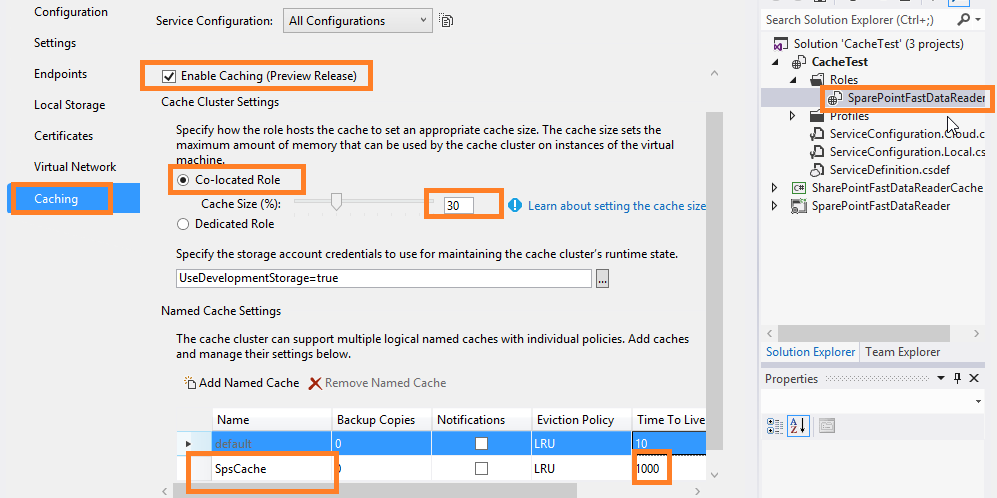
Windows Azure Caching allows a cloud service to host Caching on a Windows Azure role. The cache is distributed across all running instances of that role. Therefore, the amount of available memory in the cache is determined by the number of running instances of the role that hosts Caching and the amount of physical memory reserved for Caching on each instance.
What is Azure Caching and how does it work?
It provides a caching service that can be accessed from any Azure application, whether the application is implemented as a cloud service, a website, or inside an Azure virtual machine. Caches can be shared by client applications that have the appropriate access key.
How much storage is available to the VM for host Caching?
The amount of storage that is available to the VM for host caching is in the documentation. For example, you can see the Standard_D8s_v3 comes with 200 GiB of cache storage. You can enable host caching when you create your virtual machine and attach disks. You can also turn on and off host caching on your disks on an existing VM.
How do I monitor the performance of the cache in azure?
The Azure portal includes a convenient graphical display that enables you to monitor the performance of the cache. For example, you can view the number of connections being made, the number of requests being performed, the volume of reads and writes, and the number of cache hits versus cache misses.
Does Azure disk caching work with multiple disks?
Disk Caching is not supported for disks 4 TiB and larger. If multiple disks are attached to your VM, each disk that is smaller than 4 TiB will support caching. Changing the cache setting of an Azure disk detaches and re-attaches the target disk. If it is the operating system disk, the VM is restarted.

What is Azure Blob cache?
The Azure blob cache pluging is an extension to the caching mechanism which allows caching of images within AzureBlob Storage to serve via a content delivery network. This is extremely useful for load balanced or high traffic sites where images have to be served outwith the website for increased performance.
What is VM cached bandwidth?
VM Cached Bandwidth Consumed Percentage: The percentage calculated by the total disk throughput completed over the max cached virtual machine throughput. If this amount is at 100%, your application running is IO capped from your VM's cached bandwidth limit.
What is SSD in Azure?
Standard SSD Disks are a cost-effective storage option optimized for workloads that need consistent performance at lower IOPS levels. The new Azure Standard SSD Disks store data on Solid State Drives (SSDs), like our existing Premium Storage Disks. Whereas our Standard HDD disks store data on Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
What is host in Azure?
Azure Dedicated Host provides physical servers that host one or more Azure virtual machines. Your server is dedicated to your organisation and workloads—capacity is not shared with other customers. This host-level isolation helps address compliance requirements.
How do I increase my Azure VM performance?
Use Premium SSD managed disks – this may be another obvious one but choosing a higher performance disk type will reduce latency and increase throughput which can have a dramatic performance improvement.
How do I increase IOPS on Azure VM?
