
What is arteriosclerosis and why is it dangerous?
Arteriosclerosis is a common health condition in which your large blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the body grow stiff, thick and inflexible. The artery walls harden, so the condition earns the nickname “hardening of the arteries.” It’s a dangerous and potentially life-threatening disorder, but there are treatment options ...
What are the remedies to reverse arteriosclerosis?
The 6 Best Supplements and Herbs for Atherosclerosis
- Artichoke extract (ALE)
- Garlic
- Niacin
- Policosanol
- Hawthorn
- Red yeast rice
What is the difference between arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis?
Difference between Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis
- Summary Table
- Definitions. Atherosclerosis is the accumulation and build-up of plaque inside the arterial walls. ...
- Atherosclerosis vs Arteriosclerosis. Even though both medical conditions can lead to cardiovascular problems, there is a notable difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis.
What does arteriosclerosis do in the body?
In short, arteriosclerosis is a disease that blocks the arterial wall due to aging. Atherosclerosis, on the other hand, is a medical disorder in which plaque deposits damage the lumen of an artery. Atherosclerosis is primarily the inability to control cholesterol and fat levels in the body.
What is the difference between atherosclerosis and Arteriolosclerosis?
Verdict. In short, Arteriosclerosis is a disease that blocks the wall of arteries due to aging. Whereas atherosclerosis is a medical disorder that damages the lumen of the arteries by plaque deposits. Atherosclerosis is mostly a failure of controlled cholesterol and fat levels in the body.
What are the warning signs of arteriosclerosis?
If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to your brain, you may have sudden numbness or weakness in your arms or legs, difficulty speaking or slurred speech, temporary loss of vision in one eye, or drooping muscles in your face.
What is atherosclerosis and what causes it?
Atherosclerosis: Arterial Disease. Atherosclerosis is a hardening of your arteries caused by gradual plaque buildup. Risk factors include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, lack of exercise and a diet high in saturated fat.
Is arteriosclerosis a serious disease?
Atherosclerosis is a common condition that develops when a sticky substance called plaque builds up inside your arteries. Disease linked to atherosclerosis is the leading cause of death in the United States. About half of Americans between ages 45 and 84 have atherosclerosis and don't know it.
What is the life expectancy of someone with atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis represents a grave health problem, annually accounting for at least 30% of all deaths globally (Figure 51-1 ). It is associated with a poor prognosis and significantly reduces life expectancy in the 60-year-old patient by 8–12 years depending on the vascular event.
What are the 4 stages of atherosclerosis?
Atherogenesis can be divided into five key steps, which are 1) endothelial dysfunction, 2) formation of lipid layer or fatty streak within the intima, 3) migration of leukocytes and smooth muscle cells into the vessel wall, 4) foam cell formation and 5) degradation of extracellular matrix.
What is the treatment of atherosclerosis?
Here are some medications used to treat atherosclerosis: Statins and other cholesterol drugs. Aggressively lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol — the "bad" cholesterol — can slow, stop or even reverse the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries.
Who is most at risk for atherosclerosis?
They include being older than 60, kidney disease, having a family history of heart disease, and having high levels of the amino acid homocysteine.
How do you detect atherosclerosis?
Diagnostic testsBlood tests. Blood tests check the levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, lipoproteins, or proteins that are signs of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein.Electrocardiogram. ... Heart imaging tests. ... Coronary calcium scan. ... Stress tests. ... Ankle-brachial index (ABI) test.
Can you reverse arteriosclerosis?
Medical treatment, regular exercise, and dietary changes can be used to keep atherosclerosis from getting worse and stabilize the plaque, but they aren't able to reverse the disease.
What is the best diet for atherosclerosis?
Consume a diet rich in vegetables and fruits. Choose whole-grain, high-fiber foods. Consume fish, especially oily fish, at least twice a week.
Is arteriosclerosis hereditary?
As plaque builds up, it increases the risk of blood clots, heart attack, and stroke. Research has shown that the risk of developing atherosclerosis can be influenced by heredity.
