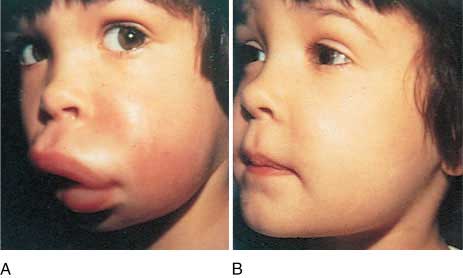
What are the signs and symptoms of angioedema?
Symptoms
- Hives. Angioedema may cause large welts below the surface of the skin, particularly around the eyes and lips.
- Angioedema. Angioedema is a reaction similar to hives that affects deeper layers of the skin. It can appear with hives or alone.
- When to see a doctor. You can usually treat mild cases of hives or angioedema at home. ...
What drugs cause angioedema?
They include:
- Penicillin
- Aspirin
- Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ), like ibuprofen and naproxen.
How to diagnose hereditary angiodema?
Signs You Can Check For:
- Swollen lips
- Swollen eyes
- Swelling of the arms or legs
- Swelling of your tongue or the back of your throat
- Unexpected swelling in any part of the body
- Discoloration: The swelling of angioedema is seen on the surface of the skin and appears puffy. ...
- Blanching: The reddish discoloration that occurs with angioedema blanches.
How does angioedema is treated?
Treatments for hives and angioedema may include prescription drugs:
- Anti-itch drugs. The standard treatment for hives and angioedema is antihistamines that don't make you drowsy. ...
- Drugs that suppress the immune system. If antihistamines are not effective, your doctor might prescribe a drug that can calm an overactive immune system.
- Drugs for hereditary angioedema. ...
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. ...

What causes angioneurotic edema?
Angioedema can be triggered by an allergic reaction to: certain types of food – particularly nuts, shellfish, milk and eggs. some types of medicine – including some antibiotics, aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen. insect bites and stings – particularly wasp and bee stings.
What is the symptom of angioneurotic edema?
The main symptom is sudden swelling below the skin surface. Welts or swelling on the surface of the skin can also develop. The swelling usually occurs around the eyes and lips.
What is meaning of angioneurotic edema?
Angioneurotic edema is a relatively common presentation in the emergency department (ED). It presents as unpredictable frequent edematous episodes of cutaneous and mucosal tissues such as lips, eyes, oral cavity, larynx, and gastrointestinal system (GIS).
What is the difference between angioedema and angioneurotic edema?
Angioneurotic edema, hereditary: A genetic form of angioedema. (Angioedema is also referred to as Quinke's disease.) Persons with it are born lacking an inhibitor protein (called C1 esterase inhibitor) that normally prevents activation of a cascade of proteins leading to the swelling of angioedema.
Is angioedema life threatening?
Hives and angioedema are usually treated with antihistamine medication. Angioedema can be life-threatening if swelling of the tongue or in the throat blocks the airway.
What is the best treatment for angioedema?
Medication is the main treatment for angioedema, although many cases get better after a few days without treatment. Allergic angioedema and idiopathic angioedema are usually treated in the same way, using a combination of antihistamines and corticosteroids to help relieve the swelling.
Who is most at risk for angioedema?
Significant risk factors for severe cases of angioedema included older age, Hispanic race, ACEi-induced angioedema type, American Society of Anesthesiologists class III or above, coexistent cardiopulmonary disease, and a positive smoking history.
Should I go to the hospital for angioedema?
If your angioedema is severe you will need to be treated in a hospital right away. At the hospital, the staff will give take necessary steps to stop the allergic reaction and help ease your symptoms. If your symptoms are mild, you might not need treatment.
How can I reduce swelling from angioedema at home?
If you're experiencing mild hives or angioedema, these tips may help relieve your symptoms:Avoid triggers. ... Use an anti-itch drug available without a prescription. ... Apply cold. ... Take a comfortably cool bath. ... Wear loose, smooth-textured cotton clothing. ... Protect your skin from the sun.
What is the most common cause of angioedema?
The most common cause of angioedema was allergic angioedema. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced angioedema and idiopathic angioedema were detected in 20% and 18%, respectively. Among patients with allergic angioedema, 41.7% were caused by food, 39.6% by drugs.
Which drugs can cause edema?
Many medicines can cause edema, including:NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen and naproxen)Calcium channel blockers.Corticosteroids (like prednisone and methylprednisolone)Pioglitazone and rosiglitazone.Pramipexole.
