What is formed in the outwash plain?
Formation. The material in the outwash plain is often size-sorted by the water runoff of the melting glacier with the finest materials, like silt, being the most distantly re-deposited, whereas larger boulders are the closest to the original terminus of the glacier.
What are outwash plains used for?
Outwash plains made up of outwash deposits are characteristically flat and consist of layers of sand and other fine sediments. Such plains with their sandy soils are often used for specialized kinds of agriculture, such as the potato production in Montcalm County.
What are the characteristics of outwash?
The sheet of outwash may be pitted with undrained kettles or dissected by postglacial streams. Outwash plains are commonly cross-bedded with units of alternating grain size. The ordinarily gentle slope causes the larger material to be dropped nearest the glacier, while the smaller grain sizes are spread over greater distances.
What is the difference between a till plain and an outwash?
The till plain has a gently undulating to hilly surface; the outwash is flat or very gently undulating where it is a thin veneer on the underlying till. As a rule flourishing farms are on the till plains; the majority of abandoned farms in the northern part of the Lower Peninsula are on sandy outwash plains.

What is outwash soil?
OUTWASH PLAINS. The large quantities of water that flowed from the melting ice deposited various kinds of materials, the most important of which is called glacial outwash. Outwash plains made up of outwash deposits are characteristically flat and consist of layers of sand and other fine sediments.
What is an outwash plain for kids?
Ans. Outwash is a deposit of sand and gravel transferred by running water from the melting ice of glaciers and laid down in stratified deposits.
What are the holes created in the outwash plains of glaciers known as?
kettle, also called Kettle Hole, in geology, depression in a glacial outwash drift made by the melting of a detached mass of glacial ice that became wholly or partly buried.
What is a glacial outwash feature?
Glacial outwash channels are alluvial channels with gradients less than 3 %. Being associated with glaciers these streams carry turbid water with extremely high sediment loads, except for peri-glacial subalpine cirque basin channels.
Are outwash plains good for farming?
Immediately to the south are outwash plains that are composed of well sorted sand and gravel deposited by high energy streams of glacial melt water. These outwash plains are highly desirable for agriculture and for sand and gravel deposits because of their good drainage.
What is the difference between a moraine and an outwash plain?
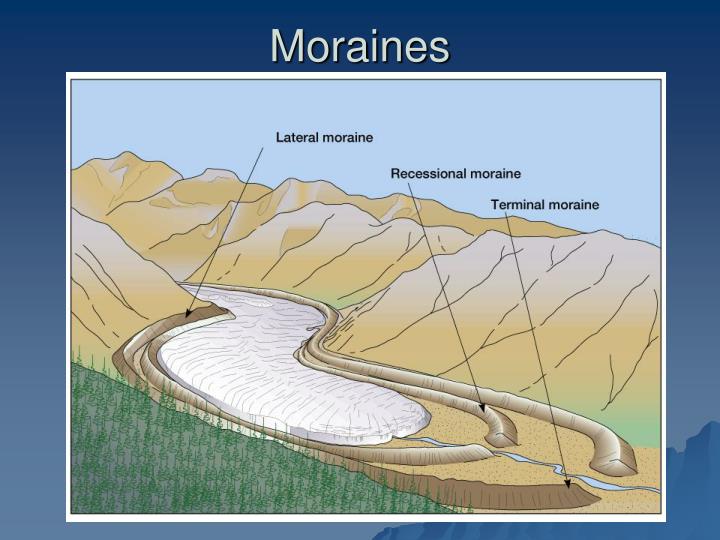
1. Landforms formed by the glacial deposits of the valley or continental glaciers are termed moraines. An outwash plain consists of glacial sediments deposited by the melting ice at the terminus of a glacier. 2.
How does an outwash plain developed?
Outwash plains and eskers form due to the flow of meltwater in front of (outwash plains) or beneath (eskers) that glacier ice. They are composed of glacial sediments that have been reworked by flowing water.
How are kettle holes formed?
Depressions, known as kettles, often pockmark these outwash plains and other areas with glacial deposits. Kettles form when a block of stagnant ice (a serac) detaches from the glacier. Eventually, it becomes wholly or partially buried in sediment and slowly melts, leaving behind a pit.
Why are they called kettle holes?
As the glacier retreats the block of ice is left stranded. The ice then gets surrounded and possibly buried by subsequent meltwater deposits and outwash. Eventually, when the temperature increases and the ice block melts it leaves a large depression in the ground that the ice occupied. These are known as kettle holes.