Enable ReadOnly Cache on premium storage disks with Read heavy operations to get higher Read IOPS. Enable ReadOnly Cache on premium storage disks with Ready heavy operations to get very low Read latencies. Use multiple disks and stripe them together to get a combined higher IOPS and Throughput limit.
What is LRS and Zrs in Azure?
LRS is the least expensive replication option, but isn't recommended for applications requiring high availability or durability. Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) copies your data synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region.
What are the types of storage in Azure?
Types of storage accountsType of storage accountSupported storage servicesStandard general-purpose v2Blob Storage (including Data Lake Storage1), Queue Storage, Table Storage, and Azure FilesPremium block blobs3Blob Storage (including Data Lake Storage1)Premium file shares3Azure FilesPremium page blobs3Page blobs onlyJul 14, 2022
What are types of disk in Azure?
Choose from four types of disks for the cloud—Ultra Azure Disk Storage, Premium SSD, Standard SSD and Standard HDD—and use multiple disks with each virtual machine.
Can Azure host a VM?
Azure Dedicated Host is a service that provides physical servers - able to host one or more virtual machines - dedicated to one Azure subscription. Dedicated hosts are the same physical servers used in our data centers, provided as a resource.
How do I make an Azure host?
Open the Azure portal. Select Create a resource in the upper left corner. Search for Host group and then select Host Groups from the results. In the Host Groups page, select Create.
Can you host a server on Azure?
Deploy your Azure VMs in a dedicated environment Azure Dedicated Host provides physical servers that host one or more Azure virtual machines. Your server is dedicated to your organisation and workloads – capacity isn't shared with other customers. This host-level isolation helps address compliance requirements.
How many IOPS does a VM need?
50-100 IOPS per VM can be a good target for VMs which will be usable, not lagging.
What is host caching?
Host caching works by bringing storage closer to the VM that can be written or read to quickly. The amount of storage that is available to the VM for host caching is in the documentation. For example, you can see the Standard_D8s_v3 comes with 200 GiB of cache storage.
What is an IOP storage?
IOPS (input/output operations per second) is the standard unit of measurement for the maximum number of reads and writes to non-contiguous storage locations.
What is IOPS and throughput?
IOPS measures the number of read and write operations per second, while throughput measures the number of bits read or written per second. Although they measure different things, they generally follow each other as IO operations have about the same size.
What is Azure Cache?
Azure Cache for Redis provides access to Redis servers that are hosted at an Azure datacenter. It acts as a façade that provides access control and security. You can provision a cache by using the Azure portal.
Why is caching important?
That's because caching reduces the latency and contention that's associated with handling large volumes of concurrent requests in the original data store.
How to use a cache effectively?
The key to using a cache effectively lies in determining the most appropriate data to cache, and caching it at the appropriate time. The data can be added to the cache on demand the first time it is retrieved by an application.
Why is shared cache slower?
There are two main disadvantages of the shared caching approach: The cache is slower to access because it is no longer held locally to each application instance.
How does cache aside work?
For the cache-aside pattern to work, the instance of the application that populates the cache must have access to the most recent and consistent version of the data. In a system that implements eventual consistency (such as a replicated data store) this might not be the case.
Why avoid using a cache as the primary repository of data?
Avoid using a cache as the primary repository of data; this is the role of the original data store from which the cache is populated. The original data store is responsible for ensuring the persistence of the data.
What is cache in a process?
The most basic type of cache is an in-memory store. It's held in the address space of a single process and accessed directly by the code that runs in that process. This type of cache is quick to access. It can also provide an effective means for storing modest amounts of static data, since the size of a cache is typically constrained by the amount of memory available on the machine hosting the process.
How does disk performance work?
Azure virtual machines have input/output operations per second (IOPS) and throughput performance limits based on the virtual machine type and size. OS disks and data disks can be attached to virtual machines. The disks have their own IOPS and throughput limits.
Virtual machine uncached vs cached limits
Virtual machines that are enabled for both premium storage and premium storage caching have two different storage bandwidth limits. Let's look at the Standard_D8s_v3 virtual machine as an example. Here is the documentation on the Dsv3-series and the Standard_D8s_v3:
Combined uncached and cached limits
A virtual machine's cached limits are separate from its uncached limits. This means you can enable host caching on disks attached to a VM while not enabling host caching on other disks. This configuration allows your virtual machines to get a total storage IO of the cached limit plus the uncached limit.
