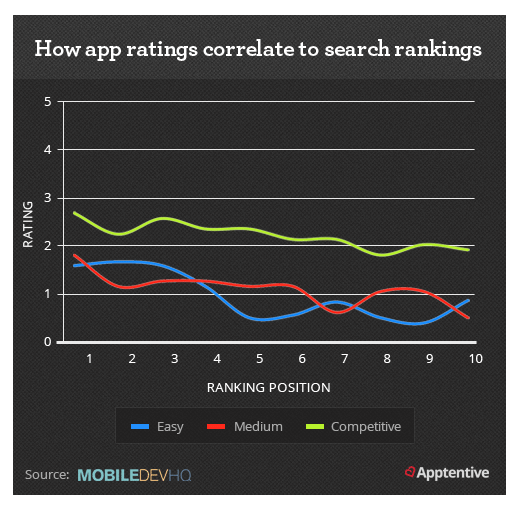
In ASO arrangements, the insurance company provides little to no insurance protection, which is in contrast to a fully insured plan sold to the employer. As such, an ASO plan is a type of self-insured or self-funded plan. The employer takes full responsibility for claims made to the plan.
What is an ASO insurance plan?
In ASO arrangements, the insurance company provides little to no insurance protection, which is in contrast to a fully insured plan sold to the employer. As such, an ASO plan is a type of self-insured or self-funded plan. The employer takes full responsibility for claims made to the plan.
What is the true cost of claims for ASO?
The true comparison of cost of claims for the fully insured model is therefore 33.3% versus 25% of paid claims for the ASO contract. That makes the insured contract 33% more expensive to operate [ (33.3-25)/25 = 33%].
Is an ASO right for your company?
An ASO may allow an employer to take greater control of benefit costs to meet the organization's needs. However, ASO arrangements may not be suitable for all companies, and they come with certain risks . A traditional administrator agreement is an arrangement whereby an insurance company fully administers claims.
What are the cost savings of Aso?
These cost savings can offset rises in claims and be used to help the company grow. Alternatively, if claims consistently exceed forecasts, the cost for ASO may exceed that of a traditional administrator plan. On the other hand, employers would be responsible for any deficit if claims exceed budgeted amounts.
What does Aso mean in insurance?
Administrative services onlyAdministrative services only is used by employers who self-fund employee health benefits instead of purchasing health insurance for their workers. These employers pay claims out of their own pocket and hire a third-party administrator, often an insurance company, to run the program and process claims.
What is the difference between ASO and TPA?
ASO arrangements are an extension of big insurance carriers. Some may be beholden to revenue goals, limiting employers' contract or plan design capabilities. TPAs on the other hand, are not typically owned by larger parties like hospital systems or insurance carriers.
What is the difference between fully insured and level funded?
Level-funded insurance and self-funded insurance are alternatives to traditional fully insured plans. Unlike self-funded plans, level-funded health insurance offers little control over plan elements like TPAs, PBMs, or network providers.
What does self-insured vs fully insured mean?
A fully-insured health plan is the traditional model of structuring an employer-sponsored health plan and is the most familiar option to employees. On the other hand, self-insured plans are funded and managed by an employer, often to reduce health insurance costs.
What is fully insured mean?
With a fully-insured health plan, the employer pays a certain amount each month (the premium) to the health insurance company. In return, the insurance company covers the costs of the employees' healthcare. With a fully-insured plan, there is no additional risk to the employer.
How does an ASO plan work?
An ASO plan, or "Administrative Services Only," is a benefit plan in which the employer funds the benefits for employees rather than an insurance company. For example, a business can choose to pay for its employees' health care rather than using an external insurance company to cover the costs.
What is a fully funded insurance plan?
A fully-funded health plan is an employer-sponsored health plan. In these plans, your company pays a premium to the insurance carrier. These premium rates are fixed for a year and dependent on how many of your employees are enrolled in the plan each month.
Is level funded the same as self-insured?
A level-funded plan is a type of self-funded plan in which the employer contributes a steady monthly payment to cover costs for administration, claims payments, and stop-loss insurance. Level funding has its advantages when compared to fully insured plans and programs.
Is self-funded the same as self-insured?
