses.
What are the two basic type of fuse?
Fuses can be divided into two major categories, AC fuses, and DC fuses. The below block diagram illustrates the different types of the fuse under each category.
What does fuse mean in slang?
To have a tendency to become angered, enraged, or upset very quickly or easily; to have a short temper. I'm usually a pretty calm person, but whenever I start driving I find I have such a short fuse.
How do you use fuse in a sentence?
Examples from Collins dictionaries The fuse blew as he pressed the button to start the motor. Remove the circuit fuse before beginning electrical work. The wire snapped at the wall plug and the light fused. Rainwater had fused the bulbs.
Is it fuze or fuse?
Fuze: A device with explosive components designed to initiate a main charge. (The spelling fuse may also be met for this term, but fuze is the preferred spelling in this context.) Historically, it was spelled with either 's' or 'z', and both spellings can still be found.
How does fuse work?
The fuse breaks the circuit if a fault in an appliance causes too much current to flow. This protects the wiring and the appliance if something goes wrong. The fuse contains a piece of wire that melts easily. If the current going through the fuse is too great, the wire heats up until it melts and breaks the circuit.
Different Types of Fuses and their Applications - Components101
A fuse is probably the simplest electrical device, but its function is critical in protecting electrical circuits from damage.Fuses are found in every circuit in one form or another in various shapes, sizes, and ratings.
Working Principle of an Electric Fuse – Function and ... - VEDANTU
Electric Fuse is based on the principle of heating effect of Electric current. Heat is produced when current flows in the wire. When heat production is more due to excessive flow of current, it melts the Fuse which normally has a low melting point, thereby preventing any damage to the Electric circuit and appliances.
How does voltage drop affect a fuse?
The manufacturer may specify the voltage drop across the fuse at rated current. There is a direct relationship between a fuse's cold resistance and its voltage drop value. Once current is applied, resistance and voltage drop of a fuse will constantly grow with the rise of its operating temperature until the fuse finally reaches thermal equilibrium. The voltage drop should be taken into account, particularly when using a fuse in low-voltage applications. Voltage drop often is not significant in more traditional wire type fuses, but can be significant in other technologies such as resettable (PPTC) type fuses.
What are the different types of fuses?
Automotive fuses can be classified into four distinct categories: 1 Blade fuses 2 Glass tube or Bosch type 3 Fusible links 4 Fuse limiters
What is a fuse in electrical?
A fuse consists of a metal strip or wire fuse element, of small cross-section compared to the circuit conductors, mounted between a pair of electrical terminals, and (usually) enclosed by a non-combustible housing . The fuse is arranged in series to carry all the current passing through the protected circuit.
How long does it take for a fuse to blow?
A standard fuse may require twice its rated current to open in one second, a fast-blow fuse may require twice its rated current to blow in 0.1 seconds, and a slow-blow fuse may require twice its rated current for tens of seconds to blow . Fuse selection depends on the load's characteristics.
What is a fuse?
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once ...
Why are fused devices used?
Fuses have been used as essential safety devices from the early days of electrical engineering. Today there are thousands of different fuse designs which have specific current and voltage ratings, breaking capacity, and response times, depending on the application.
What is a fuse element made of?
The fuse element is made of zinc, copper, silver, aluminum, or alloys among these or other various metals to provide stable and predictable characteristics. The fuse ideally would carry its rated current indefinitely, and melt quickly on a small excess. The element must not be damaged by minor harmless surges of current, and must not oxidize or change its behavior after possibly years of service.
Why do we Need Fuse?
Fuses are used for the prevention of home appliances from the short circuit and damage by overload or high current etc. If we don’t use fuses, electrical faults occur in the wiring and it burns the wire and electric appliances and may starts fire at home. The lives of television, computers, radios and other home appliances may also put at risk. When the fuse goes, a sudden spark occurs which may lead to turning your home into sudden darkness by disconnecting the power supply which saves any further mishappenings. That’s why we need fuses to protect our home appliances from harm.
What happens when a fuse element melts?
