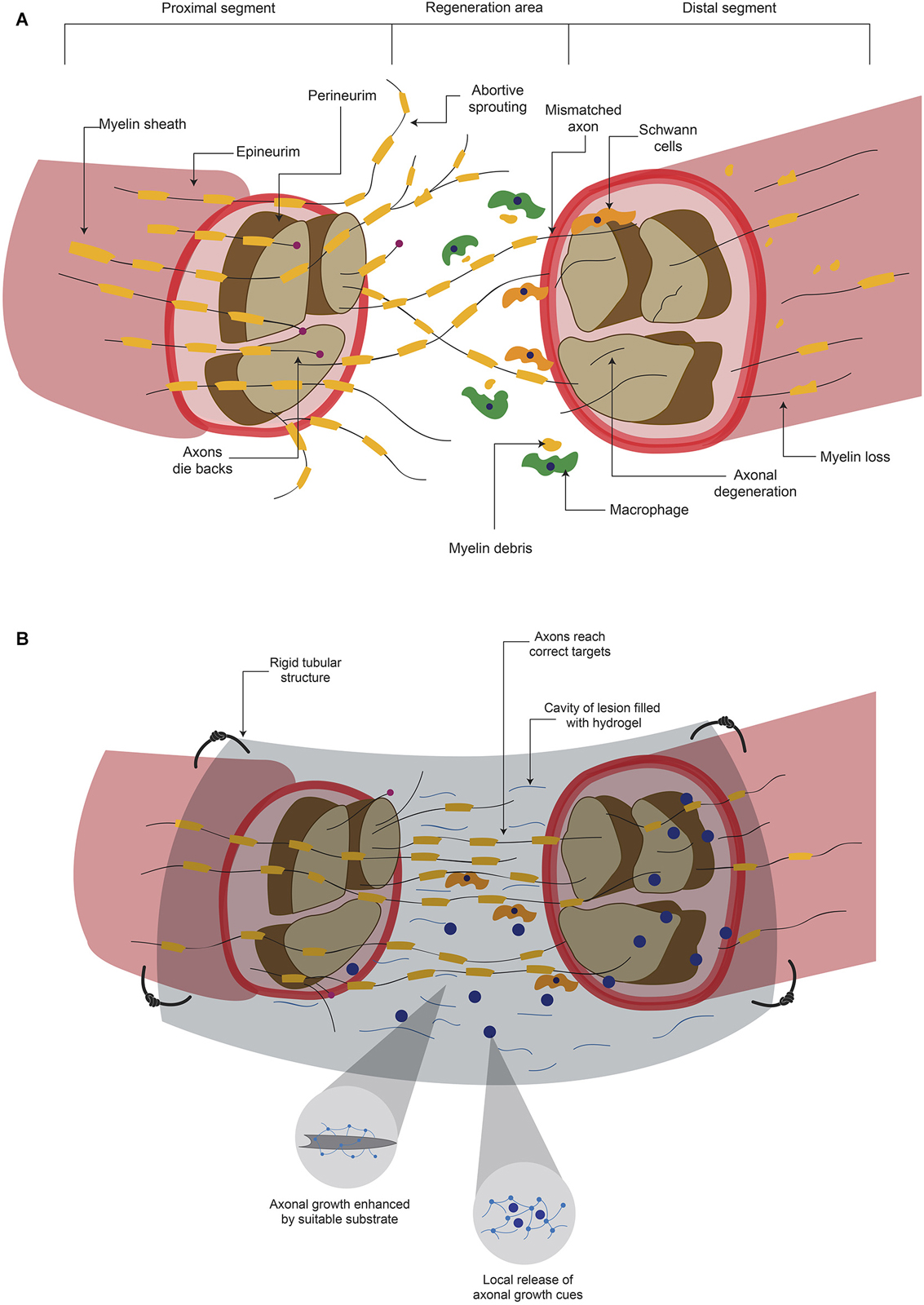
What is the function of axonal sprouting?
Feb 29, 2020 · Axonal sprouting is a process where fine nerve processes – sprouts – grow out from the intact axons to reinnervate denervated muscle fibers. Thereby the sprouting sustains the nerve supply to muscles and, in turn, the ability to move.
Is axonal sprouting in the peri-infarct brain caused by stroke?
What is neuron sprouting and how does it work?
What is neuronal sprouting in epilepsy?
Of the mechanisms of tissue repair in stroke, the formation of new connections (axonal sprouting) in brain adjacent to the stroke site occurs in rodents, primates and (with a strong correlative marker) in humans. In pre-clinical models of stroke, axonal sprouting in peri-infarct brain is causally related to recovery of motor function.