Self-insurance is also called a self-funded plan. This is a type of plan in which an employer takes on most or all of the cost of benefit claims. The insurance company manages the payments, but the employer is the one who pays the claims.
Why would a company choose to be self-insured?
Self-insurance is beneficial to businesses because it makes them more aware of their risks. Businesses must analyze their risks and how much money to save based on past and future analyses of risk. Another advantage of self-insurance is the ability to manage risk in the long term.
What are the disadvantages of self-insurance?
The primary disadvantage of self-insurance is the assumption of greater risk. A year that brings large unexpected medical claims requires that the company has the financial resources to meet its obligations. This unpredictability puts greater demands on budgeting and cash flow.
Why do employers choose to self-insure?
There are many reasons to self-insure your company, but one of the most logical reasons is to save money. According to the Self-Insurance Education Foundation, companies can save 10 to 25 percent on non-claims expenses by self-insuring. Employers can also eradicate costs for state insurance premium taxes.
What is a TPA Aso?
A TPA may operate independent of insurance companies. An ASO is typically a subsidiary of a health insurance company. Networks. A TPA often offers several PPO networks to choose from. An ASO is typically limited to provider networks from the parent insurer.
What is a TPA agreement?
The United States—Panama Trade Promotion Agreement (TPA) entered into force on October 31, 2012. The TPA is a comprehensive free trade agreement that provides elimination of tariffs and removes barriers to U.S. services, including financial services.
What is the difference between a HMO and PPO plan?
HMO plans typically have lower monthly premiums. You can also expect to pay less out of pocket. PPOs tend to have higher monthly premiums in exchange for the flexibility to use providers both in and out of network without a referral. Out-of-pocket medical costs can also run higher with a PPO plan.
What is another name for administrative services only arrangement?
Administrative services only (ASO) is an arrangement in which a company funds its own employee benefit plan, such as a health insurance program while purchasing only administrative services from the insurer.
What happens if your ASO claims are less than anticipated?
If your claims are less than anticipated, the surplus is yours to keep. Business owners need to fully understand their benefits costs as they arise. With monthly surplus and deficit reports, Budgeted ASO plans meet this need.
What is stop loss insurance?
Stop Loss Insurance is specifically designed to limit potential exposure to catastrophic health care claims. For routine health and dental claims, funding on a Budgeted ASO basis is simple and transparent.
Why are employers moving away from group benefits plans?
Weary of escalating premium costs, rigid options and a lack of transparency, smart entrepreneurial employers are moving away from traditional group benefits plans and adopting Budgeted Administrative Services Only (ASO) Plans to control costs and improve retention of key employees.
What is group benefits plan?
A group benefits plan is a promise made by an employer to their employees. Many employers regard their benefits plan as “good enough” for their purposes. However, having an acceptable solution is not the same as having the best solution strategically designed for your business and your employee population.
Is walking away a valid option?
Walking away is not a valid option, because your actual claims experience will follow. With Budgeted ASO, you pay a fixed amount every month based on your previous claims history. The budgeting process each year is straightforward. Should actual claims exceed the budgeted amount, you are responsible for the deficit.
What is an ASO plan?
Essentially a self-funded plan, an ASO arrangement is usually offered for short-term disability, extended health and dental care benefits, and sometimes long-term disability benefits. Employers rarely provide life insurance under an ASO system because of the large coverage amounts.
What is ASO insurance?
Administrative services only (ASO) is an arrangement in which a company funds its own employee benefit plan, such as a health insurance program while purchasing only administrative services from the insurer. This alternative funding option is a group health self-insurance program often used by large employers who opt to assume responsibility for all the risk, remaining exclusively liable for all financial and legal elements of the group benefits plan.
Why do employers need stop loss insurance?
In an ASO arrangement, employers purchase stop-loss insurance to protect themselves from any catastrophic losses should their employees’ insurance needs become exorbitant because of severe illness or injury. The last thing you want is to be caught in the unlimited financial liability of ASO plans.
What is an ASO arrangement?
In an ASO arrangement, employers purchase specific administrative services from a third-party administration (TPA) to be carried out by the TPA. Typical services offered in an ASO situation can include:
Is ASO self funded?
The self-funded status of an ASO plan is not altered with stop-loss insurance. It is necessary to have an insurance plan for your insurance plan, if you will, especially to cover expenses like costly prescription drugs. Without stop-loss insurance, the financial impact on your company under a large claim could be disastrous.