What autoimmune disease causes angioedema?
In an estimated 30–50% of the cases, idiopathic angioedema may be associated with an underlying autoimmune disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
What is angioneurotic edema?
Angioneurotic edema is a relatively common presentation in the emergency department (ED). It presents as unpredictable frequent edematous episodes of cutaneous and mucosal tissues such as lips, eyes, oral cavity, larynx, and gastrointestinal system (GIS). Urticaria (hives) and angioedema are part of a spectrum of allergic symptoms ...
Is urticaria a non-allergic etiology?
Urticaria (hives ) and angioedema are part of a spectrum of allergic symptoms and occasionally have a non-allergic etiology. Laryngeal edema causing airway obstruction with the potentially fatal outcome if the diagnosis is late.
What is angioedema in the gastrointestinal tract?
Angioedema is a hypersensitivity disorder that manifests as an acute onset of noninflammatory edema in the subcutaneous tissues or mucosa , most often in the upper respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts. From: Pediatric Emergency Medicine, 2008. Download as PDF. About this page.
What is the cause of angioedema in the upper airway?
Of these, up to 40% of patients present with life-threatening angioedema of the upper airway. It is thought to result from inhibition of kininase II, which breaks down bradykinin, as well as converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II in the renin–aldosterone pathway.
How long does it take for losartan to cause angioedema?
For example, losartan has been associated with angioedema from within 30 minutes after administration to 3 years after starting therapy.
How long does it take for an ACE I to develop?
Diabetics appear to be at a reduced risk. The interval between starting an ACE-I and developing angioedema is usually less than 1 month; frequently it begins within the first week, but is greater than 6 months in over 25% of cases and can be as long as 10 years. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
How long does it take for angioedema to develop after ACE?
Although in most cases angioedema develops within the first week of treatment with ACE inhibitors, the onset of symptoms may occur several years later. Treatment involves discontinuation of ACE inhibitor therapy. Angioedema often recurs on re-exposure to ACE inhibitors.
How is angioedema diagnosed?
Angioedema is diagnosed clinically and from a history of atopic disease and/or exposure to allergen, and sometimes by allergy testing (prick test), but only where there are appropriate resuscitation facilities and an emergency kit containing injectable adrenaline at hand. Mast cell tryptase levels may be raised.
What is angioedema type 1?
AETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS. Allergic angioedema is a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction that may be induced by: ▪. Foods: nuts are a well-known cause but many other foods (e.g. shellfish, eggs, milk) may be implicated. ▪.
What are the symptoms of angioedema?
This will lead to the following signs: sudden or rapidly escalating breathing problems. fainting or dizziness.
What is the treatment for angioedema?
This means that in an emergency, a breathing tube might be placed for safety. An allergic reaction may be treated with epinephrine, which is the drug in an EpiPen. Other medications include antihistamines and corticosteroids.
What is the swelling of the skin?
Swelling is the main symptom of angioedema. Angioedema is a swelling of the area beneath the skin, similar to urticaria, or hives. However, urticaria affects only the upper dermis, or top layer of skin. Angioedema affects the deeper layers, including the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, the mucosa, and submucosal tissues.
Why does my mucosa swell?
Types. Diagnosis. Complications. Angioedema is the rapid edema, or swelling, of the area beneath the skin or mucosa. It is normally an allergic reaction, but it can also be hereditary. The swelling happens because fluid accumulates.
What test is used to confirm angioedema?
A person with angioedema may be referred for further tests to confirm the type. These may include: a skin prick test to confirm a link to possible allergies, in which the skin is pricked with a very small amount of the allergen that is suspected. a blood test to see how the immune system reacts to a certain allergen.
What is the most common type of angioedema?
Allergic angioedema. This is the most common type, and it usually affects those with an allergy to a type of food, a medication, venom, pollen, or animal dander. In serious cases, there may be a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis. The throat may swell, making it hard for the patient to breath.
Can angioedema be hereditary?
If the cause is hereditary, the patient may receive specialized medications. Trusted Source. , a concentrate of the C1 inhibitor, the protein they are missing, or fresh frozen plasma. Where appropriate, identifying and avoiding the allergen that leads to angioedema is key to preventing the occurrence of this condition.
What is angioedema in medical terms?
an·gi·o·e·de·ma. ( an'jē-ō-ĕ-dē'mă) 1. Recurrent large circumscribed areas of subcutaneous edema of sudden onset, usually disappearing within 24 hours; seen mainly in young women, frequently as an allergic reaction to foods or drugs. 2.
