The anode angle is the angle between the vertical and the target surface with most x-ray tubes having an anode angle of 12-15°. A smaller angle results in a smaller effective focal spot. The whole anode is not included in x-ray production.
What is the function of an anode?
Anodes are designed as bevelled disks attached to a large copper rotor of the electric motor, rotating them at the speeds up to 10,000 rpm, with a temperature of 2000°C. The purpose of the rotation is to dissipate heat.
How does the anode angle affect the focal spot?
When the electron beam hits the anode (at the actual focal spot), interactions of the electrons with the target material produces the x-ray beam. The anode angle is the angle between the vertical and the target surface with most x-ray tubes having an anode angle of 12-15°. A smaller angle results in a smaller effective focal spot.
How does anode heel effect change with anode angle?
*** Increasing SID, decreasing field size and an increased anode angle will all lead to decreased anode heel effect. Remember the relationships of all of these specifications share with the anode heel effect.
What is the anode angle of an xray tube?
The anode angle is the angle between the vertical and the target surface with most x-ray tubes having an anode angle of 12-15°. A smaller angle results in a smaller effective focal spot. The whole anode is not included in x-ray production. X-rays are produced on the rather small rectangular surface, the focal spot.

Why is the anode angle?
0:135:31Anode Heel Effect (X-Ray Tube) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd 20 degrees. And this is a good thing for two main reasons the anode angle actually increases theMoreAnd 20 degrees. And this is a good thing for two main reasons the anode angle actually increases the surface area of the focal spot which increases.
What is the target angle in radiography?
In diagnostic radiology, the target angles are quite small (6–17 degrees) to produce apparent focal spot sizes ranging from 0.1 × 0.1 mm to 2 × 2 mm. In most therapy tubes, however, the target angle is larger (about 30 degrees) and the apparent focal spot ranges between 5 × 5 mm and 7 × 7 mm.
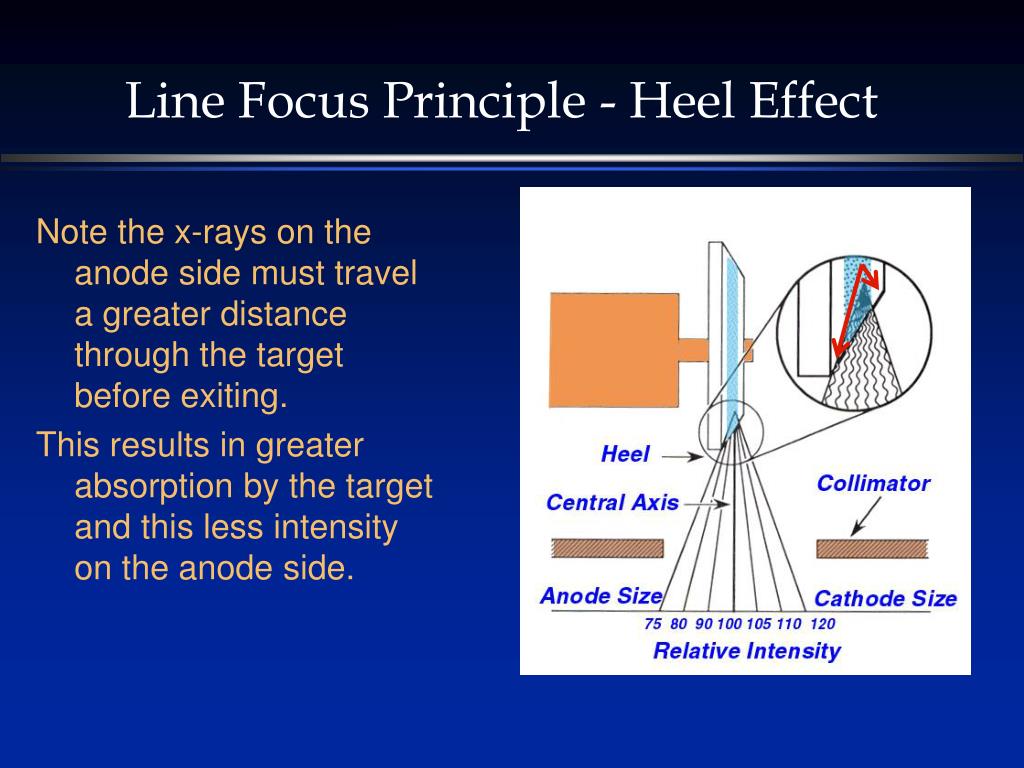
What is anode heel?
The anode heel effect in radiography is a well-described physical phenomenon,1,2 whereby radiation intensity varies along the anode–cathode axis of the X-ray tube, decreasing towards the anode. Photons emitted towards the tube's anode side are attenuated more than those emitted towards the cathode.
What is anode and cathode in xray tube?
As with any vacuum tube, there is a cathode, which emits electrons into the vacuum and an anode to collect the electrons, thus establishing a flow of electrical current, known as the beam, through the tube.
What is radiotherapy anode?
It consists of a copper screen, or "grid," and is an anode. An anode is a surface with a positive electrical charge.
What is anode heat?
The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x-rays dissipating heat as a byproduct. Most x-ray tube anodes are made of tungsten (the target material). Tungsten has a high atomic number (Z=74) and a high melting point of 3370°C with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation.
Why is anode heel effect important?
Introduction: The anode heel effect can be used to optimize image quality and/or patient dose in digital radiography (DR). In film-screen radiography, the effect can equalize optical density in regions of varying attenuation.