Who can benefit from ASO?
Smaller companies, if it’s financially feasible, can also benefit from an ASO arrangement, especially start-ups and small businesses that are not prepared to manage the complicated legal and administrative details of group health insurance and benefits.
What should an association investigate after confirming the presence of appropriate licensure or registration?
After confirming the presence of appropriate licensure or registration, an association should investigate the reputation of the TPA or ASO it is considering. Your questions should include:
Why would an ASO push back on an insurer?
In other words, given an ASO’s exclusive relationship with a single insurer, it’s less likely the ASO would push back on the insurer in order to get greater benefit customization on behalf of its clients. Likewise, if an ASO is restricted to a single insurer it’s not likely that the ASO would compare its insurer’s rates to those of other insurers.
What is an ASO in TPA?
Sometimes when associations are exploring third-party administrative (TPA) services, they come across an entity known as an “Administrative Services Organization, ” or ASO, which offers services similar to a TPA.
Can ASO compare to other insurers?
Likewise, if an ASO is restricted to a single insurer it’s not likely that the ASO would compare its insurer’s rates to those of other insurers . If your AHP is fully-insured and you wish to get the most competitive rate proposals, you should consider a TPA who works with a wide variety of insurers from which to receive competitive bids.
Is there a difference between ASO and TPA?
As mentioned earlier in this article, there is no universally recognized distinction between TPA and ASO organizations. However, in real-world experience you may notice material distinctions between these organizations. According to the Society of Professional Benefit Administrators, ASOs are more likely to be under the control of a parent insurance company. Being under the control of a single insurer could potentially mean more restricted insurance options and less benefit customization. In other words, given an ASO’s exclusive relationship with a single insurer, it’s less likely the ASO would push back on the insurer in order to get greater benefit customization on behalf of its clients.
Is TPA the same as ASO?
Technically, there is no hard and fast distinction between the two. In some cases, a TPA and an ASO might offer the same services such as: While we might associate the above services with health insurance, a TPA or an ASO might provide many of the same services for dental insurance, vision insurance, disability insurance, or even life insurance.
Do insurance companies want to provide access to claims data?
Many insurance companies do not want to provide employers with access to their claims data. A single-insurer ASO is likely a poor advocate on behalf of a company that sees the strategic importance in analyzing this data, whether itself or through a third-party firm.
What is Fully Insured?
The fully insured plan is the traditional model of insurance where the third-party insurance carrier assumes the financial risk to pay for the members’ claims in exchange for the premiums paid to them. Basically, the employer pays the premium for the given year, which is decided at the start of that year based on the number of members covered in the plan. During a year, the premiums change only when the number of members covered in the plan change. The insurance carrier pays the medical claims as per the covered benefits of the policies in exchange for the premiums received from the employer.
What is the difference between a self insured and a fully insured plan?
Some of the key differences between a self-insured plan and a fully insured plan are – who pays for the members’ claims, who takes up the insurance risk, and who saves in case the claims are less than what was estimated. In a self-insured plan, the employer is responsible for the members’ claims as it assumes the insurance risk and it also saves in case of lower claims. On the other hand, is a fully insured plan, the responsibility of members’ claims as well as the insurance risk is transferred to the insurance carrier, who is benefited in case of lower claims.
What is self insured health insurance?
The self-insured plan is also known as a self-funded plan as the employer is responsible for paying the medical claims and operating the health insurance plans with the help of vendors, who are known as third-party administrators (TPA). Basically, the employer chooses a self-insured health plan as it can result in significant savings on premiums.
Why are premiums higher?
The premiums are usually higher as the financial and insurance risk is passed on to the insurer. Flexibility to Choose Benefits.
What is financial risk?
Financial Risk Financial risk refers to the risk of losing funds and assets with the possibility of not being able to pay off the debt taken from creditors, banks and financial institutions. A firm may face this due to incompetent business decisions and practices, eventually leading to bankruptcy. read more.
Is a self-insured plan a fully insured plan?
In a self-insured plan, the employer is responsible for the members’ claims as it assumes the insurance risk and it also saves in case of lower claims. On the other hand, is a fully insured plan, the responsibility of members’ claims as well as the insurance risk is transferred to the insurance carrier, who is benefited in case of lower claims.
