/GettyImages-647619196-2-673e5e08b88a4f47b95b9943975cc6f6.jpg)
Examples of autotrophic organisms
- Cactus
- Venus Fly Traps
- Scrub
- Grass
- Green and Purple Sulfur Bacteria
- Trees
- Plants
- Flowers
- The Resurrection Fern
- The Corpse Lily
What is the difference between a producer and an autotroph?
- Photoautotrophs. Photoautotrophs are organisms who get the energy to make organic materials from sunlight.
- Chemoautotrophs.
- Plants.
- Green Algae.
- ”Iron Bacteria” – Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans.
What are three organisms that are autotrophs?
What are 4 examples of autotrophs?
- Algae.
- Cyanobacteria.
- Maize plant.
- Grass.
- Wheat.
- Seaweed.
- Phytoplankton.
What protists are autotrophs?
What types of protists are Autotrophs? Animal protists; Fungus-like protists. Plant protists -The plant protists are autotrophs as members of diatoms, unicellular prokaryotic algae, etc.
What are the similarities between autotrophs and hetrotrophs?
What are examples of heterotrophic bacteria?
- Citrus canker – Xanthomonas axonopodis.
- Crown gall – Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- Blight of beans – Xanthomonas campestris.
- Wildfire of Tobacco – Pseudomonas syringae.
- Granville wilt – Pseudomonas solanacearum.

What are 10 examples of autotrophs?
What are Autotrophs?Algae.Cyanobacteria.Maize plant.Grass.Wheat.Seaweed.Phytoplankton.
What is autotrophs answer?
Autotrophs are those organisms which synthesize their own food with the help of solar energy from inorganic raw materials like CO2 and water.
What are 5 examples of autotrophs?
Plants, lichens, and algae are examples of autotrophs capable of photosynthesis. Notice their green color due to the high amounts of chlorophyll pigments inside their cells. Synonyms: autophyte; autotrophic organism; primary producer.
What are autotrophs 7 examples?
Autotroph ExamplesPlants.Algae- Green algae and red algae.Bacteria such as cyanobacteria.
What called autotrophs?
An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. Because autotrophs produce their own food, they are sometimes called producers.
What are autotrophs Class 9?
Autotrophs are organisms that undergo autotrophic mode of nutrition. These are the organisms that can prepare their own food from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water. All green plants are examples of autotrophs.
What is called autotrophic Class 7?
Organisms which can make their own food from simple substances are called autotrophs. Organisms which can not make their own food and obtain it directly or indirectly from green plants are called heterotrophs. They are producers.
What are examples of autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Autotrophs are known as producers because they are able to make their own food from raw materials and energy. Examples include plants, algae, and some types of bacteria. Heterotrophs are known as consumers because they consume producers or other consumers. Dogs, birds, fish, and humans are all examples of heterotrophs.
What are 2 types of autotrophs?
The two different types of autotrophic bacteria are:Photoautotrophs – or photosynthetic. They derive energy from sunlight.Chemoautotrophs – or chemosynthetic. They use chemical energy to prepare their food.
What are 4 examples of autotrophs?
Examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, plankton and bacteria. The food chain is comprised of producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. Producers, or autotrophs, are at the lowest level of the food chain, while consumers, or heterotrophs, are at higher levels.
What are autotrophic plants?
See the most commonly confused word associated with autotroph. 💼 Post-College Level. noun Biology. any organism capable of self-nourishment by using inorganic materials as a source of nutrients and using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis as a source of energy, as most plants and certain bacteria and protists.
What is heterotrophic plant?
Some plants do not have chlorophyll and depend upon other plants for their food. Such plants exhibit a heterotrophic mode of nutrition and are known as heterotrophic plants. For eg., parasitic plants, insectivorous plants, symbiotic plants and saprophytic plants.
Why are autotrophs important?
Autotrophs are extremely important because without them, no other forms of life can exist. Without plants that create sugars from carbon dioxide gas ...
Why are autotrophs called producers?
Without plants that create sugars from carbon dioxide gas and sunlight via the process of photosynthesis, for example, no herbivorous animals could exist, and no carnivorous animals that eat herbivores could exist. For this reason, autotrophs are often called “producers.”.