What is the synonym for angioedema?
Synonym (s): angioedema (2) , angioneurotic edema (2) .
How to reduce edema in the lower extremities?
Bed rest helps relieve lower extremity edema. Sitting with the feet and legs elevated may also reduce edema in the lower extremities. Dietary salt should be restricted to less than 2 g/day. Fluid intake may be restricted to about 1500 ml in 24 hr. This prescription may be relaxed when free diuresis has been attained.
What is the pathological edema of the larynx?
Pathological edema in the tissues lining the vocal structures of the larynx. It may result from improper use of the voice, excessive use of tobacco or alcohol, chemical fumes, or viral, bacterial, or fungal infections. Clinically, the patient often presents with hoarseness or, in severe cases, with respiratory distress and stridor. See: epiglottitis
How are fragile edematous tissues protected?
Fragile edematous tissues are protected from damage by careful handling and positioning and by providing and teaching about special skin care. Edematous extremities are mobilized and elevated to promote venous return, and lung sounds auscultated for evidence of increasing pulmonary congestion.
What is the best treatment for pulmonary edema?
Assisted ventilation (continuous positive airway pressure [CPAP] or intubation with mechanical ventilation) may be needed to reach acceptable levels of PaO2 and improve acid-base balance. Morphine sulfate, nitrate vasodilators (IV nitroglycerin or nitroprusside) and loop diuretics are typically given to patients with cardiogenic pulmonary edema to improve dyspnea, alter preload and afterload on the heart, and promote diuresis. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, inotropic drugs (digoxin), antiarrhythmic agents, beta-adrenergic blockers, human B-type natriuretic peptide, and phosphodiesterase inhibitors may be used in selected circumstances. Bronchodilators may also be administered. Depending on the underlying cause, invasive interventions may occasionally include coronary angiography, intra-aortic balloon pump therapy, or surgical interventions such as coronary artery revascularization or valve repair, or ventricular assist device therapy.
Why does the brain swell?
It may be caused by increased permeability of brain capillary endothelial cells, focal strokes, swelling of brain cells associated with hypoxia or water intoxication, trauma to the skull, or interstitial edema due to obstructive hydrocephalus.

General Information
- Angioneurotic edema (angioedema) is an acutely developing local swelling of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, mucous membranes of an allergic or pseudoallergic nature, most often occurring on the face (lips, eyelids, cheek, tongue), less often – on the mucous membranes (respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary organs). With the develop...
Causes
- Acquired angioneurotic edema often develops in response to the penetration of an allergen into the body – a drug, a food product, as well as with insect bites and stings. The resulting acute allergic reaction with the release of inflammatory mediators increases the permeability of blood vessels located in the subcutaneous fat and submucosal layer, and leads to the appearance of l…
Classification
- According to clinical manifestations, there is an acute course of angioneurotic edema lasting less than 1.5 months and a chronic course when the pathological process lasts 1.5-3 months or longer. Isolated and combined with urticaria angioedema are isolated. Depending on the mechanism of edema development, there are diseases caused by a violation of the regulation o…
Symptoms of Angioneurotic Edema
- Angioedema develops, as a rule, acutely within 2-5 minutes, less often angioedema can form gradually with an increase in symptoms for several hours. Typical localization sites are areas of the body where there is loose fiber: in the area of the eyelids, cheeks, lips, on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, on the tongue, as well as on the scrotum in men. If edema develop…
Diagnostics
- The characteristic clinical picture, typical for angioneurotic edema with localization on the face and other exposed areas of the body, allows you to quickly establish the correct diagnosis. The situation is more difficult when a picture of an “acute abdomen” or a transient ischemic attack appears, when it is necessary to differentiate the observed symptoms with a number of disease…
Treatment of Angioneurotic Edema
- First of all, with angioedema of any etiology, it is necessary to eliminate the threat to life. To do this, it is important to restore the patency of the respiratory tract, including by intubation of the trachea or conicotomy. With allergic angioedema, glucocorticoids, antihistamines are administered, contact with a potential allergen is eliminated, infusion therapy, enterosorption is …
Prognosis and Prevention
- The outcome of angioneurotic edema depends on the severity of the manifestations and the timeliness of therapeutic measures. Thus, laryngeal edema in the absence of emergency care ends in death. Recurrent urticaria, combined with angioneurotic edema and lasting for six months or more, is further observed in 40% of patients for another 10 years, and 50% may experience pr…