What is the relationship between anode angle and heel effect?
anode angle: by increasing the angle, the amount of target material perpendicular to the anode is decreased resulting in less resorption of x-rays produced. target-to-film distance: increase in distance reduces heel effect by allowing more divergence of the beam which produces a more uniform image.
What is the 15 rule in radiography?
A 15% increase in kVp has the same effect as doubling the mAs. A 15% decrease in kVp has the same effect as decreasing the mAs by half. Increasing the kVp by 15% increases the exposure to the IR, unless the mAs is decreased.
What is anode and cathode?
The Anode is the negative or reducing electrode that releases electrons to the external circuit and oxidizes during and electrochemical reaction. The Cathode is the positive or oxidizing electrode that acquires electrons from the external circuit and is reduced during the electrochemical reaction.
Is anode positive or negative?
anode, the terminal or electrode from which electrons leave a system. In a battery or other source of direct current the anode is the negative terminal, but in a passive load it is the positive terminal.
Is cathode positive or negative?
negativeThe cathode is the electrode where electricity is given out or flows out. The anode is usually the positive side. A cathode is a negative side. It acts as an electron donor.
What is the angle of an anode?
The anode angle is the angle between the vertical and the target surface with most x-ray tubes having an anode angle of 12-15°. A smaller angle results in a smaller effective focal spot. The whole anode is not included in x-ray production. X-rays are produced on the rather small rectangular surface, the focal spot.
What is an anode?
Anode (x-ray tube) The anode (or anticathode) is the component of the x-ray tube where x-rays are produced. It is a piece of metal, shaped in the form of a bevelled disk with a diameter between 55 and 100 mm, and thickness of 7 mm, connected to the positive side of the electrical circuit.
What is the body of an anode made of?
The body of the anode is made of materials that are light and have a good heat storage capacity, like molybdenum and graphite. Molybdenum is also often used as the target material for anodes used in mammography because it has an intermediate atomic number (Z=42) and the produced characteristic x-rays are of energies suited for this purpose. ...
What is the optimum anode angle for photon beam spectra?
Our results showed that the photon beam spectra and their mean energy are changed significantly with anode angle and the optimum anode angle of 30 degrees was selected based on less heel effect and appropriate depth dose and photon fluence per initial electron.
What is a MC model of X-RAD320?
In the current study, an MC model of X-RAD320 biological irradiator, which is being used currently for animal and cell culture irradiation, was built based on the manufacturer provided data. The effect of anode angle on dosimetric properties of this unit was studied and the optimum anode angle was selected for the unit. The purpose was to verify the appropriateness of anode angle for X-RAD320 biological irradiator by the MC method. Additionally, the validated MC model can be used either for further studies on its dosimetry or for the application of this unit for animal radiation therapy.
What is an anode?
The anode is a metal target electrode that is maintained at a positive potential difference relative to the cathode. With the cathode filament heated and voltage applied between the electrodes, electrons emitted by the cathode are accelerated toward the anode and deposit most of their energy as heat, with only a small fraction emitted as x-rays. Consequently, the rate of x-ray production, proportional to the tube current, is limited to avoid heat damage to the anode. The anode area impacted by the electrons, the focal spot, also limits the amount of power density (energy per unit time per unit area) that can be deposited. Tungsten is the most widely used anode material because of its high melting point (3,000°C) and high atomic number ( Z = 74). A tungsten anode can handle substantial heat deposition without cracking or pitting of its surface. An alloy of 10% rhenium and 90% tungsten provides added resistance to surface heat damage. In addition, tungsten provides greater bremsstrahlung production for the same tube current than lower Z elements ( Eq. 6-1 ).
What is the cathode in an x-ray tube?
The cathode is the negative electrode in the x-ray tube and is comprised of an electron emitter and focusing cup ( Fig. 6-8 ). The emitter is usually a tungsten wire tightly coiled in a filament configuration (often called the filament) electrically connected to the filament circuit in the x-ray generator. Some advanced x-ray tubes have flat surface tungsten emitters (see below). Most x-ray tubes for diagnostic imaging have two filaments of different lengths, each positioned in a slot machined into the focusing cup. Specialized tubes have 2 or 3 filaments of different length for angiography applications, and dental tubes have a single filament. Usually only one filament is energized for an imaging examination, although there are some x-ray tube/generator systems that produce a combined electron distribution by energizing both filaments simultaneously. On many x-ray systems, the small or the large filament can be manually selected, or automatically selected by the x-ray generator, depending on the technique factors (kV and mAs).
What happens when the angle of the anode is great?
Anode angle. When the angle of the anode is great, the usable X-ray photons will not have to travel through as much of the anode material to exit the tube. This results in a much less apparent anode heel effect, though the effective focal spot size is increased.
Which emits more intensities of the beam along the cathode-anode axis than
A large beam will emit more intensities of the beam along the cathode-anode axis than a small beam. A large image receptor will also capture more of this beam than a small receptor. Both of these factors will greatly influence the visibility of the anode heel effect.
What are the parts of an angle?
Parts of an Angle: Arms : The two rays joining to form an angle are called arms of an angle. Here, OA and OB are the arms of the ∠AOB. Vertex: The common end point at which the two rays meet to form an angle is called the vertex. Here, the point O is the vertex of ∠AOB.
What is the symbol for an angle?
In geometry, an angle can be defined as the figure formed by two rays meeting at a common end point. An angle is represented by the symbol ∠. Here, the angle below is ∠AOB. Angles are measured in degrees, using a protractor.
Where does the word "angle" come from?
Fun Facts. The word ‘angle’ has been derived from the Latin word Angulus, meaning “a little bending”. The concept of angle was first used by Eudemus, who defined an angle as a deviation from a straight line.