What do photoautotrophs make?
Photoautotrophs make more than just fuel and organic compounds for heterotrophs like ourselves! Many photoautotrophs take carbon from the atmosphere and use it to make sugars and other molecules that store the Sun’s energy in their molecular bonds.
What are the organisms that make organic materials?
Photoautotrophs. Photoautotrophs are organisms who get the energy to make organic materials from sunlight. Photoautotrophs include all plants, green algaes, and bacteria which perform photosynthesis. All photoautotrophs perform photosynthesis – a word that comes from the root words “light” and “to make.”. Photoautotrophs capture photons ...
What are the main energy sources of chemoautotrophs?
Chemoautotrophs use volatile chemicals such as molecular hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, ferrous iron, and ammonia as their energy sources. This makes them well-suited to live in places that would be toxic to many other organisms, as well as places without sunlight.
Where do chemoautotrophs get their energy?
Chemoautotrophs are organisms that obtain energy from inorganic chemical processes. Today, chemoautotrophs are most commonly found in deep water environments which receive no sunlight. Many need to live around deep sea volcanic vents, which produce enough heat to allow metabolism to occur at a high rate.
What is the structure that shows the flow of energy through an ecosystem?
Related Biology Terms. Energy pyramid – A structure that shows the flow of energy through an ecosystem. Heterotroph – An organism that relies on other organisms, such as plants or prey animals, for food. Photosynthesis – The process used by phototrophs to extract energy from sunlight.
What are some examples of autotrophs?
When it comes to autotrophs, there are a lot of them out there. Marine autotroph examples might spring to mind, like plankton, but even the flower growing in your backyard is an example of an autotroph. Typically, autotrophs are split into two different types: Photoautotrophs. Chemoautotrophs.
Why are autotrophs in the food web?
Autotrophs are typically at the beginning of a food web, because they can make their own food. They use both light synthesis and chemical synthesis. Now that you know about autotrophs, check out how they work in a food web.
What is the primary food source for marine autotrophs?
Unable to swim, they can be found drifting in large bodies of water. Like plants on dry land, phytoplankton are a primary food source for an array of aquatic animals.
What are organisms that make their own food called?
But, did you know there are organisms that create their own food? These organisms are known as autotrophs, and they are a critical example of a biotic factor in an ecosystem. You might also hear them called producers. Autotrophs use chemicals like carbon dioxide, the light from the sun and even water to create food.
How to remember photoautotrophs?
An easy way to remember photoautotrophs use photosynthesis is to remember the prefix “photo” in both words, which means “light.”. For examples of photoautotrophs, think of any green plant, like grass, moss, flowers, and trees. Review a few unique examples that might not instantly spring to mind.
Where do chemoautotrophs live?
For example, some chemoautotrophs live on the ocean vents on the seafloor.
Is a photoautotroph a plant or a bacteria?
Not all photoautotrophs are plants; some are bacteria. Known as pond slime or blue-green algae, these unique marine autotroph examples live in the water making food from sunlight. Not only are these little organisms unique, but they also have a fossil record that goes back 3.5 billion years.
What is an autotroph?
Encyclopedic Entry. Vocabulary. An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. Because autotrophs produce their own food, they are sometimes called producer s. Plant s are the most familiar type of autotroph, but there are many different kinds of autotrophic organisms.
What do autotrophs use to make energy?
In photosynthesis, autotrophs use energy from the sun to convert water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air into a nutrient called glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar. The glucose gives plants energy. Plants also use glucose to make cellulose, a substance they use to grow and build cell wall s.
What is the function of autotrophic bacteria?
The autotrophic bacteria oxidize these chemicals to produce energy. Autotrophs in the Food Chain. To explain a food chain —a description of which organisms eat which other organisms in the wild—scientists group organisms into trophic, or nutritional, levels. There are three trophic level s.
What is the food chain in a hydrothermal vent?
In hydrothermal vents, the food chain’s producer is autotrophic bacteria. Primary consumers such as snail s and mussel s consume the autotrophs. Carnivores such as octopus consume the snails and mussels. An increase in the number of autotrophs will usually lead to an increase in the number of animals that eat them.