How do you detect arteriosclerosis?
Heart imaging tests Your doctor may order a heart imaging test to take pictures of your heart and find problems in blood flow in the heart or coronary arteries. Examples of heart imaging tests used to diagnose atherosclerosis appear below. Angiography is a special type of X-ray using a dye.
How do I know if my arteries are hardening?
Atherosclerosis does not cause symptoms until blood flow to part of the body becomes slowed or blocked. If the arteries supplying the heart become narrow, blood flow can slow down or stop. This can cause chest pain (stable angina), shortness of breath, and other symptoms.
What foods to avoid if you have atherosclerosis?
Avoid fruits canned in heavy sugar-based syrup, and frozen fruits with sugar added. Grains Whole grains should form the basis of your grain intake....Avoid or limit the following items:Fatty or marbled meats.Spareribs.Chicken wings.Hot dogs and sausages.Lunchmeat.Bacon.Breaded or fried meat, fish, or poultry.
Can you reverse arteriosclerosis?
Medical treatment, regular exercise, and dietary changes can be used to keep atherosclerosis from getting worse and stabilize the plaque, but they aren't able to reverse the disease.
What is the name of the disease that causes hardening of the arterioles?
Right breast mammograms showing several calcified arterioles. Patient 94 years old. Arteriolosclerosis is a form of cardiovascular disease involving hardening and loss of elasticity of arterioles or small arteries and is most often associated with hypertension and diabetes mellitus.
What is hyaline arteriolosclerosis?
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis. Also arterial hyalinosis and arteriolar hyalinosis refers to thickening of the walls of arterioles by the deposits that appear as homogeneous pink hyaline material in routine staining. It is a type of arteriolosclerosis, which refers to thickening of the arteriolar wall and is part of the ageing process.
What is the term for the hardening of an artery specifically due to an atheromatous plaque?
Atherosclerosis is a hardening of an artery specifically due to an atheromatous plaque. The term atherogenic is used for substances or processes that cause atherosclerosis. Micrograph showing hyaline arteriolosclerosis in the kidney. PAS stain.
What are lesions in nephrosclerosis?
Lesions reflect leakage of plasma components across vascular endothelium and excessive extracellular matrix production by smooth muscle cells, usually secondary to hypertension. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis is a major morphologic characteristic of benign nephrosclerosis, in which the arteriolar narrowing causes diffuse impairment of renal blood supply, with loss of nephrons. The narrowing of the lumen can decrease renal blood flow and hence glomerular filtration rate leading to increased renin secretion and a perpetuating cycle with increasing blood pressure and decreasing kidney function.
How does arteriolar sclerosis affect blood pressure?
This may in itself increase the blood pressure further by raising the peripheral resistance. The left ventricle enlarges to cope with the extra pressure but eventually it dilates and fails. Increased rate of atheroma formation narrows many arteries and reduces blood supply to vital organs (e.g. the heart, causing ischaemic heart disease). Arteries may become aneurysmal (abnormally dilated) and rupture (e.g. aortic aneurysm). Organs commonly affected by hypertension are shown in Figure 2.3.
What is hyaline arteriolosclerosis?
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis: It is characterized by thickening of the arteriolar wall due to the accumulation of homogeneous material that stains pink in hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides. The nature of this hyaline is unknown. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis is typically found in the kidneys of patients who have diabetes mellitus or benign arterial ...
What is the term for the changes that develop in the intima of larger vessels, the medium and large arteries
Atherosclerosis refers to the changes that develop in the intima of larger vessels, the medium and large arteries. Lipid deposition in the intima is often associated with calcification and fibrosis, which can compromise the lumen and predispose the artery to thrombosis.
What are the most common vascular lesions in Lupus nephritis?
Vascular Lesions. The most common vascular lesions in lupus nephritis are arteriosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis. They are similar to those seen in benign hypertension. These vascular lesions are common in patients with chronic lupus nephritis and in those receiving long-term corticosteroid treatment.
Can hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis cause obliteration of lumen?
Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis may severely limit flow and eventually result in the obliteration of the lumen. This would be detected on physical examination by the weakness or absence of the peripheral pulses.
Which layer of the arteriole is replaced by collagen?
With long-standing hypertension, elastic tissue forms multiple concentric layers in the intima of the arteriole. The muscular layer can be replaced by collagen fibers, and the intima can be replaced by hyaline thickening.
Is hypertension a vascular disease?
Primary hypertension is commonly associated with renal arteriolosclerosis and hyalinosis with variable degrees of glomerulosclerosis and ischemic tubular injury. Whereas renal function is often normal or only slightly depressed, renal vascular resistance is high due to intense vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole. It is likely that overt structural changes are the consequence of hypertension; yet experimental induction of microvascular disease and renal inflammation in normal rats also results in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension.
How to tell if you have atherosclerosis?
This test can tell if you have atherosclerosis in the arteries in your legs and feet. During an ABI test, your doctor compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm. An abnormal difference may be a sign of peripheral vascular disease, which is usually caused by atherosclerosis.
How to reduce risk of atherosclerosis?
Lose extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. If you're overweight, losing even just a few pounds can reduce your risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol, two of the major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. Ask your doctor what your target weight should be. Eat healthy foods.
What is a heart scan?
A heart scan (coronary calcium scan) provides pictures of your heart's arteries. Doctors may use this test to look for calcium deposits in the coronary arteries that can narrow your arteries and increase your heart attack risk. The image on the left shows where the heart is located in the body ...
How to control blood pressure and cholesterol?
Eat healthy foods. A heart-healthy diet full of fruits, vegetables and whole grains — and low in refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fat and sodium — can help you control your weight, blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar. Try substituting whole-grain bread in place of white bread.
What is the best test for atherosclerosis?
High levels of blood sugar and cholesterol raise your risk of atherosclerosis. A C-reactive protein (CRP) test also may be done to check for a protein linked to inflammation of the arteries. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This simple and painless test records the electrical signals in your heart. Exercise stress test.
How to reduce the risk of heart disease?
Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of conditions that increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Aim to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. If you can't fit it all into one session, try breaking it up into 10-minute intervals.
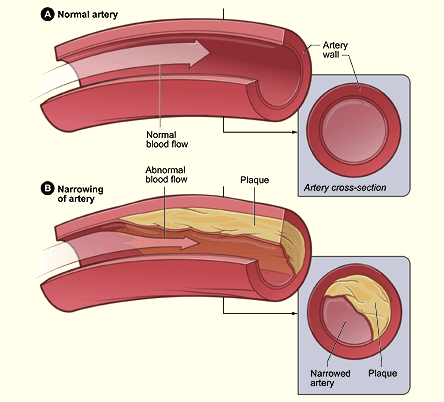
What is the narrowing of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque?
What is atherosclerosis ? Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body. As you get older, fats, cholesterol, and calcium can collect in your arteries and form plaque.
How do you know if you have atherosclerosis?
Most symptoms of atherosclerosis don’t show up until a blockage occurs. Common symptoms include: chest pain or angina. pain in your leg, arm, and anywhere else that has a blocked artery. shortness of breath. fatigue. confusion, which occurs if the blockage affects circulation to your brain.
What happens to your arteries as you get older?
As you get older, fats, cholesterol, and calcium can collect in your arteries and form plaque. The buildup of plaque makes it difficult for blood to flow through your arteries. This buildup may occur in any artery in your body, including your heart, legs, and kidneys. It can result in a shortage of blood and oxygen in various tissues of your body.
What happens if you eat too much cholesterol?
If the levels of cholesterol in your blood are too high, it can clog your arteries . It becomes a hard plaque that restricts or blocks blood circulation to your heart and other organs.
Why do arteries become less elastic?
As you age, your heart and blood vessels work harder to pump and receive blood. Your arteries may weaken and become less elastic, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
How does high blood pressure affect your blood vessels?