Does self-insured insurance limit the risk of a claim?
But it is important to note that a self-insured plan exposes the employer to a major risk in case the claims are much higher than the estimation. However, the employer can limit this risk by purchasing excess-loss or stop-loss insurance, which reimburses for the claims that go beyond a pre-determined level.
What is fully insured insurance?
With fully insured plans, the company pays the insurance carrier a set premium price each year based on the number of employees who are enrolled in the plan each month. If any claims exceed the projections created at the start of the year, the insurance company assumes all legal and financial risk. As the price is fixed until the employer makes a new deal, there are no financial surprises.
How many employees does self insured health insurance cover?
However, self insured health insurance plans make sense for approximately 70 percent of companies that have a total of 25 or more employees as well as adequate cash flow. However, self insured plans also work well for some smaller businesses as well.
Why is it important to have fully insured health insurance?
Fully insured plans are also convenient as claims are managed by the medical care provider and insurance provider which allow employers to focus solely on their business. This also lessens the financial strain on employees. With fully insured health insurance plans, profits made by the insurance company are retained by the organization.
What are the two types of health insurance?
The two primary types of health insurance plans include fully insured plans and self insured plans. Understanding how both types of health plans work can help you make an informed decision and could even save your company money. Here is a look at how fully insured health insurance plans compare to self insured plans.
Why do employers need self insured?
Self insured plans allow employers to save money in the long-run. Stop-loss insurance prevents companies from assuming all the financial risk. With a self insured plan employers have more control over benefits. Employers can remove insurer profit from their healthcare spending.
Why do employers need insurance brokers?
Insurance brokers can help employers compare the range of health plans available to them. As the process of sorting through health insurance plans can be daunting, having an insurance broker there to explain terms and provide advice can make the process run much more smoothly.
How to choose an insurance broker?
Choose an insurance broker that has a good reputation in the industry. Check licenses, references, and ask other professionals in the industry about their experience with a broker.
What is the difference between fully-insured and self-insured health plans?
A fully-insured health plan is the traditional route of insuring employees. Employers pay a fixed premium to an insurance carrier that in turn covers employees’ medical claims. Fully-insured health plans are typically more expensive, but they can save you money in the long run by providing great benefits to your employees—a proven way to increase retention. Other potential downsides include higher taxes, potential for rate hikes, and tough carrier negotiations.
What is QSEHRA insurance?
A QSEHRA allows employers to reimburse employees tax-free for health insurance premiums and other out-of-pocket expenses. Reimbursements can also be free of income tax if the employee is covered by a minimum essential coverage (MEC) policy.
What is an HRA?
An HRA is an alternate type of self-insured health plan where employers reimburse employees for qualifying medical expenses. Because traditional group health insurance is often too expensive for small employers, HRAs can be a simple and budget-friendly way to offer health benefits. HRAs are fixed in cost, so they’re not subject to annual premium rate hikes like group health insurance plans.
How does a fully insured plan work?
In a fully-insured plan, you pay a premium to an insurance carrier. The premium rates are annually fixed based on the number of enrolled employees you have in the plan each month and will only change if the number of employees changes. The insurance carrier pays claims based on the benefit outline and employees must pay any deductibles or copays required for covered services under the policy.
Why do employers want to set aside funds for healthcare?
As healthcare costs continue to rise, employers are eagerly searching for ways to control costs without negatively impacting their employees’ health coverage. That’s why more companies are choosing to set aside funds to pay for the healthcare needs of their own employees instead of offering a traditional group health insurance plan.
What is stop loss insurance?
To reduce the risk that comes with self-insured plans, you can implement stop-loss or excess-loss insurance which will reimburse you for claims that exceed a set amount. This coverage can be used to cover catastrophic claims on one covered person (AKA specific coverage), or cover claims that significantly exceed the expected level for the group of covered persons (AKA aggregate coverage).
How many expenses are eligible for reimbursement?
There are over 200 IRS-regulated expenses that are eligible for reimbursement, such as various medical, dental, and vision expenses. This flexibility helps employers attract and retain employees by laying a traditional group plan alongside a more customizable supplemental option to fill in the gaps with tax-free reimbursements.