How do autotrophs make food?
Instead, they make food using energy from chemical reactions, often combining hydrogen sulfide or methane with oxygen.
Which trophic level is the first?
Because autotrophs do not consume other organisms, they are the first trophic level. Autotrophs are eaten by herbivore s, organisms that consume plants. Herbivores are the second trophic level. Carnivore s, creatures that eat meat, and omnivore s, creatures that eat all types of organisms, are the third trophic level.
Why are some bacteria not autotrophs?
However, these bacteria are not autotrophs, because they must rely on chemicals besides carbon dioxide for carbon. These strange bacteria are called photoheterotrophs. algae. Plural Noun.
What are some examples of autotrophs?
Examples of Autotroph: 1. Green plants and algae: These are examples of photoautotrophs using light as an energy source. In this type, electromagnetic energy is converted from sunlight into chemical energy in the form of reduced carbon. Green plants and algae are fundamental to the food chains of all ecosystems in the world.
What is an autotroph?
Autotroph Examples. Autotroph. An autotroph is an organism identified as a producer on the primary level of a food chain. Only about 5% of all living organisms are autotrophs. They are often referred to as self-feeders. In fact, the Greek origin of the term autos and trophe can be translated as "self-nourishing".
What are the sources of energy for chemoautotrophs?
The chemoautotrophs use electron donors from organic or inorganic sources as a source of energy. The electron donors come from inorganic chemical sources such as hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, ammonium and ferrous iron. In the food chain, autotrophs are consumed by heterotrophs.
How does the autotroph produce energy?
It will produce these from substances present in the autotroph's surroundings using the process of photosynthesis, obtaining energy from light; or through chemosynthesis, using energy from inorganic chemical reactions.
Do autotrophs need carbon?
The chemical reactions are usually between hydrogen sulfide/methane with oxygen. Autotrophs do not need organic carbon or a living energy source survive. They are known to reduce carbon dioxide to make organic compounds for biosynthesis. In addition, autotrophs can store chemical energy.
Do autotrophs use water?
In addition, autotrophs can store chemical energy. Autotrophs commonly use water as the reducing agent, but there are those that use other hydrogen compounds such as hydrogen sulfide. Autotrophs can be photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs. Photoautotrophs use light as an energy source.
What are some examples of chemoautotrophic bacteria?
Examples of chemoautotrophic bacteria are nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in deep sea thermal vents. Living things that need to eat other living things to survive are called heterotrophs, or 'other feeders.'. Because heterotrophs cannot make their own food, they are called consumers.
How do photoautotrophs get their energy?
Photoautotrophs get their energy from sunlight and convert it into usable energy (sugar). This process is called photosynthesis. During the process of photosynthesis, not only is sunlight turned into energy, but carbon dioxide is taken from the air and oxygen is released in its place.
Why are heterotrophs called consumers?
Because heterotrophs cannot make their own food, they are called consumers. Autotrophs are self-feeders, and they get their energy from non-living sources such as the sun and carbon dioxide. Autotrophs are called producers because they provide energy and food sources for all heterotrophic organisms.
What are inorganic substances?
Inorganic substances are those that are not from biological sources, and they do not contain carbon as a main element. Chemoautotrophs are able to survive in very harsh environmental conditions because the only source of carbon they need is carbon dioxide.
What is it called when a living thing needs energy?
Autotrophs Defined. Every living thing needs energy in order to survive. We get this energy from the foods that we eat. The things that we eat were once living things and are full of energy themselves. Living things that need to eat other living things to survive are called heterotrophs, or 'other feeders.'.
What are the structures that plants use to capture sunlight?
Plants have structures called chloroplasts that allow them to capture the sunlight used for photosynthesis. Plants also get nutrition from water, various minerals in the soil, such as nitrogen and phosphorous, and carbon dioxide in the air. Algae are also photoautotrophs.
Do algae have chloroplasts?
Algae are also photoautotrophs. Algae are small organisms that are usually found in aquatic environments. While algae also have chloroplasts and may sometimes look like plants, they are very different. Plants are stationary - they set up roots and do not move once they start to grow.
What is an Autotroph?
