What is the antecubital fossa of the arm?
The antecubital fossa is the shallow depression located in front of the median cubital vein of your arm. The median cubital vein joins the two longest vessels that run up the length of your arm, called the cephalic vein and the basilic vein.
What veins pass through the antecubital fossa?
Veins that pass through or just under the antecubital fossa include: 1 Basilic vein 2 Cephalic vein 3 Median Basilic vein 4 Median cubital vein 5 Median antebrachial vein 6 Median antebrachial cephalic vein 7 Antebrachial basilic vein 8 Median antebrachial basilic vein More ...
What is the antecubital vein?
The median cubital vein joins the two longest vessels that run up the length of your arm, called the cephalic vein and the basilic vein. Furthermore, the antecubital fossa is a main point of access for venipuncture, which could refer to either drawing blood or intravenous therapy, which is the administration of medication through a vein.
Why is the median cubital vein used the most?
The median cubital vein is used the most for its accessibility. It is large and near the skin’s surface, making it easier for phlebotomists to see before anchoring the vein. The median cubital creates less bruising and pain than other draw sites. Within the antecubital fossa, this vein poses the least amount of risk.

What and where is the antecubital fossa?
The Cubital Fossa is a triangular-shaped depression, located between the forearm and the arm on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow.
What is the function of the antecubital?
Antecubital Fossa Muscles This muscle gets its nerve supply from the median nerve, and its main function is pronation of the forearm. The pronator teres has two heads known as the ulnar and humeral heads. The ulnar head starts at the coronoid process of the ulna, and the humeral head starts at the median epicondyle.
What vein should be avoided?
While hand veins may be utilized for blood draws and intravenous infusions, veins in the feet and legs should be avoided for adults. Drawing from these sites can cause blood clotting and hemostasis.
Is antecubital fossa a preferred IV site?
[4] The antecubital fossa (ACF) and the dorsum of the hand (DOH) are the commonly preferred sites for routine venous cannulation.
Why is blood taken from the antecubital fossa?
Of these three veins, the preferred one for venipuncture is the median cubital vein because it is larger and has a lower tendency to move or roll when the needle is inserted. There are also fewer nerve endings surrounding this vein making venipuncture less painful at this site.
What is the vein in your elbow called?
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein is a superficial vein in the arm. The most frequent variations of the veins of the forearm. It communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein at the elbow and is located in the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps.
Which vein should be avoided to reduce chances of nerve damage?
Risk of nerve damage is higher especially when the cephalic vein is punctured in the lower part of the cubital fossa, making it a dangerous area for venipuncture.
What vein do you draw blood from in the arm?
The median antecubital vein is the most common for blood draws. It is in the inner arm, anterior of the elbow joint. This vein is associated with minimal pain and is the most prominent when anchored. Located on the lateral portion of the arm, the cephalic vein is the second most common draw site choice.
How do you know if you hit an artery instead of a vein?
Puncture of an artery may be more uncomfortable than puncture of a vein. This is because arteries are deeper than veins. Arteries also have thicker walls and have more nerves. When the needle is inserted, there may be some discomfort or pain.
What are the best veins to start an IV?
Since you're still learning, the natural tendency is to go for the easiest veins, often found in the antecubital fossa (AC) pit area of the elbow. Instead, challenge yourself by starting IVs on the top of the patient's hand or along the forearm.
Which vein is used for IV injection?
Median antecubital, cephalic and basilic veins are easy to hit and tend to last quite well if splinted properly. These veins are the preferred sites for insertion of percutaneous central venous catheters.
Where do you put IV in your arm?
The most common site for an IV catheter is the forearm, the back of the hand or the antecubital fossa. The catheters are for peripheral use and should be placed where veins are easy to access and have good blood flow, although the easiest accessible site is not always the most suitable.
What is antecubital artery?
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel supplying blood to your upper arm, elbow, forearm and hand. It starts in your upper arm, just below your shoulder, and runs down through the crease in front of your elbow. It separates into several branches along its route.
What two antecubital veins should be used for venipuncture quizlet?
The median cubital vein, the preferred one to use, is found close to the center, and the basilic vein is located on the inner, or medial part of the antecubital area.
Where is the right antecubital?
elbowThe antecubital region of the body is a triangular region on the anterior side of the elbow between the forearm and the anatomical arm. The antecubital fossa on the right arm is known as the right antecubital and the antecubital fossa on the left arm is known as the left antecubital.
Which vein is the last choice for venipuncture?
Summary. The basilic vein is responsible for taking blood that doesn't have oxygen from the arms back to the heart and lungs, where it's given oxygen again. While you can usually see it clearly, it's considered a last resort in medical procedures.
What does antecubital mean in medical terms?
