How is anomalous retinal correspondence treated?
Treatment for Anomalous Retinal Correspondence It corrects certain eye alignment and other binocular vision problems. Vision therapy includes specific eye exercises paired with special lenses, prisms or eye patches to help improve poor visual skills and binocular vision problems.
What is abnormal correspondence?
Abnormal correspondence is a binocular condition with disparate retinal elements receiving the impression of a single object or image viewed. The fixating eye uses the fovea and has no suppression, but the squinting eye uses a more peripheral element and has suppression between the periphery and the fovea.
What causes abnormal retinal correspondence?
The cause of ARC begins due to foveal misalignment which can occur due to a variety of reasons. The first major risk factor is strabismus, which is one of the most common pediatric ophthalmologic pathologies and is a risk factor for ARC.
Is retinal correspondence normal?
Normal retinal correspondence (NRC) is a binocular condition in which both foveas work together as corresponding retinal points, with resultant images fused in the occipital cortex of the brain.
What is the correspondence problem in vision?
In motion perception, the correspondence problem refers to how the visual system knows if an object seen at Time 1 is the same object at Time 2. In most normal vision settings, we know that an object is the same because most objects do not go through rapid changes across time when they are in motion.
What are retinal corresponding points?
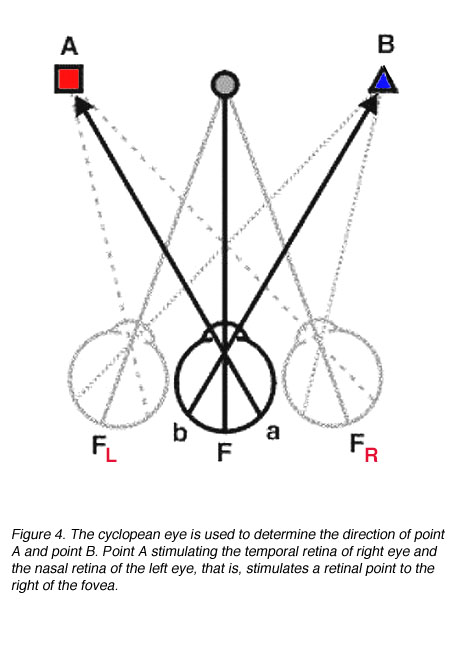
Corresponding retinal points are points stimulated on the retina that give rise to the same visual direction. When objects stimulate non-corresponding points, this gives rise to different visual directions. These retinal points are called disparate points.
Is anomalous retinal correspondence?
Background: Anomalous retinal correspondence (ARC) is a neural adaptation to eye misalignment in which non-corresponding retinal points are linked in the visual cortex to provide binocular fusion.
What do eye anomalies result in?
What Causes Eye Problems?Infection, allergy, vitamin deficiency, chemical irritants, genetics, smoking etc are some of the common causes of eye problems.Cataract - Etiology could be aging, hereditary, UV-Rays, dietary deficiency of vitamin E, C , B, and proteins.More items...
What is the most common cause of retinal detachment?
Aging is the most common cause of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. As you get older, the vitreous in your eye may change in texture and may shrink. Sometimes, as it shrinks, the vitreous can pull on your retina and tear it.
Are there warning signs before retinal detachment?
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as: The sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision. Flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
What does vision look like with retinal detachment?
Symptoms include flashes of light, floaters or seeing a shadow in your vision. Floaters are dark spots and squiggles in your vision. You may experience warning signs like these before the retina detaches, as in the case of retinal tears. Retinal detachment often happens spontaneously, or suddenly.
What is normal eye alignment?
In order to achieve normal binocular vision, the eyes must see well, be aligned (i.e., look in the same direction), and be focused on the same object. To maintain alignment, the eyes must also move in a coordinated manner. Misalignment of the eyes is called strabismus (or squint).
What is the correspondence problem quizlet?
Each part of the scene will have a retinal disparity and the sign and magnitude of this will give us depth. The brain has to find the corresponding parts of the image in the left and right views and calculate this disparity. We could call this the correspondence problem.
Is anomalous retinal correspondence?
Background: Anomalous retinal correspondence (ARC) is a neural adaptation to eye misalignment in which non-corresponding retinal points are linked in the visual cortex to provide binocular fusion.
What is crossed and uncrossed diplopia?
Crossed and uncrossed disparities result when objects produce images that are formed on closely separated retinal points. Any point within Panum's area yields a percept of a single image, while points outside Panum's area produces diplopia.
What is Microtropia?
Microtropia is an unilateral strabismus of less than 5 degrees, usually with harmonious anomalous correspondence. Three forms may be distinguished: Primary constant, primary decompensating and consecutive microtropia.
Why is correspondence between points in the retina important for binocular vision?
Because the eyes have thousands and thousands of corresponding points between each eye, the brain can sort and combine images from both the right and left eye into one single image. Otherwise stated, correspondence between points in the retina of each eye is important for single binocular vision.
Can unilateral deviations cause ARC?
The eye deviation must be unilateral (eye deviations that alternate won't cause ARC as it's easier for the brain to simply switch which eye is being used and suppress the deviating eye) If the above criteria are met, the brain may adapts to eye misalignment and develops ARC to create single vision.
What is retinal correspondence?
retinal correspondence, abnormal (ARC) A type of retinal correspondence in which the fovea of one eye is associated with an extrafoveal area of the other eye to give rise to a perception of a single object. This phenomenon is common in strabismus, but may also occur as a result of a macular lesion. ARC is often classified in three types: (1) ...
What is ARC in strabismus?
A type of retinal correspondence in which the fovea of one eye is associated with an extrafoveal area of the other eye to give rise to a perception of a single object. This phenomenon is common in strabismus, but may also occur as a result of a macular lesion. ARC is often classified in three types: (1) Harmonious, in which the angle of anomaly is equal to the objective angle of deviation. This indicates that the ARC fully corresponds to the strabismus. (2) Unharmonious, in which the angle of anomaly is less than the objective angle of deviation. (3) Paradoxical, when the angle of anomaly is greater than the objective angle of deviation. ARC can be detected by examination with a major amblyoscope, with the after-image test, or by comparison between the objective and the subjective angles of deviation measured with the alternate cover test and either a Maddox rod or the von Graefe's test, respectively (a difference between the objective and the subjective angles indicates ARC) (Fig. R10). Syn. anomalous retinal correspondence; ret-inal incongruity. See incongruous diplopia; physi-ological diplopia; phi movement; after-image test; Bagolini's test.