Why is it so important to save the rainforest? Is it to save the animals? Is it to save the natural resources of a particular tribe or people? Is it because green is a better color than brown? Maybe all three and many more reasons. Trees are autotrophs, organisms that make their own energy or food.
Types of Autotrophs
As there are many types of heterotrophs, there are different types of autotrophs. Remember, autotrophs make their own energy, they can also be labeled as producers. Photosynthesis, the process of turning light and water and carbon dioxide into glucose, is the most common type of process used by photoautotrophs.
Photoautotrophs vs. Chemoautotrophs
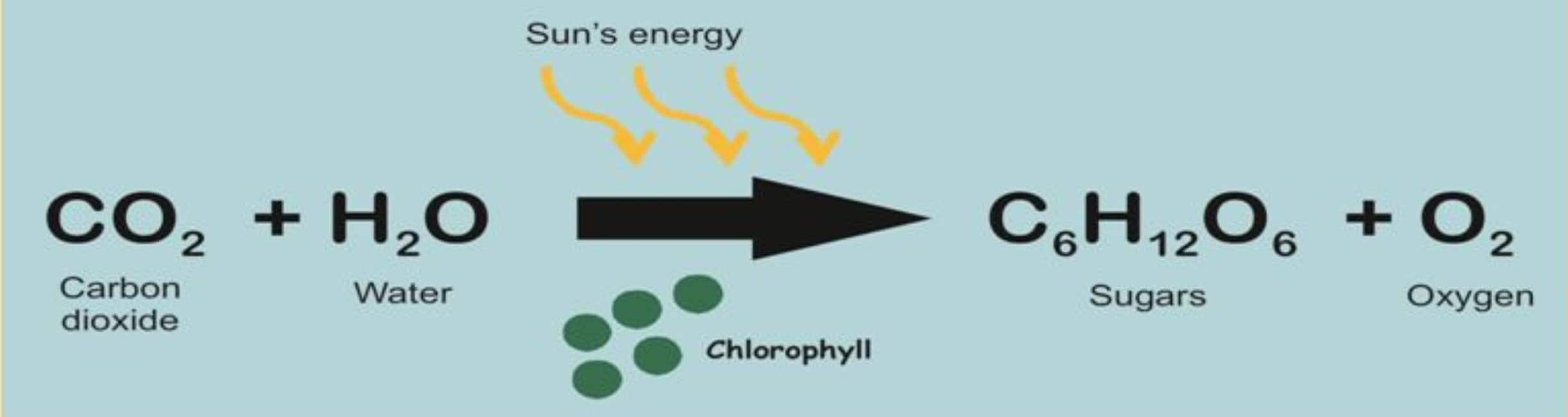
Photosynthesis is a complex chemical reaction where light, carbon dioxide, and water is converted into glucose and oxygen. {eq}6CO_2 + 6H_2O ->_ {light}-> C_6H_12O_6 + 6O_2 {/eq}
What is an Autotroph?
Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food, rather than ingesting other organisms as a source of nutrition. These organisms can come in various sizes and shapes. For example, plants are autotrophs, as they use photosynthesis to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugar.
Types of Autotrophs
There are two main types of heterotrophs: photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs
Examples of Autotrophs
Examples of Autotrophs Autotrophs are organisms that can photosynthesize. Plants are the two types of autotrophs, the ones most commonly seen by the average person. The other type of plant autotroph is algae. Algae are types of autotrophs that make use of chlorophyll and sunlight to make food.
Autotrophic Plants
Plants are the largest group of autotrophs. They use energy from sunlight to make sugars from carbon dioxide and water. Plants can be found in every part of the world and on all continents except Antarctica. As a result, they may be the first life that any traveler will see.
Heterotrophs
Heterotrophs are organisms that cannot make their own food, and therefore must rely on other organisms for energy. There are many types of heterotrophs in the animal kingdom. Fungi, some types of bacteria, and worms are all examples of heterotrophs.
Examples of Heterotrophs
A heterotroph, or “consumer,” is an organism that cannot fix carbon from inorganic material. A heterotroph either feeds on organic molecules and/or other organisms for its carbon and energy needs, or lives off the photosynthetic fixation of plants.