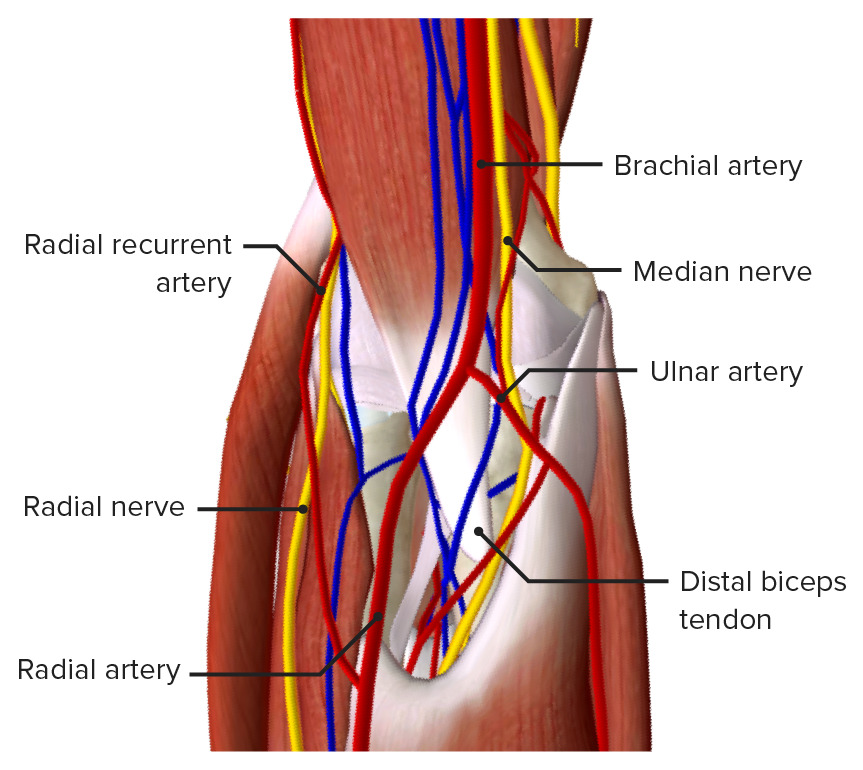
The word "antecubital" refers to the space inside the crook of the elbow. It contains four main structures: the median nerve, the radial nerve, the...
Which region of the body contains the antecubital fossa?
The antecubital fossa is the area of depression anterior to the elbow joint. It is the region of transition between the forearm and anatomical arm.
Is the antecubital fossa a bone?
It is not a bone. The word "antecubital" refers to the triangular space anterior to the elbow. It contains the pronator teres, brachioradialis, bra...
What are the three main veins in the antecubital fossa?
The three main veins in the antecubital fossa are the median cubital vein, the basilic vein, and the cephalic vein.
What is the Antecubital Fossa?
The antecubital fossa is one of the primary locations on the body where doctors and nurses insert an IV. The antecubital fossa is a small triangular space where the arm and forearm meet. This is also the area on the opposite side of the elbow joint.
What is the major intersection of major veins and arteries?
At the antecubital fossa there is a major intersection of major veins and arteries.
How to draw blood into a patient's limbs?
Place your patient’s hand pointing downwards or towards the floor and have them open and close their hand. With the hand pointing downwards, gravity will draw blood into your patient’s limbs. Opening and closing the hand will make the veins more visible.
What is the antecubital fossa?
The antecubital fossa, or simply elbow pit, is the small triangular depression in the arm which is formed by the connection of the humerus with the radius and ulna of the forearm. A fossa, in anatomical terms, is from the Latin word meaning small ditch or groove. The numerous muscles and tendons ...
Which nerve supplies the hand and runs directly through the antecubital fossa?
Median Nerve – The nerve that supplies the hand, and runs directly through the antecubital fossa.
What happens when the brachial artery stops?
The doctor is listening to the sounds coming from the brachial artery, which runs through the elbow pit. When there is too much pressure in the cuff, blood flow through the brachial artery stops in the antecubital fossa. As the doctor lets pressure out of the cuff, blood begins to flow when the pressure in the artery is equal to or greater than ...
What is the fossa in anatomy?
A fossa, in anatomical terms, is from the Latin word meaning small ditch or groove. The numerous muscles and tendons that surround the muscles, as well as the synovial joint formed between the bones of the arm create the antecubital fossa. Specifically, the antecubital fossa exists in the triangular region created by end ...
Which structure connects the biceps to bone?
Part of the structure that forms the antecubital fossa is the biceps brachii tendon, which connects the biceps to bone. Lastly, the brachial artery supplies blood to much of the arm, and often divides in the antecubital fossa to become the radial and ulnar arteries.
Which nerve passes on the same side of the arm as the radius?
Brachioradialis. The antecubital fossa houses several important structures. The radial nerve passes on the same side of the arm as the radius. The radial nerve supplies many of the muscles of the arm.
Which nerve is the main blood supply vessel in the arm?
Related Biology Terms. Brachial Artery – The main blood supply vessel in the arm, supplying both the upper arm directly and the forearm and hand through smaller divisions. Radial Nerve – A nerve which bounds the edge of the elbow pit, and supplies many of the muscles which operate the arm.