Voltage Drop: When excessive current flows, the fuse element melts and opens the circuit. Due to this resistance change and the voltage drop will become lesser.
What is a link type fuse?
Link Type Or HRC (High Rupturing Capacity) Fuses :- In this type of fuse, the flow of current by fuse element is given under normal condition. To control the arc which is produced by fuse blown we use the fuse which is made up of porcelain, silver &ceramic. The fuse element container filled with silica sand. The HRC type is again divided into two parts that are:- 1 Blade Type/Plug-in Type :- The body of this fuse is made up of plastic and it is easily replaceable in the circuit without any load. 2 Bolted Type :- In this type of fuse, the conducting plates are fixed to the fuse base.
What is a fuses strip?
Also, it works as a circuit breaker or stabilizer which protects the device from damage.In the market, many types, features, and design of fuses are available nowadays. Their strips are made up of aluminum, copper, zinc & it is always connected in series with the circuit to protect from overcurrent in the running cables.
How does a fuse work?
The fuses work on the principle of the heating effect of the current. It’s made up of thin strip or strand of metallic wire with noncombustible material. This is connected between the ends of the terminals. Fuse is always connected in series with the electrical circuit.
Why does a fuse melt down?
Fuse is always connected in series with the electrical circuit. When the excessive current or heat is generated due to heavy current flows in the circuit, the fuse melts down due to the low melting point of the element and it opens the circuit.
What happens when a fuse goes out?
When the fuse goes, a sudden spark occurs which may lead to turning your home into sudden darkness by disconnecting the power supply which saves any further mishappenings.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
Circuit breakers are specially designed switches that automatically open to stop current in the event of an overcurrent condition. Small circuit breakers, such as those used in residential, commercial and light industrial service are thermally operated. They contain a bimetallic strip (a thin strip of two metals bonded back-to-back) carrying circuit current, which bends when heated. When enough force is generated by the bimetallic strip (due to overcurrent heating of the strip), the trip mechanism is actuated and the breaker will open. Larger circuit breakers are automatically actuated by the strength of the magnetic field produced by current-carrying conductors within the breaker, or can be triggered to trip by external devices monitoring the circuit current (those devices being called protective relays ).
Why do automobiles use fusible links?
It should be noted that some automobiles use inexpensive devices known as fusible links for overcurrent protection in the battery charging circuit, due to the expense of a properly-rated fuse and holder. A fusible link is a primitive fuse, being nothing more than a short piece of rubber-insulated wire designed to melt open in the event of overcurrent, with no hard sheathing of any kind. Such crude and potentially dangerous devices are never used in industry or even residential power use, mainly due to the greater voltage and current levels encountered. As far as this author is concerned, their application even in automotive circuits is questionable.
How does a fuse work?
Although their operation depends on the self-generation of heat under conditions of excessive current by means of the fuse’s own electrical resistance, they are engineered to contribute a negligible amount of extra resistance to the circuits they protect. This is largely accomplished by making the fuse wire as short as is practically possible. Just as a normal wire’s ampacity is not related to its length (10-gauge solid copper wire will handle 40 amps of current in free air, regardless of how long or short of a piece it is), a fuse wire of certain material and gauge will blow at a certain current no matter how long it is. Since length is not a factor in current rating, the shorter it can be made, the less resistance it will have end-to-end.
Why are fuses rated in terms of voltage?
If the fuse isn’t made long enough on a high-voltage circuit, a spark may be able to jump from one of the melted wire ends to the other, completing the circuit again: Consequently, fuses are rated in terms of their voltage capacity as well as the current level at which they will blow.
Why are fuse connections connected in series?
Fuses are always connected in series with the component (s) to be protected from overcurrent, so that when the fuse blows (opens) it will open the entire circuit and stop current through the component (s). A fuse connected in one branch of a parallel circuit, of course, would not affect current through any of the other branches.
What is a slow blow fuse?