Why do we use caching?
By using caching, the web browser can avoid making multiple round-trips to the server and instead access the same data locally, thus saving time and resources. Caching is well-suited for locally managing small, static data such as static images, CSS files, and JavaScript files.
Why is caching important in a CDN?
Caching is integral to the way a CDN operates to speed up delivery and reduce origin load for static assets such as images, fonts, and videos. In CDN caching, static resources are selectively stored on strategically placed servers that are more local to a user and offers the following advantages:
Why is cached content important?
Resource freshness. Because a cached resource can potentially be out-of-date, or stale (as compared to the corresponding resource on the origin server), it is important for any caching mechanism to control when content is refreshed.
Why is CDN caching important?
Because most web traffic is static ( for example, images, fonts, and videos), CDN caching reduces network latency by moving content closer to the user, thus reducing the distance that data travels. By offloading work to a CDN, caching can reduce network traffic and the load on the origin server.
How to control caching in a CDN?
Similar to how caching is implemented in a web browser, you can control how caching is performed in a CDN by sending cache-directive headers. Cache-directive headers are HTTP headers, which are typically added by the origin server.
What is a CDN shared cache?
In a CDN shared cache, a file that is requested by one user can be accessed later by other users, which greatly decreases the number of requests to the origin server.
When is a cached resource considered fresh?
A cached resource is considered to be fresh when its age is less than the age or period defined by a cache setting.
What is Azure Cache for Redis?
Azure Cache for Redis provides an in-memory data store based on the Redis software. Redis improves the performance and scalability of an application that uses backend data stores heavily. It's able to process large volumes of application requests by keeping frequently accessed data in the server memory, which can be written to and read from quickly. Redis brings a critical low-latency and high-throughput data storage solution to modern applications.
What is cache-aside pattern?
Data cache. Databases are often too large to load directly into a cache. It's common to use the cache-aside pattern to load data into the cache only as needed. When the system makes changes to the data, the system can also update the cache, which is then distributed to other clients.
Does Redis use Azure Cache?
Redis, by design, uses only one thread for command processing. Azure Cache for Redis uses other cores for I/O processing. Having more cores improves throughput performance even though it may not produce linear scaling. Furthermore, larger VM sizes typically come with higher bandwidth limits than smaller ones.
Introduction to Caching
- Caching is the process of storing data locally so that future requests for that data can be accessed more quickly. In the most common type of caching, web browser caching, a web browser stores copies of static data locally on a local hard drive. By using caching, the web browser can avoid making multiple round-trips to the server and instead access...
Cache-Directive Headers
- Azure CDN supports the following HTTP cache-directive headers, which define cache duration and cache sharing. Cache-Control: 1. Introduced in HTTP 1.1 to give web publishers more control over their content and to address the limitations of the Expiresheader. 2. Overrides the Expires header, if both it and Cache-Controlare defined. 3. When used in an HTTP request from the clien…
Validators
- When the cache is stale, HTTP cache validators are used to compare the cached version of a file with the version on the origin server. Azure CDN Standard/Premium from Verizon supports both ETag and Last-Modified validators by default, while Azure CDN Standard from Microsoft and Azure CDN Standard from Akamai supports only Last-Modifiedby default. ETag: 1. Azure CDN St…
Determining Which Files Can Be Cached
- Not all resources can be cached. The following table shows what resources can be cached, based on the type of HTTP response. Resources delivered with HTTP responses that don't meet all of these conditions cannot be cached. For Azure CDN Premium from Verizononly, you can use the rules engine to customize some of these conditions. For Azure CDN Standard from Microsoftca…
Default Caching Behavior
- The following table describes the default caching behavior for the Azure CDN products and their optimizations. Honor origin: Specifies whether to honor the supported cache-directive headers if they exist in the HTTP response from the origin server. CDN cache duration: Specifies the amount of time for which a resource is cached on the Azure CDN. However, if Honor origin is Yes and th…
Next Steps
- To learn how to customize and override the default caching behavior on the CDN through caching rules, see Control Azure CDN caching behavior with caching rules.
- To learn how to use query strings to control caching behavior, see Control Azure CDN caching behavior with query strings.