Are outwash plains constructive or destructive?
How is outwash formed and is it constructive or destructive? It is a plain formed of glacial sediments deposited by meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. It is constructive.
What is an outwash moraine?
In southern Michigan, most moraines have a substantial clay component, while in northern Michigan, many moraines have much more sand than clay. Outwash: relatively level to gently rolling topography, usually found at lower elevations in the landscape.
1. What is an Outwash?
Ans. Outwash is a deposit of sand and gravel transferred by running water from the melting ice of glaciers and laid down in stratified deposits. Th...
2. What are the Three Major Depositional Landforms Formed By the Glaciers?
Ans. The three major depositional landforms formed by the glaciers are:EskersOutwash PlainsDrumlins
3. What is the Flow Pattern of Glacial Rivers Across the Outwash Plain?
Ans. The flow pattern of glacial rivers across the outwash plain is generally not channelized and dispersed, but in the conditions where the snout...
4. What are Braided Streams?
Ans. A braided stream is a stream consisting of multiple shallow streams that divide and recombine multiple times forming a pattern that resembles...
Formation
Sandurs are found in glaciated areas, such as Svalbard, Kerguelen Islands, and Iceland.
The prototype sandur
Unimpeded by topographic obstructions, sand-bearing katabatic winds can be fierce enough on Skeiðarársandur to strip paint from cars. Here, sand is blown in the air in front of the peak Lómagnúpur.
Fossil sandar
Fossil sandar (i.e. no longer active) are found in areas which were formerly glaciated. An example would be the Usk Valley of South Wales where towards the end of the last ice age, the receding Usk valley glacier left behind a series of recessional moraines and sandar deposits down-valley of them.
What is Outwash Plain?
An outwash plain is both an erosional and depositional surface formed by meltwater coming from the glaciers. These plains are generally identified by braided streams and found in the front of the glaciers. The streams are generally small and braided because the size of the sediment varies and the original stream gets split up.
Define Outwash Plain
A wide, tenderly sloping sheet of outwash accumulated by meltwater streams flowing in front of or beyond a glacier, and formed by coalescing outwash fans is defined as an outwash plain.
Outwash Plains Formation
A fluvioglacial landform formed by both deposition and erosion by meltwater is a glacial outwash plain or sandur that generally has braided streams.
Outwash Plains Occurrence
The Kerguelen Islands, Svalbard, and Iceland are the islands where the outward plains are found. Outwash plains are also most commonly found where geothermal activities below the ice caps accelerate the deposits of the sediments by meltwater.
Glacial Outwash
The considerable amount of water that flowed from melting ice deposited different kinds of materials, the most important of which are glacial outwash. Glacial outwash plains made up of outwash deposits are flat and consist of layers of sand and other fine sediments.
Did You Know?
An outwash, also known as sandur, is a plain formed by melting glaciers.

Overview
An outwash plain, also called a sandur (plural: sandurs ), sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and carries the debris along. The meltwater at the snout of the glacier deposits its load of sediment over the outwash plain, with larger boulders being deposited near th…
Formation
Sandurs are found in glaciated areas, such as Svalbard, Kerguelen Islands, and Iceland. Glaciers and icecaps contain large amounts of silt and sediment, picked up as they erode the underlying rocks when they move slowly downhill, and at the snout of the glacier, meltwater can carry this sediment away from the glacier and deposit it on a broad plain. The material in the outwash plain is often size-…
The prototype sandur
One of the sandurs from which the general name is derived is Skeiðarársandur, a broad sandy wasteland along Iceland's south-eastern coast, between the Vatnajökull icecap and the sea. Volcanic eruptions under the icecap have given rise to many large glacial bursts (jökulhlaups in Icelandic), most recently in 1996, when the Ring Road was washed away (minor floods have also occurred since …
Fossil sandar
Fossil sandar (i.e. no longer active) are found in areas which were formerly glaciated. An example would be the Usk Valley of South Wales where towards the end of the last ice age, the receding Usk valley glacier left behind a series of recessional moraines and sandar deposits down-valley of them. Many of the sandar surfaces are still visible albeit degraded over succeeding millennia. Extensive sandar are also recorded in the eastern part of the Cheshire Plain and beneath Moreca…
See also
• Kankakee Outwash Plain
• Terminal moraine – Type of moraine that forms at the terminal of a glacier
External links
• NASA page about the Skeiðarársandur
• A study of sandur formation in western Greenland