If fast-blowing fuses were to be used in an application like this, the motor could never get started because the normal inrush current levels would blow the fuse (s) immediately! The design of a slow-blow fuse is such that the fuse element has more mass (but no more ampacity) than an equivalent fast-blow fuse, meaning that it will heat up slower (but to the same ultimate temperature) for any given amount of current.
What is the most common device in use for overcurrent protection in high-current circuits today?
Unlike the fuse block just shown, where all the metal clips are openly exposed, this type of fuse holder completely encloses the fuse in an insulating housing: The most common device in use for overcurrent protection in high-current circuits today is the circuit breaker.
What is a thermal fuse?
According to SWE, a thermal fuse is a component that serves as a safety device. It is also known as a thermal cutoff. It opens circuits to prevent overheating. Thermal fuses are designed to detect heat that arises from an overcurrent that occurs within an electrical system. The cause for the overcurrent could either be due to a breakdown in a component or a short circuit.
Is a thermal fuse the same as electrical fuses?
Some of the functions of a thermal fuse are the same, e.g. the safety factor, but it is different than traditional fuses. When a thermal fuse is triggered it interrupts the current or stops it to stop the overheating of a circuit. This is the same way that a traditional fuse works. The major difference between the two is that once the thermal fuse is triggered it is no longer useful. While a traditional fuse will reset itself, a thermal fuse does not reset and it must immediately be replaced. The same is true if a thermal switch fails. It is not designed to reset itself like other fuse types. A second difference is that a thermal fuse will only react when there is an excess in heat, versus excessive current. The overcurrent must be high enough to cause an excessive amount of heat that can be detected by the thermal fuse. The heat causes the thermal fuse to heat up to trigger the response that provides safety from electrical fires.
How do you know if a thermal fuse is working?
According to Hunker, you should use a multimeter to test a thermal fuse. Simply touch the right side of the device’s lead to the right side of the fuse. You should also repeat the process on the left multimeter lead. If the needle moves this means that the fuse is still in operation. If the needle doesn’t move, then you can assume that the fuse is blown and must be replaced. Various appliances that use thermal fuses will stop working if the fuse is blown. If there are no other defects or problems with the unit, then simply replacing the thermal fuse may make them function normally again.
How do you replace a thermal fuse?
After testing a thermal fuse as recommended, a blown fuse is not that difficult to replace, depending on the kind of appliance it is in. For a clothing dryer, in most cases, the back panel must be removed. The fuse is usually found behind the back panel. It’s always recommended to refer to the owner’s manual of any appliance for the exact placement of the thermal fuse. Sometimes it is located in the top part of the dryer. If you don’t have a paper manual you can usually find one online. Simply remove the old blown fuse and replace it with a compatible model.
Where do you find thermal fuses?
Thermal fuses are easy to find if you know where to look. Most hardware stores carry them. They are also sold in home improvement stores, appliance stores, and you can also order them online. The average cost is $10 per fuse.
What appliances use thermal fuses?
Some common household appliances that use thermal fuses include hairdryers and clothing dryers that are used for everyday laundering tasks. They are also used in the construction of coffee makers. The thermal fuse works by disconnecting the current to the heating element when there is a faulty thermostat or some other type of malfunction.
Why are thermal fuses different from traditional fuses?
They’re different than traditional fuses because they only interrupt current flows when there is enough of a problem to cause overheating. When the fuse becomes overheated itself, the sensors detect the heat and interrupt the current. Once a thermal fuse does its job it must be replaced immediately.
What is a fuse?
FUSE is a userspace filesystem framework. It consists of a kernel module (fuse.ko), a userspace library (libfuse.*) and a mount utility (fusermount).
What is a filesystem connection?
A connection between the filesystem daemon and the kernel. The connection exists until either the daemon dies, or the filesystem is umounted. Note that detaching (or lazy umounting) the filesystem does not break the connection, in this case it will exist until the last reference to the filesystem is released.
What does "waiting" mean in filesystem?
The number of requests which are waiting to be transferred to userspace or being processed by the filesystem daemon. If there is no filesystem activity and ‘waiting’ is non-zero, then the filesystem is hung or deadlocked.
What is a filesystem?