High blood pressure can damage your blood vessels by making them weak in some areas. Cholesterol and other substances in your blood may reduce the flexibility of your arteries over time.
What are the best medications for atherosclerosis?
Medications for treating atherosclerosis include: cholesterol-lowering medications, including statins and fibrates. angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which may help prevent narrowing of your arteries. beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to lower your blood pressure.
How do you know if you have an atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis Signs and Symptoms. You might not have symptoms until your artery is nearly closed or until you have a heart attack or stroke. Signs can also depend on which artery is narrowed or blocked. Pain or pressure in your upper body, including your chest, arms, neck, or jaw.
What is the term for the hardening and narrowing of the arteries?
Atherosclerosis is a hardening and narrowing of your arteries. It can put blood flow at risk as your arteries become blocked. You might hear it called arteriosclerosis or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. It’s the usual cause of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral vascular disease -- what together are called cardiovascular disease.
What is the blood vessel that keeps blood flowing?
They're lined by a thin layer of cells called the endothelium. It keeps the inside of your arteries in shape and smooth, which keeps blood flowing. Atherosclerosis begins with damage to the endothelium.
What happens when you have bad cholesterol?
When bad cholesterol, or LDL, crosses a damaged endothelium, it enters the wall of your artery. Your white blood cells stream in to digest the LDL. Over the years, cholesterol and cells become plaque in the wall of your artery. Plaque creates a bump on your artery wall. As atherosclerosis gets worse, that bump gets bigger.
How many chances of getting atherosclerosis in your lifetime?
Research has found that even teenagers can have signs. If you’re 40 and generally healthy, you have about a 50% chance of getting serious atherosclerosis in your lifetime. The risk goes up as you get older. Most adults older than 60 have some atherosclerosis, but most don’t have noticeable symptoms.
What is the test for blood pressure in the lower leg?
Angiogram, in which your doctor puts dye into your arteries so they’ll be visible on an X-ray. Ankle-brachial index , a test to compare blood pressures in your lower leg and arm. Blood tests to look for things that raise your risk of having atherosclerosis, like high cholesterol or blood sugar.
What is it called when you feel pressure in your chest?
Pain or pressure in your upper body, including your chest, arms, neck, or jaw. This is known as angina. Shortness of breath. Symptoms related to the arteries that deliver blood to your brain include: Numbness or weakness in your arms or legs.
How to treat arteriosclerosis?
Treatment for arteriosclerosis includes a healthy diet, exercise and medication to control or possibly reverse your condition. If enlarged blood vessels have been diagnosed, our goal is to develop an individualized treatment plan so blood clots do not form.
What are the complications of arteriosclerosis?
Complications of arteriosclerosis include: Coronary Arteriosclerosis (Coronary artery disease): Narrowed arteries near the heart may lead to chest pain, heart attack or heart failure.
What is the process of arteries growing thick and stiff?
What is Arteriosclerosis? Arteriosclerosis (also known as cardiovascular arteriosclerosis) occurs when arteries grow thick and stiff and restrict blood flow to organs and tissues in the body. This gradual process, also known as hardening of the arteries, weakens arteries and can develop in various organs, most commonly the heart.
How to prevent heart disease?
Practice good heart health: Watch what you eat, exercise and avoid smoking. Take your medications as prescribed: If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes, be certain to take your prescribed medications as directed.
What is the best medicine for blood clots?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors can lower blood pressure and lower the possibility of heart attack. Calcium channel blockers and diuretics (water pills) can reduce blood pressure. A clot-busting drug may dissolve blood clots. Your physician may also prescribe other medications, based on your needs.
Can a clogged artery cause a heart attack?
As arteriosclerosis progresses, clogged arteries can trigger a heart attack or stroke, with the following symptoms: Chest pain or pressure (angina) Sudden arm or leg weakness or numbness. Slurred speech or difficulty speaking.
Can arteriosclerosis cause heart disease?
Arteriosclerosis can develop into atherosclerosis. This condition can cause heart disease, strokes, circulation problems in the arms and legs, aneurysms that can cause life-threatening internal bleeding and chronic kidney disease. Baptist Health is known for advanced, superior care for patients with heart disease and the diagnosis, ...
