What is the difference between anaerobic and fermentation?
The main difference between fermentation and anaerobic respiration is that fermentation does not undergo citric acid cycle ( Krebs cycle) and electron transport chain whereas anaerobic respiration undergoes citric acid cycle and electron transport chain.
What are the purposes of anaerobic fermentation?
Anaerobic respiration — also known as fermentation — helps produce beer and wine and happens without the presence of oxygen, while aerobic respiration requires oxygen to be present. What is the main purpose of fermentation? The purpose of fermentation is to regenerate the electron carriers used in glycolysis and produce a small amount of ATP.
What are the advantages of anaerobic fermentation?
What Are the Pros of Anaerobic Respiration?
- Muscles can respire even when they don’t have oxygen available. When you’re working out, the amount of oxygen the body needs to aerobically respire increases. ...
- It assists aerobic respiration. A unique component of anaerobic respiration is the fact that it can metabolize pyruvic acid. ...
- The body can adapt the energy more quickly. ...
Is aerobic more effective than fermentation?
This makes aerobic respiration approximately 19 times more efficient than fermentation or anaerobic respiration. There’s only 2 ATP produced in fermentation because the rest of the energy is actually combined with the waste materials produced after the fermentation process.

What is fermentation anaerobic?
“Fermentation is an anaerobic process in which energy can be released from glucose even if oxygen is not available.”
What are examples of anaerobic fermentation?
Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation (which can result in yogurt and in sore muscles), and in decomposition of organic matter. The equation is: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol/lactic acid.
Why is fermentation an anaerobic process explain?
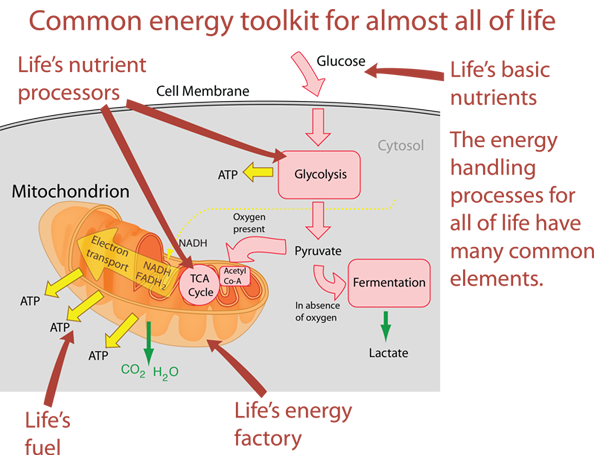
When oxygen is not present or if an organism is not able to undergo aerobic respiration, pyruvate will undergo a process called fermentation. Fermentation does not require oxygen and is therefore anaerobic. Fermentation will replenish NAD+ from the NADH + H+ produced in glycolysis.
What is difference between aerobic and anaerobic fermentation?
Aerobic and anaerobic fermentation are two types of cellular respiration involved in the production of energy from glucose. Aerobic fermentation requires oxygen while anaerobic fermentation does not require oxygen.
Where does anaerobic fermentation occur?
Fermentation is an anaerobic process in which energy can be released from glucose even though oxygen is not available. Fermentation occurs in yeast cells, and a form of fermentation takes place in bacteria and in the muscle cells of animals.
What are the 3 types of fermentation?
The three main types of fermentation are alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation and acetic acid fermentation. Also Check: Types Of Fermentation.
What is fermentation short answer?
Fermentation is the process in which a substance breaks down into a simpler substance . Fermentation refers to the metabolic process by which organic molecules ( mainly carbohydrates, such as starch or a sugar) are converted into acids, gases, or alcohol in the absence of oxygen or any electron transport chain.
What is the process of fermentation?
Fermentation is the process of sugars being broken down by enzymes of microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi have unique sets of metabolic genes, allowing them to produce enzymes to break down distinct types of sugar metabolites.
What are two types of fermentation?
The two types of fermentation are:Lactate fermentation: This type of fermentation produces lactic acid.Alcoholic fermentation: It is also called ethanol fermentation, which involves converting pyruvate to acetaldehyde and CO2.
Is yeast fermentation anaerobic or aerobic?
Yeast fermentation In the presence of oxygen, yeast undergo aerobic respiration and convert carbohydrates (sugar source) into carbon dioxide and water. In the absence of oxygen, yeasts undergo fermentation and convert carbohydrates into carbon dioxide and alcohol (Figure 2).
Is all fermentation anaerobic?
Fermentation products are considered waste products, since they cannot be metabolized further without the use of oxygen. Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O2, NADH, and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration.
What is aerobic and anaerobic process?
There are two types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What is anaerobic fermentation?
Anaerobic fermentation is usually a slower process. In the mid-1850s, the French chemist Louis Pasteur produced anaerobiosis by boiling the medium to drive out oxygen and then introducing inert gas for cultivation. He showed that a microorganism, probably Clostridium butyricum, was responsible for butyric acid fermentation. In the 1960s and 1970s, anaerobic chambers were invented that allowed the cultivation of numerous anaerobic cultures for certain strictly anaerobic organisms, including C. botulinum. During World War I, industrial anaerobic fermentation was further demonstrated by Perkins and Weizmann, who worked on acetonebutanol-ethanol (ABE) fermentation with C. acetobutylicum.