A filesystem in which data and metadata are provided by an ordinary userspace process. The filesystem can be accessed normally through the kernel interface.
What happens when another user accesses files?
If another user is accessing files or directories in the filesystem, the filesystem daemon ser ving requests can record the exact sequence and timing of operations performed. This information is otherwise inaccessible to the mount owner, so this counts as an information leak.
What causes a call back to the filesystem?
This one needs a carefully crafted filesystem. It’s a variation on the above, only the call back to the filesystem is not explicit, but is caused by a pagefault.
What does "Writing anything into this file" mean?
This means that all waiting requests will be aborted an error returned for all aborted and new requests.
How to fix a faulty outlet?
The Fix: Make sure the faulty device is unplugged and there is no damage to the outlet. First, test the circuit. Then check for any damage on or around the electrical panel. If you see any damage, call an electrician before doing anything else with it.
What is fuse box?
First, A Word About Fuses. Most people nowadays have had the old-fashioned fuse panels (also known as fuse boxes) in their homes replaced by modern electrical panels with circuit breakers –if the fuse boxes were even still there when they purchased their houses.
How often do you think about what might have caused the fuse to blow?
But how often do you actually think about what might have caused the fuse to blow, much less called an electrician to make sure everything’s OK? If you’re like most people, the answer to that is probably “Never.”
Why do kitchens have GFCI outlets?
The danger of shock increases when a person is in direct contact with the weak path to the ground. That’s why kitchens and bathrooms usually are equipped with GFCI ( ground fault circuit interrupter) outlets. The Fix: This is essentially the same as the fix for a short circuit.
Why is my circuit breaker cutting off?
If so, the circuit breakers are doing what they were meant to do: cutting off the flow of electricity because of some type of surge (fault) or other problem. The Fix: Before resetting the breaker, check for any indications of damage. If the breaker trips again, there could be a problem.
How to tell if a fuse is blown?
You might be wondering, then, how to tell if a fuse is blown–an actual fuse, that is. You will see that the fuse has melted, and there might be charring on the panel.
What causes a short circuit?
Cause 2: A Short Circuit. A short circuit is a type of electrical fault. Faults, in general, occur when an electrical current strays beyond its intended path (circuit) due to a lack of resistance (e.g., from insulation or a circuit breaker).
What is fuse in SaaS?
Fuse has a large collection of connectors to many SaaS systems to make integration and data exchange easier. Many of these integrations are accomplished with a single and simple URI command string. For example, using these URIs, you can exchange data with external websocket and AWS servers, send notifications to Apple iOS devices, download files stored on Box and OneDrive, and integrate with various databases, including CouchDB, Elasticsearch, and Hadoop.
What is Red Hat fuse?
Red Hat Fuse comes with a series of connectors —called components in Apache Camel— so you can programmatically tie together various external SaaS services. Fuse enables you to build collaborative and agile Java applications using microservices and containers. Fuse packages together Apache Camel with ten other open source projects into a coherent whole that will save you time in implementation, while allowing you to use a variety of specific application development tools (such as ApiCurio, Swagger, and Undertow) to build apps with your own preferences and create powerful links with these interfaces. Fuse also is designed to appeal to developers at various skill and experience levels in their careers.
Why is fuse used?
Fuse also is designed to appeal to developers at various skill and experience levels in their careers. Because Fuse is based on containers, you can create a distributed environment that can isolate faults, deploy consistently, allow for continuous improvement, and be extensible.
What is fuse platform?
Fuse is a single platform that can be deployed in three different ways, on-prem up to total cloud. You can build your apps once and then run them anywhere with no change in functionality or coding. Fuse collects the numerous open source projects into a single place to make installation simple and to be able to start quickly building apps.
How does voltage drop affect a fuse?
The manufacturer may specify the voltage drop across the fuse at rated current. There is a direct relationship between a fuse's cold resistance and its voltage drop value. Once current is applied, resistance and voltage drop of a fuse will constantly grow with the rise of its operating temperature until the fuse finally reaches thermal equilibrium. The voltage drop should be taken into account, particularly when using a fuse in low-voltage applications. Voltage drop often is not significant in more traditional wire type fuses, but can be significant in other technologies such as resettable (PPTC) type fuses.