What happens if you have arteriosclerosis?
If you begin to experience symptoms of arteriosclerosis such as chest pain, shortness of breath, sudden slurred speech, or difficulty with your vision, you may be having a heart attack or stroke. This a medical emergency. If you or a loved one experiences any of these symptoms seek immediate medical attention.
What is the most common procedure for arteriosclerosis?
The most widely used surgeries and procedures for arteriosclerosis are angioplasty also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and bypass surgery.
What is the term for the hardening of the arteries?
Arteriosclerosis occurs when arteries grow stiff and restrict blood flow. Another term commonly used to describe this chronic condition is the hardening of the arteries. There are three types of arteriosclerosis: atherosclerosis, arteriolosclerosis, and Mönckeberg medial calcific sclerosis.
What is plaque in arteries?
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which plaque builds up in your arteries. Technically, atherosclerosis is a subtype of arteriosclerosis although the two terms are often used interchangeably. No matter which term you use, the disease process is the same. Plaque is made up of cholesterol and other fatty substances that harden and narrow your arteries, ...
How to reduce risk of cardiovascular disease?
The best way to decrease your risk of having a cardiovascular event is to prevent arteriosclerosis by eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, never smoking, controlling your blood pressure, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing your cholesterol levels.
How does age affect arteriosclerosis?
Older age: As you get older, your risk for arteriosclerosis increases. We all develop some arteriosclerosis as we age, but as you age lifestyle factors can worsen the condition. Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol, eating a balanced diet, and exercising can stop the impact of arteriosclerosis on our blood vessels.
Why is blood sugar high in arteriosclerosis?
Diabetes: With this disease, the body's blood sugar level is too high because the body doesn't make enough insulin or doesn't use its insulin properly.
What is the most famous form of arteriosclerosis?
This image shows atherosclerosis, the most famous form of arteriosclerosis. An artery is a blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood and nutrients to an organ or tissue. This is important to remember for later. Each artery has an inner layer called the endothelium.
What is the term for the thickening and hardening of the walls of small arteries?
Hyaline arteriosclerosis refers to the thickening and hardening of the walls of small arteries as a result of glassy-looking precipitations/deposits. Hyaline refers to glass and arteriosclerosis refers to the hardening and thickening of arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood in the body.
What is the protein that is found in the arterial wall?
This condition occurs when an immune system protein found in blood, called C3, leaks through the inner layer of the arterial wall, the endothelium . It enters the subendothelium and spontaneously transforms to a protein called C3b.
What is the term for the hardening of small arteries?
You'll find out soon enough. Regardless, hyaline arteriosclerosis , also called arteriolar hyalinosis, is a term that refers to a specific thickening and hardening of small arteries throughout the body as a result of the accumulation of a 'glassy' substance in their walls.
What happens when C3 enters the arterial wall?
Once C3 enters into the arterial wall, it spontaneously changes to another protein called C3b. The problem is that the arterial wall, especially the subendothelium, is rich in something called hyaluronic acid (HA). The subendothelium is the part of the arterial wall immediately underneath ('sub') the endothelium.
When does hyaline arteriosclerosis become common?
Evidence of hyaline arteriosclerosis in the spleen has been observed in infants as young as 1-month-old, and it becomes common by age 4-5 and almost certain by old age. In most people, hyaline arteriosclerosis is of no significant medical consequence. This is especially true for the young and otherwise healthy individuals.
What are the proteins that are floating around in the blood stream?
Floating around in your blood stream are numerous types of proteins. Some of these proteins are called complement proteins, like C3. These are proteins involved in your immune system.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
- Mild atherosclerosis usually doesn't have any symptoms. Atherosclerosis symptoms usually don't happen until an artery is so narrowed or clogged that it can't supply enough blood to organs and tissues. Sometimes a blood clot completely blocks blood flow. The clot may break apart and ca…
Preparing For Your Appointment