Why is anaerobic fermentation important?
Because less biomass is produced in anaerobic fermentations, more carbon can be converted to the end product, and a higher product yield is attained . Anaerobes can utilize a wide range of substrates, including agricultural waste streams.
What is the role of acetogenic bacteria in methanogenic archaea?
The acetogenic bacteria are responsible for oxidation of the products generated in the acidogenic phase into suitable substrates (H 2 and acetic acid) for methanogenic archaea. In the last step, the methanogenic archaea convert the H 2 and acetic acid into CH 4 and CO 2 ( Sá et al., 2014; Christy et al., 2014 ).
What are the factors that affect the productivity and stability of anaerobic fermentation?
Several factors can affect the productivity and stability of the anaerobic fermentative system for biogas production, such as temperature, pH, carbon-to-nitrogen mass ratio (C:N ratio), redox potential, organic loading rate (OLR), and retention time.
What is the first step of hydrolysis?
The first phase involves the hydrolysis of complex organic materials into simple organic materials such as sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids. In the acidogenic phase, the soluble products from the previous step are converted into volatile organic acids, alcohols, CO 2, H 2, and new bacterial cells.
How is riboflavin obtained?
Riboflavin is chemically obtained from d -ribose by the long and tedious Karrer–Tishler process. In this process, an overall yield of 60% can be obtained using many organic solvents and protection/deprotection steps. Roche in collaboration with OmniGene carried out the biosynthesis using a GMO. The key to the success was gene deregulation, replacement of native promoters by constitutive ones, and increasing gene copy numbers. Downstream processing of riboflavin from fermentation is easy because the riboflavin precipitates from the fermentation broth and the crystals are collected by centrifugation (purity > 95%). After conventional crystallization, > 99% purity can be achieved ( Figure 4 ).
How is lactic acid produced?
Lactic acid is chemically produced by hydrocyanation ( Figure 1) followed by hydrolysis of the cyanohydrin. The main drawbacks are the manipulation of hydrogen cyanide (HCN), the production of (NH 4) 2 SO 4 (1 eq), and the complex purification steps to obtain food-grade lactic acid because the racemic acid is obtained.
How is fermentation used in coffee processing?
From the point that the coffee cherry is picked from the coffee tree, a chemical change begins inside. This change is present in all coffee processing methods, it’s simple bio-chemistry. Sugars in a fruit with air present bacteria begin a what we call fermentation.
Anaerobic Fermentation
If all coffee is fermented, what is so special or different about anaerobic fermentation? Anaerobic fermentation occurs when oxygen is removed from the equation. This process rapidly changes the coffee fruit, resulting in a flavor much different than traditional fermentation methods.
What is the fermentation method used by animals?
This occurs routinely in mammalian red blood cells and in skeletal muscle that does not have enough oxygen to allow aerobic respiration to continue (such as in muscles after hard exercise). The chemical reaction of lactic acid fermentation is the following:
Why can't the citric acid cycle occur in the absence of oxygen?
However, the citric acid cycle can not occur in the absence of oxygen because there is no way to regenerate the NAD+ that is required for the citric acid cycle to proceed.
What happens to lactic acid after it is removed from the body?
Once the lactic acid has been removed from the muscle and is circulated to the liver, it can be converted back to pyruvate and further catabolized for energy . Note that the purpose of this process is not to produce lactic acid (which is a waste product and is excreted from the body).
What is the process of regenerating NAD?
Processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD + from NADH are collectively referred to as fermentation. In contrast, some living systems use an inorganic molecule (such as nitrate or sulfur) to regenerate NAD +. Both of these methods are anaerobic (do not require oxygen) to achieve NAD + regeneration and enable organisms ...
What happens when NADH and FADH 2 give up their electrons?
When NADH or FADH 2 give up their high energy electrons to the electron transport chain, NAD + and FAD are regenerated. These low energy molecules cycle back to glycolysis and/or the citric acid cycle, where they pick up more high energy electrons and allow the process to continue.
What is the process of fermentation?
Fermentation – Anaerobic Respiration. Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration where respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation is an anaerobic pathway- a common pathway in the majority of prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes. In this process, glucose is partially oxidised to form acids and alcohol.
What enzymes catalyze lactic acid fermentation?
The whole reaction is catalyzed by the enzymes, pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase. In certain bacteria and animal muscle cells, under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase. This is called lactic acid fermentation. The end products of these anaerobic pathways make them hazardous ...
What is the process of converting starch into lactic acid?
Lactic Acid Fermentation. In this, starch or sugar is converted into lactic acid by yeast strains and bacteria. During exercise, energy expenditure is faster than the oxygen supplied to the muscle cells. This results in the formation of lactic acid and painful muscles.
What is the respiration of the cell?
The respiration that happens at the minute level in our body , viz., in the cell is called the cellular respiration. It occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen. Any type of cellular respiration begins with glycolysis where a 3-C molecule, pyruvic acid is formed as the end product.
Is ATP released during fermentation?
The energy released in both the processes is not much and the total sum of ATP molecules produced during fermentation is two , which is very less as compared to aerobic respiration. However, this is commercially employed in the food and beverage industries, and pharmaceutical industries.