What are the different types of fuses?
Automotive fuses can be classified into four distinct categories: 1 Blade fuses 2 Glass tube or Bosch type 3 Fusible links 4 Fuse limiters
What is a fuse in electrical?
A fuse consists of a metal strip or wire fuse element, of small cross-section compared to the circuit conductors, mounted between a pair of electrical terminals, and (usually) enclosed by a non-combustible housing . The fuse is arranged in series to carry all the current passing through the protected circuit.
How long does it take for a fuse to blow?
A standard fuse may require twice its rated current to open in one second, a fast-blow fuse may require twice its rated current to blow in 0.1 seconds, and a slow-blow fuse may require twice its rated current for tens of seconds to blow . Fuse selection depends on the load's characteristics.
What is a fuse?
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once ...
Why are fused devices used?
Fuses have been used as essential safety devices from the early days of electrical engineering. Today there are thousands of different fuse designs which have specific current and voltage ratings, breaking capacity, and response times, depending on the application.
What is a fuse element made of?
The fuse element is made of zinc, copper, silver, aluminum, or alloys among these or other various metals to provide stable and predictable characteristics. The fuse ideally would carry its rated current indefinitely, and melt quickly on a small excess. The element must not be damaged by minor harmless surges of current, and must not oxidize or change its behavior after possibly years of service.

Overview
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, and must be replaced or rewired, depending on its type.
History
Breguet recommended the use of reduced-section conductors to protect telegraph stations from lightning strikes; by melting, the smaller wires would protect apparatus and wiring inside the building. A variety of wire or foil fusible elements were in use to protect telegraph cables and lighting installations as early as 1864.
A fuse was patented by Thomas Edison in 1890 as part of his electric distribution system.
Construction
A fuse consists of a metal strip or wire fuse element, of small cross-section compared to the circuit conductors, mounted between a pair of electrical terminals, and (usually) enclosed by a non-combustible housing. The fuse is arranged in series to carry all the charge passing through the protected circuit. The resistance of the element generates heat due to the current flow. The size and construction of the element is (empirically) determined so that the heat produced for a norm…
Characteristics
A maximum current that the fuse can continuously conduct without interrupting the circuit.
The speed at which a fuse blows depends on how much current flows through it and the material of which the fuse is made. Manufacturers can provide a plot of current vs time, often plotted on logarithmic scales, to characterize the device and to allow comparison with the characteristics of protective devices upstream and downstream of the fuse.
Voltage drop
The manufacturer may specify the voltage drop across the fuse at rated current. There is a direct relationship between a fuse's cold resistance and its voltage drop value. Once current is applied, resistance and voltage drop of a fuse will constantly grow with the rise of its operating temperature until the fuse finally reaches thermal equilibrium. The voltage drop should be taken into account, particularly when using a fuse in low-voltage applications. Voltage drop often is not significant in …
Temperature derating
Ambient temperature will change a fuse's operational parameters. A fuse rated for 1 A at 25 °C may conduct up to 10% or 20% more current at −40 °C and may open at 80% of its rated value at 100 °C. Operating values will vary with each fuse family and are provided in manufacturer data sheets.
Markings
Most fuses are marked on the body or end caps with markings that indicate their ratings. Surface-mount technology "chip type" fuses feature few or no markings, making identification very difficult.
Similar appearing fuses may have significantly different properties, identified by their markings. Fuse markings will generally convey the following information, either explicitly as text, or else implicit with the approval agency marking for a particular type:
Packages and materials
Fuses come in a vast array of sizes and styles to serve in many applications, manufactured in standardised package layouts to make them easily interchangeable. Fuse bodies may be made of ceramic, glass, plastic, fiberglass, molded mica laminates, or molded compressed fibre depending on application and voltage class.
Cartridge (ferrule) fuses have a cylindrical body terminated with metal end caps. Some cartridg…