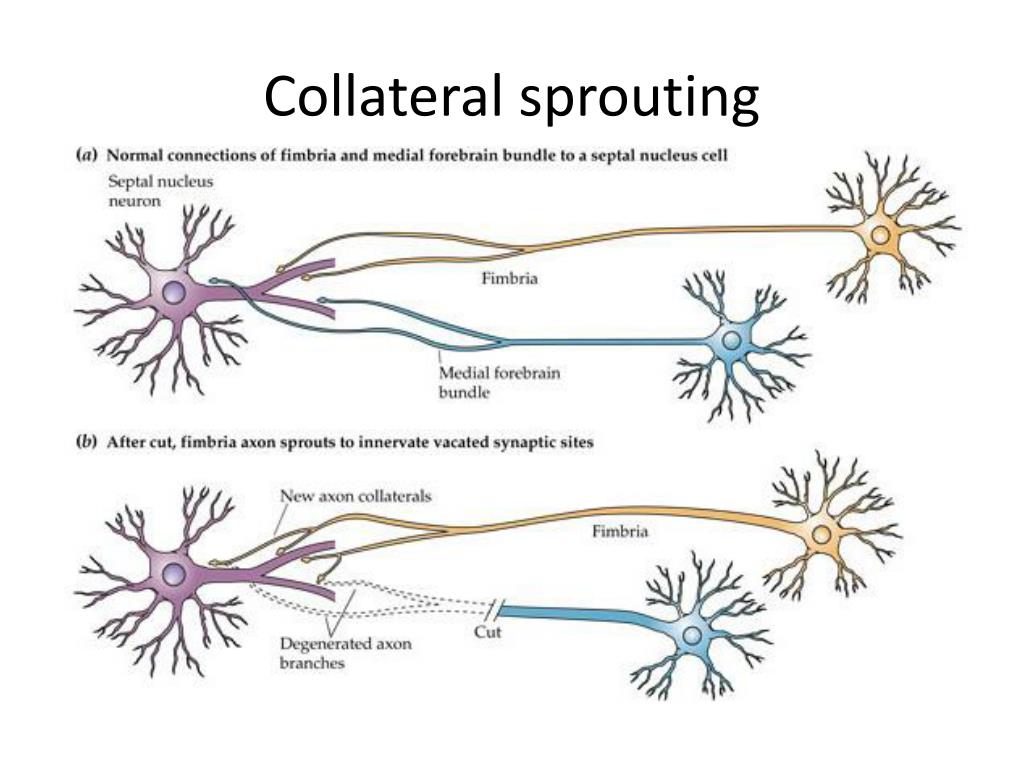
What is sprouting of neurons?
Definition. (cell biology) The process whereby a neuron generates additional branches (outgrowths) to establish new links between existing neurons.Jan 20, 2021
When does axonal sprouting occur?
After entorhinal cortex lesions, the embryonic form of NCAM is expressed on dendrites and axons within the denervated outer molecular layer by 24 hr. Astrocytes express NCAM at a later time, between 2 and 4 days, which may support and guide the sprouting reaction [16].
What is axonal disease?
Giant axonal neuropathy is an inherited condition characterized by abnormally large and dysfunctional axons called giant axons. Axons are specialized extensions of nerve cells (neurons) that transmit nerve impulses.Aug 17, 2021
What is axonal plasticity?
Axon plasticity is defined here as the ability of axons to undergo structural changes to adapt to an altered environment. It occurs on the levels of axon regeneration and sprouting, the modulation of which has the potential to restore functions in patients with spinal injuries.Sep 10, 2014
What causes axonal sprouting?
Axonal sprouting is commonly seen to compensate for motoneuron loss at least in part, in aging and/or in diseases such as poliomyelitis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and/or partial nerve injuries due to the loss of axonal contact and/or death of many of the motoneurons [1].
How does sprouting work?
Sprouting involves soaking seeds, nuts, legumes or grains for several hours, then repeatedly rinsing them until they begin to develop a tail-like protrusion. Soaking softens the hull, allowing the sprout to grow. They are usually ready to use when the sprout is ¼ inch.
Is axonal neuropathy curable?
Acute motor axonal neuropathy does not necessarily signify a poor prognosis as patients with nodal or motor nerve terminal dysfunction or injury without significant axon degeneration can recover quickly. Treatment should include intravenous immunoglobulins or plasmapheresis as well as supportive therapy.
Can you live without axons?
- Spinal cord injury can disrupt communication between the brain and muscles when neurons lose their connection to axons located below the site of injury. These neurons may still live, but they lose their ability to communicate.Dec 16, 2019
What happens when axons are damaged?
When an axon is damaged with a laser, it sends out signals to the surrounding tissue to be 'cleaned up', triggering the release of proteins that hastens degeneration of the axon. If such molecules are prevented from showing up, it could slow down the progress and extent of nerve damage.Mar 18, 2021
What is inside axon terminals?
At the end of an axon, there is a so-called axon terminal that is button-like and is responsible for providing synapses between neurons. The axon terminal contains specialized chemicals called neurotransmitters that are initially contained inside the synaptic vesicles.Mar 18, 2022
What is a synapse?
synapse, also called neuronal junction, the site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two nerve cells (neurons) or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell (effector). A synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell is called a neuromuscular junction. synapse; neuron.
Are sensory neurons found in the brain?
Neurons in the brain Certainly, there are brain neurons involved in sensory processing – like those in visual or auditory cortex – and others involved in motor processing – like those in the cerebellum or motor cortex.Mar 26, 2018